Every third person is infected with the papilloma virus. In the body, the virus for a long time may not manifest itself in any way, but as soon as a person’s immunity decreases, it is activated, and growths and warts appear on the skin. In the absence of therapy, after some time the disease will progress, and ugly skin growths will spread throughout the body.
I must say that it will not work to completely remove the virus from the body – once infected with it, a person is doomed to live with it all the time. But, it is possible to deactivate it, therefore, at the first signs of the disease, it is necessary to contact a specialist and begin competent treatment.

Содержание:
- 1 What is HPV and what causes it?
- 2 HPV types by code and their features
- 3 What is the danger of virus No. 10 according to the international classification of diseases?
- 4 Signs of illness
- 5 Mechanism of infection
- 6 Places of localization
- 7 Diagnostic methods
- 8 Infection prevention
- 9 Conclusion and Conclusions
What is HPV and what causes it?
Skin papilloma is a benign skin disease that develops after the papillomavirus enters the human body. The incubation period of the virus lasts from several days to several months. After the virus enters the human body, it begins to actively multiply and infect epithelial cells. A cell infected with a virus becomes a benign tumor cell.
In 60% of cases, HPV infection occurs during sexual contact, and the virus can also enter the body through damaged mucous membranes.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of skin growths and warts:
- decreased immunity;
- disorders of the nervous system, including stress and depression;
- bad habits;
- taking medications for a long time;
- recent infectious diseases.
HPV types by code and their features
So, according to the ICD 10 HPV are divided as follows:
- if the growths affect the lips, this is the D23.0 group;
- eyelids – D23.1;
- ears and external auditory canal – D23.2;
- facial area – D23.3;
- head and neck area – D23.4;
- stomach, back and sternum – D23.5;
- shoulders and arms – D23.6;
- the area of the hip joint – D23.7;
- if it is not possible to clarify the localization – D23.9.
Such outgrowths may have an increased oncogenicity, they are allocated to a special group – B97.7, and anogenital outgrowths and warts belong to the A63.0 group.
As for warts localized on internal organs, they are classified as follows:
- growths on the pharynx and oral cavity – D10;
- formations in the intestines and in the anal area – D12;
- on the respiratory organs and in the middle ear – D14;
- in the mammary gland – D24;
- neoplasms of a benign order in the uterus – D26;
- in the urinary organs – D30.
What is the danger of virus No. 10 according to the international classification of diseases?
ICD 10 virus , just like other types of papilloma, can lead to the development of cancer. To a greater extent, this affects people who are at risk:
- HIV-infected;
- alcohol abusers;
- smokers;
- having multiple and promiscuous sexual relations.
In addition, a virus according to ICD 10, localized on the eyelid , can lead to chronic eye diseases and even complete blindness, papilloma located in the sky can provoke respiratory spasms and oncological processes in the larynx, in the tongue – to loss of sensitivity, in the nose – to loss of smell.
Signs of illness
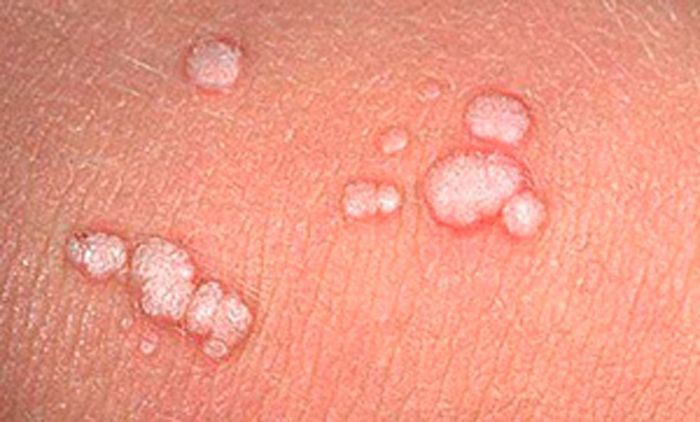
Most often, warts appear on the hands . This localization is typical for children and adolescents.
Simple warts are hard formations with a size of 1 mm. Such formations tend to merge, so they often capture large areas.
Plantar warts can be painful to walk on and are often confused with calluses, however, unlike warts, calluses have a smooth surface and skin pattern. Flat warts have the color of normal skin and are represented by dense papules. Their form can be different, and they are often accompanied by itching, flushing, soreness and inflammation.
Acrochords are most common after 50 years of age. These are filiform warts that are most often localized around the eyes, in the groin, in the armpits and on the neck. In fact, these are long elastic skin formations, reaching a length of 5 mm. When traumatized, the formations can become inflamed. Often formed in the presence of polyps in the large intestine.
Warty epidermodysplasia is quite rare. These are multiple red plaques on the feet and hands. This pathology often transforms into squamous cell carcinoma.
Local hyperplasia is a neoplasm in the oral cavity. Represents papillary papules that tend to merge.
Genital warts sometimes do not pose a danger, and in other cases are extremely susceptible to malignant transformation. Very often they are formed simultaneously with oncological neoplasms in the cervix.
The rare disease juvenile papillomatosis of the larynx is accompanied by an overgrowth of tissue on the vocal cords, which leads to impaired air circulation and difficulty in speech.
Mechanism of infection
Infection is facilitated by microtrauma to the skin – scratches, wounds, abrasions.
The routes of transmission of the virus are as follows:
- the most common way is sexual contact;
- non-compliance with personal hygiene when visiting public toilets, showers, gyms, baths, etc.;
- infection can occur from an infected mother to a child during childbirth;
- self-infection – damage to one’s own neoplasms when shaving, rubbing with clothes, etc.
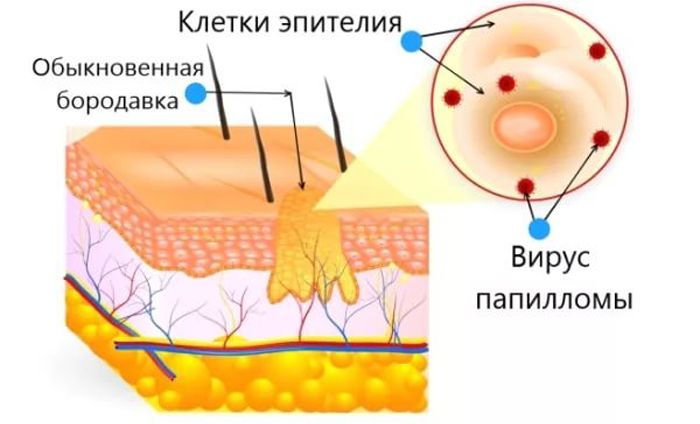
Places of localization
In principle, papillomas can appear on any part of the body, on:
- head – may be in the form of a thickened formation or formation on a leg;
- genitals ;
- hands and feet;
- chest, back and neck;
- face;
- ears;
- eyes;
- lips, tongue, mouth;
- in the armpits;
- internal organs.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of labor disease is not. With a visual examination of the formation, the specialist will determine the presence of the disease. If papillomas are localized on the genitals, a woman needs to contact a gynecologist, and a man – to an andrologist. At the same time, women most often have a visual examination, and men will have to undergo ureteroscopy, since genital warts in men can also affect the urethra.
In order to finally verify the correctness of the diagnosis, as well as to determine the type of disease according to the ICD, it is necessary to undergo an additional examination – PCR. To do this, the patient must donate blood and scrapings.
Treatment of papilloma according to ICD 10.
Treatment of papilloma is based on its removal. There are many ways to remove the build-up, and the optimal method is determined by a specialist based on the localization of the formation and the vastness of the affected area.
It could be:
- scalpel removal;
- laser removal ;
- electrocoagulation ;
- cryotherapy.
Immunomodulatory drugs
In addition, patients are prescribed immunomodulatory drugs:
- drug Likopid;
- drugs from the interferon groups – Viferon, Kipferon;
- herbal immunomodulators – Panavir , echinacea preparations.
Antiviral agents may be prescribed:
- Isoprinosine
- Indinol .
The task of treatment is to reduce the activity of the virus, strengthen the immune system and prevent the spread of growths on the skin and internal organs.
Infection prevention
Unfortunately, by the age of 20, almost all people are infected with the papillomavirus, this is because the virus is transmitted through any skin contact (with the exception of anogenital warts, which are transmitted only through intimacy).
To prevent an exacerbation of the infection, you must:
- undergo a diagnostic examination every six months;
- strengthen immunity;
- if necessary, remove the warts that have appeared.
To prevent HPV infection, you must:
- observe hygiene rules;
- use barrier methods of contraception;
- vaccinate with Gardasil or Cevarix.
Pregnant women in order to avoid transmission of the virus to the child are recommended to diagnose the presence of the disease in a timely manner and be treated.
Asymptomatic carriers of the virus need to undergo cytostatic therapy as a preventive measure – they will inhibit the development of the infection.
Conclusion and Conclusions
There are more than 100 viruses that can cause skin growths. That is why they need a certain systematization and special designations.
ICD – the international classification of diseases includes information about the virus itself, the causes of the development of pathology, symptoms and drugs that can help cope with the disease.
From time to time there is a revision of the classification, in which case its number changes. ICD 10 is the tenth version of the classification, using which each doctor can check the therapy prescribed by him in accordance with the indicators, and in the case of papilloma, also determine the type of virus.