Despite the wide distribution of the papillomavirus, few people know everything about this virus and are aware of its danger to health. Moreover, most people do not even realize that there is a pathogenic microorganism in their body, which can, under certain conditions, lead to serious problems. Currently, scientists have studied more than 100 types of human papillomavirus infection, and 18 strains among them are the most dangerous.

Содержание:
- 1 The essence of the problem, what is it – the human papillomavirus?
- 2 Risks and consequences of human papillomavirus infection
- 3 Ways of infection in women and men
- 4 Clinical manifestations of the disease
- 5 How the disease is detected, obtaining information about the DNA of the virus
- 6 Treatment
- 7 Prevention and vaccination
The essence of the problem, what is it – the human papillomavirus?
Papillomaviruses differ from each other in the structure of DNA. This virus can cause a variety of ailments, which are expressed in the formation of pathological growths on the skin and mucous membranes. Almost all strains of the virus have either a low or medium oncogenic index, however, there are also highly oncogenic strains that can provoke the development of malignant diseases.
One of these highly oncogenic strains of papillomavirus is strain 18. With a long stay of this virus in the human body, the processes of cervical neoplasia, dysplasia, and cervical cancer are triggered. Also, the formation of malignant processes in the vulva and in the anus is possible. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material: papilloma ICD 10 .

Risks and consequences of human papillomavirus infection
According to statistics, women with papillomavirus strain 18, a couple of years after infection, have problems with the cervix in 7%, and the transformation of pathological growths into malignant neoplasms is observed in 25% of women with this virus.
However, it must be understood that the likelihood of developing dangerous complications of the virus increases if the pathological microorganism is in the human body for a long time. If the virus has been present for more than 15 years, the risk of developing cancer increases 100 times.
Since infection most often occurs at the woman’s fertile age, in the absence of adequate therapy closer to the menopause, it is possible to diagnose malignant processes in the cervix, which could have been avoided if the papilloma virus had been detected in a woman in a timely manner.
Ways of infection in women and men
Any strain of papillomavirus is transmitted from an infected person by contact. Most often, infection occurs during intimacy, which is associated with the manifestation of infection precisely on the genitals.
I must say that barrier contraception does not guarantee 100% protection against papillomavirus. This is due to the fact that the condom does not completely cover the genitals, which means that the contact of the mucous membranes still occurs. The form of sexual intercourse also does not matter, the virus can be transmitted both during vaginal and anal or oral sex.

In addition, papillomavirus strain 18 can be transmitted as follows :
- upon contact with skin or mucous membranes, on which there are visible manifestations of papilloma;
- through items and personal hygiene products that an infected person has touched;
- from mother to fetus during childbirth.
But such methods of infection do not occur often, so the papillomavirus 18 strain is classified as an infection that is sexually transmitted.
At risk are people who :
- early sexual activity;
- have unprotected sex;
- often change sexual partners.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
In most cases, papillomavirus manifests itself in the formation of growths. They can be flat or pointed. The 18 strain of the virus provokes the appearance of growths mainly in the area of \u200b\u200bthe intimate organs or in the anus. Most often, mucous membranes are affected – the vaginal wall and the cervical region.
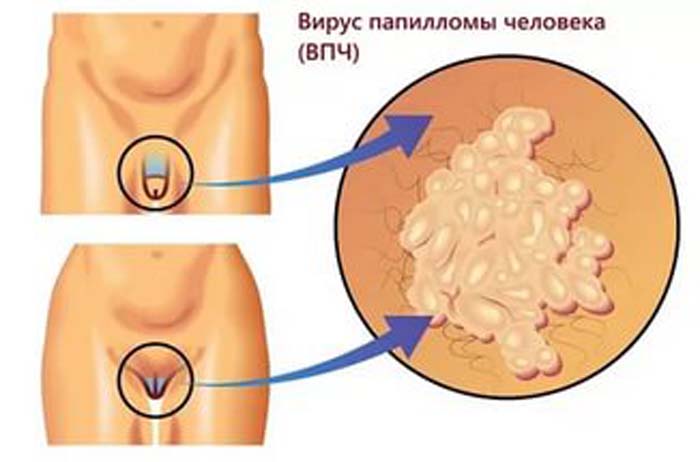
The structure of the neoplasms is heterogeneous, and if the growths accumulate in close proximity to each other, a formation resembling a cauliflower is formed. As for the color of the growths, it varies from white to flesh, pink neoplasms are found. Black and brown growths on the intimate organs are almost never observed.
These growths may not appear immediately after infection, but after a fairly long period of time. However, it is possible that signs of infection will appear a couple of months after contact with a carrier of the virus.
If the papillomas do not have close contact with the linen, and are not located in the cervical region of the genital organ, they may not bother the woman for a long time. But if the growth is damaged, pain, bleeding may appear, and when a secondary infection is attached, an inflammatory process occurs. When papilloma develops, itching may appear.
How the disease is detected, obtaining information about the DNA of the virus
To diagnose the presence of papillomavirus and determine its strain, you must undergo the following diagnostic examination:
- Colposcopy . This is a visual examination of the cervical region of the uterus, carried out by a special device called a colposcope. During this examination, you can examine in detail the structure of the mucous membrane, and if there are growths on it, enlarge the picture and examine them.
- Cytology. For this test, a swab is taken from the vagina. When examining the obtained material, the main criterion for the presence of a pathological microorganism is the presence of modified cells. An indicator of 1–2 is normal, at 3 a histology is prescribed, and if there is a result with an indicator of 4–5, this means that malignant cellular structures are present in the biomaterial.
- Histology. The resulting tissue sample is examined under a microscope and the presence of malignant cells is determined.
- Blood test . With papillomavirus, antibodies to it will be present in the patient’s blood. But it is impossible to determine the type of virus with 100% accuracy.
- Digen test . This is a relatively new and most accurate method for determining the papillomavirus. It can be used to determine the strain of the virus, find out its concentration, and determine the oncogenic risk. For the study, a scraping from the vaginal mucosa is needed.
- PCR. Allows you to get information about the DNA of the virus, even if there are only single modified cells.
- Reaction test . The cervix is treated with a special compound, and if a virus is present on it, the mucosa becomes mosaic.
The only thing is that it is recommended not to use antibacterial personal hygiene products, not to drink antiviral drugs and not to use vaginal gels, ointments and suppositories a few days before the tests . A blood test is taken on an empty stomach; when taking a smear, it is recommended to refrain from sexual intercourse for a couple of days before the analysis.
Treatment
It is impossible to get rid of papillomavirus. Once an infection has occurred, the virus remains in the human body forever. But with appropriate therapy, the virus will remain latent and not activated.
The main treatment is aimed at:
- elimination of neoplasms;
- suppression of the virus (antiviral therapy);
- increase in immune forces.
Drug antiviral therapy is prescribed if there are genital warts on the skin and mucous membranes. This treatment is combined with surgery. In addition to antiviral drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed that will restore the natural microflora of a woman’s intimate organs, as well as immunomodulators . Improving immunity is a very important point in the treatment of human papillomavirus infection. Mostly drugs based on interferon are prescribed.
Surgical removal of pathological growths is an extremely necessary manipulation, which consists in removing the source of infection, and, therefore, prevents the spread of the virus to healthy cells.
Ways to remove papillomas:
- Surgical . Removal is performed with a scalpel under local anesthesia.
- laser therapy . The impact of the laser leads to the evaporation of fluid from pathological cells, as well as to adhesions of blood vessels. After the procedure, a crust forms at the site of exposure, which disappears after a while.
- Radio waves . This is the most progressive method of treatment, in which point exposure to radiation causes cell death. This method does not require anesthesia.
- Electrocoagulation . Removal of neoplasms with electric current.
- Cryodestruction . Freezing with liquid nitrogen. The method is painless, but it has a minus – the inability to take material for research.
- Cauterization with aggressive chemicals . Solkvagin is most often used. The disadvantage of the method is that, unlike other removal methods, it may take several sessions.

As for alternative methods of treating papillomavirus, they can only be used as additional methods, and in no case should they replace the main treatment (especially when it comes to strains with a high oncogenic risk).
It is safest to use traditional medicine recipes to increase immunity. Infusions and decoctions of the following plants are used :
- plantain;
- nettle;
- dandelion;
- hop cones;
- coriander;
- valerian;
- Melissa;
- oregano;
- linden and others.

Independent exposure to the neoplasm with chemicals, as well as celandine juice, is not recommended. First you need to consult with a specialist.
With the timely detection of the 18th strain of papillomavirus infection, the forecasts can be quite optimistic, however, if the infection is not treated, a malignant disease will occur, and its prognosis will be completely different.
Prevention and vaccination
Prevention of the papilloma virus is a rather complicated matter. Given the number of people infected with this virus, it is easy to catch it. However, some measures can still be taken:
- have only one verified sexual partner;
- preventive medical examinations;
- personal hygiene in public places.
The most effective preventive measure today is vaccination. The vaccine is indicated for girls from 10-14 years old. In this case, a strong immunity to the virus will be formed. However, before vaccination, it is imperative to be tested for the presence of the virus, since vaccination of an infected person is completely ineffective.
Currently, there are two types of vaccination against the 18 strain of the virus :
The vaccination course consists of three injections. These injections should be carried out within six months, that is, the first vaccination is done arbitrarily, then a month later, and the final one 6 months after the first.
The vaccine is considered safe, but in some cases the following side effects are possible:
- itching at the injection site;
- slight swelling;
- mild pain;
- redness of the skin.
The discovery of the 18th strain of papillomavirus should not be a cause for panic, however, a number of measures must be taken to prevent the virus from reactivating. The most important thing is to take the drugs prescribed by the doctor and strengthen the immune system with all your might. It is important to remember that with this virus you can live an absolutely normal, full life, but only if you carefully monitor your health.