During pregnancy, a woman’s body is completely rebuilt, including – reduced immunity. For this reason, the risk of occurrence and manifestation of various diseases increases.
The human papillomavirus can be in the body for years without disturbing the carrier, but at the moment of weakening the protective forces makes itself felt. What to do if this happened during pregnancy, when many methods and procedures of therapy are prohibited?

Содержание:
- 1 The impact of papillomavirus on pregnant women
- 2 Is it possible to remove papillomavirus during childbearing?
- 3 Localization and appearance of HPV, accompanying symptoms
- 4 Causes of HPV
- 5 Diagnosis of human papillomavirus
- 6 What to do if they appeared during the period of bearing a child?
- 7 The consequences of the onset of the disease
- 8 Prevention of HPV during pregnancy
The impact of papillomavirus on pregnant women
Many women are interested in the question: can HPV harm the fetus? There is no single answer to it, since the data of different studies vary greatly. However, most experts are inclined to believe that there is no serious danger to the unborn baby.
On a woman
The greatest danger is the appearance of papillomas in the genital area. Outgrowths in the intimate area are more often exposed to mechanical stress, therefore there is a high risk of damage, severe pain and bleeding.
A damaged papilloma is an open path for various infections, so a pregnant woman may experience the penetration of pathogenic organisms into the vagina and unpleasant consequences: hormonal imbalance, decreased immunity.
In addition, papillomas in the genital area have a high spread rate, which causes severe physical and psychological discomfort to a pregnant woman.
If the papilloma is located elsewhere, it is removed or drug therapy is used, which is allowed during pregnancy. Too much papilloma in the genital area may be an indication for a caesarean section.
There is also a hypothesis that HPV during pregnancy can lead to its termination.
per child
During childbirth, HPV is rarely transmitted to the baby. If this happens, it is highly likely that the child’s body will cope with it without outside intervention and the disease will take on an asymptomatic phase.
Much less often in infants, as a result of infection, papillomas on the vocal cords are formed – papillomatosis of the respiratory tract. This is a more dangerous condition, but its occurrence is very low.

Is it possible to remove papillomavirus during childbearing?
During pregnancy, any manipulations that can become stressful for the body are highly undesirable. However, modern medicine has come a long way, and many non-traumatic, safe and painless therapies and surgical treatments have appeared.
Remove papillomas during pregnancy if they do not cause much discomfort to the expectant mother – it is better to leave this procedure for the postpartum period. In other cases, removal is possible: pregnancy is not a contraindication to various kinds of manipulations.
The methods of laser papilloma removal and cryodestruction are considered the most successful . It is advisable to remove only very large papillomas, since in most cases, after pregnancy, the neoplasms disappear on their own.
The most favorable period for the removal of papilloma during pregnancy is the 1st trimester.
Localization and appearance of HPV, accompanying symptoms
Papillomas can appear on any part of the body, have a different color, size, shape. Associated symptoms depend on this. Usually during pregnancy, papillomas appear in the chest, neck and nipples.
On breasts, nipples and areolas
On the chest most often appear soft warts from light brown to black. They can be located anywhere on the chest, but are usually found in the nipples and areolas.
The danger of this place is that papillomas can be internal and external, and the latter can penetrate into the mammary glands. This will make breastfeeding impossible.
External papillomas on the chest do not have concomitant symptoms, while with internal ones there is a seal in the breast tissues, whitish discharge, burning and tingling.
In intimate places
In the genital area, papillomas appear on the labia, near the anus, in the vagina or in the cervix. The last location is the most dangerous.
In intimate places , small growths in the form of a cockscomb or single genital warts are formed. In the genital area, papillomas tend to grow rapidly.
In this place, the formation is easily damaged, which causes bleeding and pain. Sometimes there are pathological discharge with an unpleasant odor.
On the labia
On the labia, papillomas are usually light, on the mucous membrane they are darker. The shape can be any: round, oval, in the form of a cockscomb or cauliflower. Most often, wide growths on a narrow leg form here.
In this area, the growth rate of papillomas is lightning fast: the number of outgrowths can increase several times in a few hours.
By themselves, papillomas on the labia are painless, but with hygienic procedures and mechanical action (rubbing with linen) they cause discomfort and bleeding.
Into the vagina
Papillomas near or inside the vagina can be in the form of genital warts, resemble cauliflower, cockscomb, small papillae, flat formations. The shape is usually elongated, the size is from 1 to 8 mm.
More often, single papillomas form in the vagina, but very quickly there are several of them. They are found during hygiene procedures.
Associated symptoms: itching, slight pain.
On the neck
Papillomas on the neck often appear in girls with long hair. Outgrowths prefer the back of the neck.
In this zone, the size of formations reaches 1-5 mm. They have a pointed shape, color – from light to brownish, can be single or multiple.
Neck warts do not bother a woman if they are not subjected to mechanical friction with clothing or jewelry.
On other parts of the body
Papillomas can appear on any part of the body and have a different shape, size, color. During pregnancy, neoplasms affect the neck, genitals, breasts and nipples, armpits, and face.
As a rule, they do not bother a woman, but rubbing and damage with various fabrics and accessories and with different movements can lead to damage to the papillomas.
Causes of HPV
Causes of benign neoplasms include:
- Hormonal restructuring, in which sex hormones are actively produced, causing increased growth of epithelial cells.
- Friction of the skin. During pregnancy, a woman quickly gains weight, which is why the old clothes are already tight. Underwear rubs when walking, like other clothes (for example, a T-shirt in the armpits), which can cause papillomas.
- Natural weakening of immunity during childbearing, which can trigger HPV activation.
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus
If a woman herself discovered formations in the genital area, one examination in the gynecological chair and scraping (from the surface of the cervix or cervical canal) is enough for diagnosis. A colposcopy may also be performed.
In other cases, a blood test is taken for HPV .

What to do if they appeared during the period of bearing a child?
As mentioned above, treatment during pregnancy is not mandatory, since symptoms often disappear after childbirth. However, if a woman experiences discomfort, and the disease progresses rapidly, drug therapy or surgical removal of papillomas is used.
Medical treatment of growths
Medicines during pregnancy are prescribed depending on the severity of the disease, the characteristics of the course of pregnancy and the state of health.
At the initial stage, until about the second trimester, the doctor prescribes the drug ” Viferon ” – an antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative ointment.
Its use is due to low toxicity, which makes it absolutely safe during pregnancy. The application of the ointment creates conditions in the epithelium under which the virus protein cannot exist, therefore, with its regular use, the papilloma disappears.
The drug ” Infagel ” is an antiviral and immunostimulating gel based on interferon. In addition, it has antitumor properties and prevents the reproduction of atypical cells.
The drug is prescribed for the treatment of herpes, STIs and other drugs. The instructions say that use during pregnancy is allowed, but doctors do not recommend using it in the 1st trimester, since the fetus does not have a protective barrier in the form of a placenta.
” Solcoderm “, due to the presence of concentrated acids and copper nitrate in the composition, has analgesic, antibacterial and antitumor effects. In this regard, it is often called an alternative to laser removal of papillomas.
It is a solution for external use. It is prescribed to pregnant women if the risk from using the drug is lower than the possible risk to the fetus.
Gel ” Panavir ” is used during pregnancy to curb the growth of papillomas. The safest use of the drug is in the 3rd trimester.
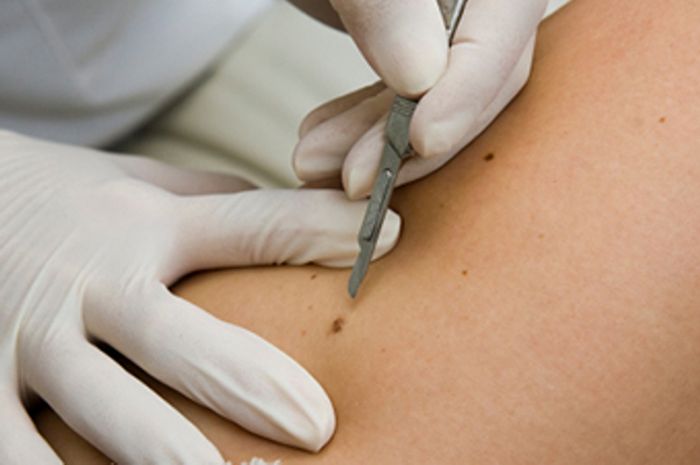
Surgical removal
Removal of papilloma during pregnancy by surgery is permissible in the 1st trimester with a small size of neoplasms.
Currently, several methods are used:
- Excision . Possible consequences are bleeding and ugly scars.
- Removal using radioknife . Painless method, excluding relapses.
- laser removal . Modern safe and painless method. Most often used.
- Cryosurgery – freezing with liquid nitrogen.
After surgery, a course of taking immunomodulators or immunostimulants may be prescribed.
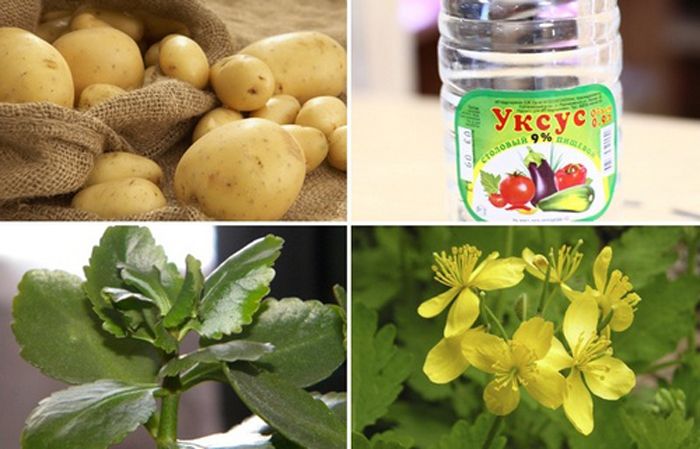
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are safe and effective in the initial stages of the disease. Their use is possible only with the permission of a doctor.
Potato gruel
For this method, you will need a raw potato, a bandage, and a band-aid. Before going to bed, you need to grind the potato on a grater, place it in a bandage, attach it to the affected area and fix it with a plaster for the night. In 3-4 weeks, the papilloma may disappear.
garlic-vinegar mixture
The mixture is made from a clove of garlic, 1st tsp. vinegar and 0.5 tsp. rye flour. The components are thoroughly mixed (garlic is pre-crushed using a garlic press).
Healthy skin around the papilloma should be isolated with adhesive tape. The mixture is applied to the papilloma, fixed with a bandage or plaster and left for 3 days.
apple cider vinegar compress
The compress is applied every 12 hours for 3-5 days. Healthy skin is also isolated with a plaster. A cotton swab should be moistened in apple cider vinegar, squeezed well, applied to the papilloma and fixed.

The consequences of the onset of the disease
HPV does not cause significant harm to the fetus and mother, but its nature must be investigated. Possible consequences of the disease:
- Extensive growth of papillomas and the need for surgical treatment.
- Complicated delivery or caesarean section.
- Abortion.
- Transmission of HPV to a child with the appearance in the form of papillomatosis of the trachea, throat, bronchi, eyes and other organs.
The most dangerous consequence of HPV, which occurs in isolated cases, is the risk of asphyxia due to bronchial papillomatosis.
Prevention of HPV during pregnancy
Since HPV is predominantly transmitted sexually, a woman should take care of protection. Even having sex with one partner, there is a risk of infection if he is a carrier, because a woman’s immunity during pregnancy is significantly weakened.
A pregnant woman should wear only her own clothes, have individual cutlery and personal hygiene items, a towel, a toothbrush. You can not use other people’s things and objects.
Visiting public places such as a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, massage room is not recommended. Be sure to monitor weight gain and, if necessary, purchase clothes and underwear in larger sizes.
General preventive measures to strengthen immunity are proper nutrition, healthy sleep, walks in the fresh air and the absence of stress and nervous strain. Without fail, a woman must observe personal hygiene measures, regularly visit a gynecologist and pay attention to her own health.
HPV during pregnancy is not uncommon, but, fortunately, papillomavirus is rarely dangerous for both the expectant mother and the fetus. You should not panic when growths appear on the skin or mucous membranes, but you need to consult a doctor. Self-medication for HPV is contraindicated.