39 papillomavirus strain is a type of infection with a high oncogenic index. This virus can cause the development of pathological processes in healthy cellular structures and lead to oncological diseases.

Содержание:
- 1 Human papillomavirus – what is dangerous, what is it?
- 2 How is papillomavirus transmitted and manifested?
- 3 Symptomatic manifestations
- 4 The specifics of the course in women
- 5 The specifics of the course in men
- 6 How to identify this genotype, DNA features – methods for diagnosing papillomavirus pathology
- 7 Principles of treatment
- 8 Infection prevention
Human papillomavirus – what is dangerous, what is it?
Papillomavirus 39 strain belongs to a large group of viruses that affect the skin and mucous membranes. The vast majority of papillomaviruses are successfully neutralized by the human body, but sometimes a viral infection is activated, and in this case a person becomes not only sick with papillomavirus, but also its carrier, that is, it poses a real threat to people around.
The papillomavirus has many strains, and viruses with a low oncogenic status are most often diagnosed. They lead to the appearance of genital warts, which rarely or almost never transform into a malignant formation.
However, the 39 strain of the virus has a potential health hazard, and can give impetus to the development of precancerous and cancerous diseases of the female genital organs. The insidiousness of the papillomavirus lies in the long and secretive course of the initial form. The incubation period ranges from six months to several years. At the same time, the woman does not notice any alarming symptoms in herself, and her state of health does not change.
In the later stages, the papillomavirus 39 strain provokes the development of genital warts and papillomas on the mucosa.
How is papillomavirus transmitted and manifested?
Infection with papillomavirus occurs through skin contact with the patient, including contact with the genitals. Therefore, the virus is most often spread through sexual contact. And it does not matter what kind of contact was – vaginal, anal or oral.
Of course, the use of barrier contraception is a reliable protection against sexually transmitted infections, but not the papillomavirus. The condom does not interfere with the skin contact of partners, so infection is quite possible. A pregnant woman can pass the virus to her baby during labor, but this is rare.

The risk of contracting HPV type 39 is increased in women who:
- early sexual intercourse;
- often change sexual partners;
- have group sex;
- do not adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
After the virus enters the body, the following provoking factors can contribute to its activation:
- prolonged stress;
- hypothermia;
- avitaminosis;
- abuse of certain medications;
- hormonal disorders;
- unfavorable ecological situation;
- chronic diseases in the period of exacerbation;
- low immunity.
Symptomatic manifestations
In women, the 39 strain of papillomavirus provokes the appearance of genital warts, which are most often found during a gynecological examination. Their growth begins approximately in the first six months after infection with the virus, and most often they are localized on the labia minora, in the vaginal region, on the neck of the reproductive organ or in the anus. These neoplasms have uneven edges and a wide leg.
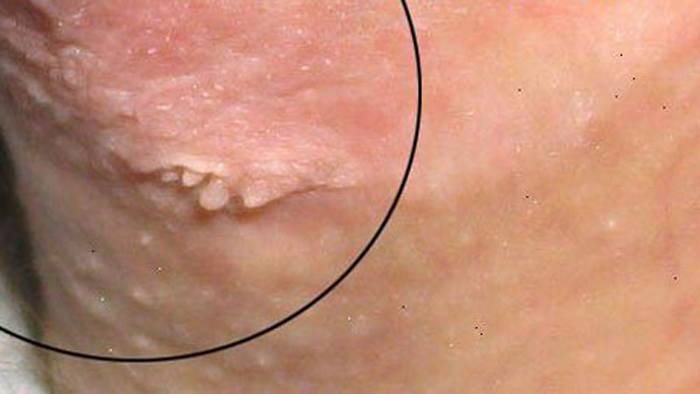
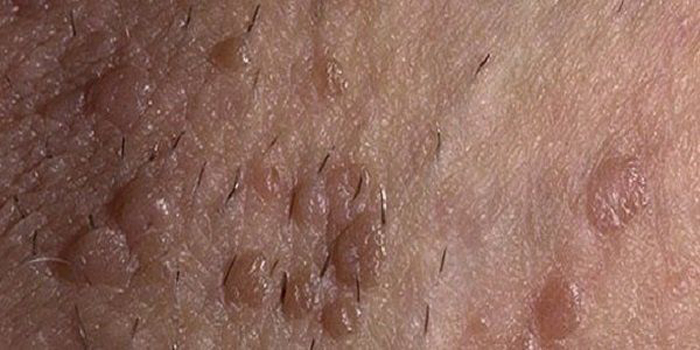
Also, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, which provokes a violation of the maturation of cellular structures and is a precancerous condition, is considered a symptom of the disease in women.
Basically, genital warts are observed in women under 35 years of age, and all this time, apart from the presence of growths, there are no other signs. But with the onset of menopause, the virus can lead to the development of cancer.
In general, the disease in both women and men proceeds in 4 stages :
- latent flow. The virus is already present in the human body, but there are no manifestations of it. It is possible to detect an infection only by doing a PCR analysis.
- The appearance of clinical signs – skin and mucous growths.
- Dysplasia. The DNA of the virus begins to interact with the DNA of healthy cells, which leads to a change in the latter.
- Carcinoma. The virus provokes mutation processes in cells, that is, invasive cancer develops.
The specifics of the course in women
Infection of the female half of the population occurs more often, however, the risk of becoming infected during vaginal sex is slightly lower than during oral or anal sex. The first signs of a viral infection in the female body are associated with the appearance of warts and genital warts. These growths can be flat or pointed, and can be localized not only on the genitals, but also on the eyelids, under the breast or in the armpit.
If these neoplasms are localized in close proximity to each other, their colony resembles a cockscomb. In terms of color, warts can be flesh-colored or reddish.
Condylomas located on the genitals have their own characteristics :
- if treatment is not carried out, quite often suppuration is observed in the places of neoplasms;
- with trauma, a bleeding sore appears;
- in the absence of adequate treatment, the growth of neoplasms continues.
Cervical cancer
Cancer of the cervical region of the reproductive organ is one of the malignant diseases, the cause of which has been established. This is a papilloma virus of oncogenic strains.
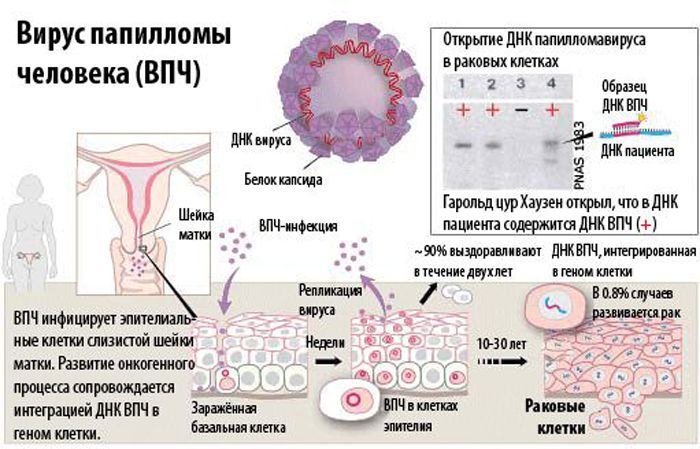
When diagnosing the disease in the initial stages, it is possible to cope with the disease, but, unfortunately, these stages are most often not noticed by women. Later clinical signs of the disease are as follows :
- unreasonable bleeding during sexual contact or immediately after it;
- pain in the pelvic region;
- severe and constant fatigue;
- loss of appetite, weight loss;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor.
If a woman has strong immunity, then the disease can take a couple of decades, with weak immune protection, an advanced stage can develop in 5-7 years.
The specifics of the course in men
In men, the infection also first proceeds in a latent form, and then genital warts may appear in the penis and anus. If such neoplasms in men transform into oncology, this usually concerns the anus.
How to identify this genotype, DNA features – methods for diagnosing papillomavirus pathology
It is not always possible to determine the presence of a virus visually. Modern diagnostic methods consist of the following activities:
- examination of the genital organs with the help of mirrors;
- colposcopy using Lugol’s solution;
- cytological studies for the presence of malignant neoplasms;
- PCR analysis ;
- a special test, during which it is possible to determine the strain of the virus and the degree of its oncogenicity.

In the presence of neoplasms, a tissue biopsy is performed.
Principles of treatment
Since the papillomavirus 39 strain can infect anyone, it is important for everyone to know the principles of treatment. Proper therapy will help keep the spread of the virus, however, it is impossible to completely destroy it – once infected, a person is forced to live with the virus all his life. At the same time, relapses of the disease will occur from time to time, which will need to be carefully treated.
In the initial stages of the disease, drug treatments can be used to help increase the body’s immune defenses, which will lead to a decrease in the activity of the virus.
In the presence of growths, doctors most often advise to remove them surgically, for this there are various methods that will be discussed below.
As for traditional medicine, it cannot cope with the pathology on its own, and if it is prescribed, it is only as an additional treatment and as a preventive measure.
Medical treatment
It must be understood that antiviral drugs do not eliminate the virus from the body, but only reduce its activity. Most often, the following forms of antiviral agents are prescribed :
- solutions;
- sprays;
- drops;
- ointments;
- candles;
- pills.
For example:
- Isoprinosine is an effective agent that partially provokes the death of the virus, and also blocks the production of infection enzymes. Take the remedy for two weeks, but if necessary, the course of treatment can be extended.
- Cycloferon . This tool removes growths on the skin and prevents the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. The preparation may be in the form of an injection solution or tablets.
- Allokin alpha . The drug inhibits the manifestations of the virus, leads to the partial death of microorganisms, and also enhances the production of interferon in the body.
- Amiksin . This is a human interferon inducer, which is approved for use by children from 7 years of age.
- Panavir . Available in the form of injections, as well as ointments and sprays. The action of the drug is anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, regenerating.

In addition to antiviral drugs, immunomodulators are prescribed:
- Lykopid .
- Immunomax.
- Polyoxidonium .
- transfer factor.
- Interferon.
- Cordyceps and others.
Treatment of warts on the cervix
To get rid of genital warts, complex treatment is necessary, which includes not only drug treatment, but also surgical removal of growths.
Removal is carried out in the following ways:
- Cryodestruction is the safest and most painless method, but it can only be used with full confidence in the good quality of the neoplasm.
- Cauterization with acids . Most often, Solkvagin is used, which is applied several times to the growth, as a result of which the neoplasm disappears.
- laser removal .
- Electrocoagulation .
- Removal with a scalpel . This method is used in cases where the size of the growth exceeds 1 cm, as well as in a malignant neoplasm.

Of the medicines, immunostimulants (Genferon), antiviral drugs, cytological agents that destroy virus cells are most often prescribed.
folk therapy
If the disease is diagnosed at the initial stage, and no complications arise, the doctor may advise the use of alternative methods of treatment.
- Castor oil is mixed with soda in a ratio of 1:1. The agent is applied to the growths in the morning and evening, and closed with a bandage.
- Celandine . You can use either freshly squeezed juice from a plant or its fresh leaves, or a tincture bought at a pharmacy. The infusion of celandine is mixed with olive oil and the growths are smeared several times a day. It is important to understand that celandine is a poisonous plant, and it must be used very carefully.
- Dandelion infusion has good reviews . For its preparation, the flowers of the plant are placed in a jar, poured with alcohol, and insisted for two weeks. The resulting product is lubricated with warts several times a day until they disappear.

Infection prevention
In order to prevent infection with the papillomavirus, it is necessary to be more selective in sexual relations, use barrier contraception, monitor the state of immunity and lead a healthy lifestyle. It is very important to regularly undergo scheduled examinations by a gynecologist.
However, the only way to prevent infection today is vaccination. It should be carried out before sexual activity, the optimal age for vaccination is 16 years. Before vaccination, it is imperative to take tests for the absence of the papilloma virus in the body, because if the virus is already present, the vaccine will be useless.
After treatment of the papillomavirus, it is necessary to carefully adhere to preventive measures aimed at strengthening the immune system, since with a decrease in the functioning of the immune system, a recurrence of the manifestation of the virus is possible. Both partners should be treated at the same time to avoid re-infection.
Many people, having found rashes and growths in their intimate area, do not attach any importance to them, especially if they do not bother in any way. It is very important to understand that the consequences of such a negligent attitude to one’s health can end in failure. Therefore, it is very important to explain to young people about the dangers of the papillomavirus, especially its highly oncogenic strains.