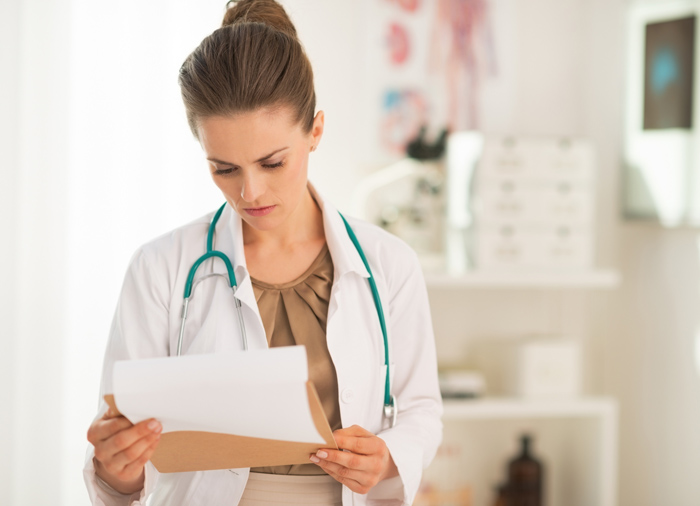
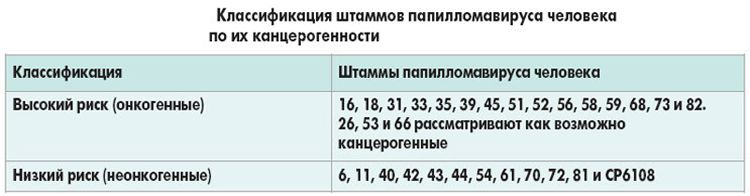
Currently, scientists have studied about 80 strains of the papillomavirus, but there are many more. Some of them have a low oncogenic index, which means that they cannot transform into cancerous diseases, while others, on the contrary, lead to the development of malignant tumors.
The 35 strain of papillomavirus is characterized by an average risk of malignancy, rarely leads to oncology, but it cannot be called safe. The papilloma virus is a class of pathological microorganisms that contain DNA that has a gene that can affect the rate of cell division.

Содержание:
Characteristics of papillomavirus and features of its DNA
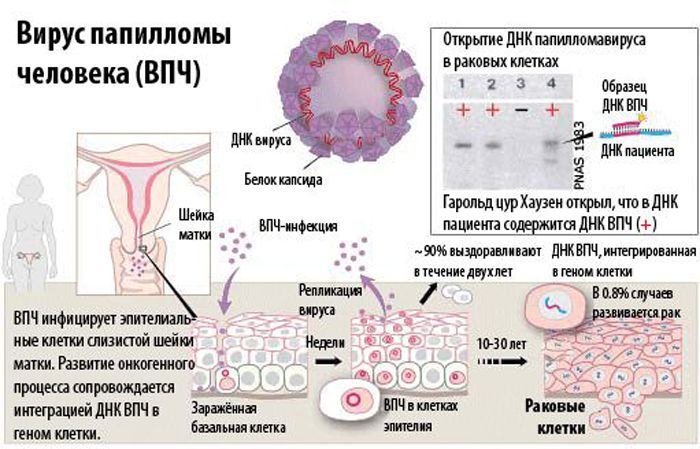
The DNA of this strain, as well as other strains of papillomavirus, when introduced into the human body, leads to a change in the epidermis at the cellular level. In this case, the cells begin to divide intensively, as a result of which growths appear on the skin and mucous membranes. 35 papillomavirus strain is potentially oncogenic, and in 60% of all cases it can cause the development of cervical cancer.
Despite the fact that the 35th strain of papillomavirus does not always provoke cervical cancer in women, it is imperative to treat and monitor it, since there is still a risk of dangerous consequences.
Danger of human papillomavirus, what kind of disease is it
When the virus is activated on the skin and mucous membranes, it provokes the appearance of genital warts. Often these formations are located in groups, and such a cluster of them resembles a cauliflower or a rooster’s comb. Neoplasms are prone to rapid growth, and in which time they occupy large surfaces.
Since the main route of infection with papillomavirus is sexual, warts are most often localized on the intimate organs, in the anus or in the oral cavity.
When warts grow, they can cause significant discomfort – irritation, discomfort during sexual intercourse. Often neoplasms are injured and bleed. In this case, the likelihood of a secondary infection is high, which provokes various complications in the form of inflammatory and infectious processes.
If the virus enters the cervical mucosa, it causes polypous formations, dysplasia, erosion. All this is considered a precancerous condition, and without urgent and proper treatment can lead to sad consequences.
Condylomas in the oral cavity are injured very often, and, therefore, can provoke infectious processes in the mouth. With a significant growth of genital warts in the mouth, the risk of transformation of neoplasms into cancer of the mucous membrane increases significantly.
How the virus is transmitted
For a long time, papillomavirus may not manifest itself at all, but at the same time a person becomes a carrier of this infection and infects the people around him. The virus is transmitted sexually, and the form of intimacy does not matter – infection occurs with the same frequency during vaginal, oral or anal sex.
A condom does not provide a 100% guarantee of protection against a pathogenic microorganism, since it does not cover all mucous membranes. Moreover, it is possible to become infected with the papillomavirus without even having direct sexual contact – intimate caresses, kisses and touches can also cause infection. Most often, human immunity fights back against the virus, but with a weakened immune system, the infection still settles in the tissues and begins to develop.
The domestic route of infection is much less common, but this possibility cannot be completely discounted. In this case, the virus can enter the human body through wounds, scratches and cracks in the skin.

Also, the virus can sometimes be transmitted from mother to fetus during childbirth. The likelihood that an infected person will transfer the infection himself from one area of \u200b\u200bthe skin to another is extremely small, but the spread of a virus activated on the genitals in this way is quite possible. This is due to the fact that the mucous membrane is not as dense as the skin, and is more susceptible to trauma.
If the virus is in an inactive state in the human body, it may not manifest itself for a long period of time, the activation of the virus occurs at the moment when the status of the immune system changes.
Provoking factorsthat can “awaken” the virus and bring it out of its latent state are the following:
- depression and stress;
- hormonal disorders;
- pregnancy, in which there is almost always a decrease in the functionality of the body’s defenses;
- chemotherapy;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives, as well as other hormonal drugs;
- hypothermia;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Symptoms
The manifestations of the 35 strain of the virus do not differ from the signs of the presence of other strains. They consist in the formation of growths:
- Warts . A large number of warts may indicate the presence of any type of infection.
- Pointed warts . Most often they appear in people after 18 years of age, they can form on various parts of the skin and mucous membranes, but in most cases they can be observed in the intimate or anal area.
- Flat warts . The 35 strain of HPV rarely causes such neoplasms, but if they are present, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible – such growths may indicate the onset of an oncological process.
In addition, a person has :
- fever without manifestation of bacterial or viral infection;
- in places where the build-up is formed, itching and redness are noted;
- women may develop inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
The course of the disease in men and women
The clinical picture in women and men is somewhat different.
Among women:
- genital warts;
- flat warts;
- genital herpes;
- papillomas;
- skin rashes of various localization;
- itching;
- feverish state;
- redness;
- signs of cervical disease.
For men:
- warts on the frenulum of the penis;
- inflammatory processes of the foreskin;
- polyps in the genital area;
- itching of intimate organs;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- burning when urinating.
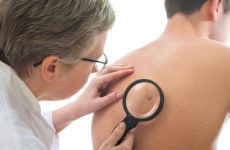
Diagnosis of pathology
To identify the 35th strain of the papillomavirus, the following methods are used :
- PCR test. A fairly effective analysis that allows you to determine the strain of the virus.
- Digene-test – a study that provides information about the amount of the virus.
- Visual gynecological or urological examination.
- Histological examination of affected tissues.
- Cytology of a smear from the cervical canal to determine changes at the cellular level.
Treatment Methods
There is no complete cure for papillomavirus. If a virus infection has occurred, it will remain in the body until the end of a person’s life. The entire fight against the virus, which is currently available, is based on silencing its development and suppressing the activity of the infection. Self-medication is not safe, so a doctor’s consultation is required.
Depending on the course of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the following therapy :
- The use of traditional medicine, which can be effective only at the very beginning of the development of pathology.
- Medical treatment. Antiviral and immunostimulating therapy is prescribed.
- Surgical removal of growths.
As for traditional medicine, celandine juice is most often used, which lubricates the neoplasm several times a day. It is important to remember that celandine is a poisonous plant, so you need to use it very carefully and follow the doctor’s instructions exactly.
Also effective are :
- castor oil ;
- garlic juice;
- aloe juice;
- ammonia;
- tincture of green walnuts.

If surgical intervention is necessary, the manifestations of papillomavirus are eliminated in the following ways:
- removal of the build-up with a scalpel;
- cauterization with a laser;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave method;
- cryotherapy;
- cauterization with chemical compounds (Solkvagin).
Antiviral drugs help block the development of infection, and also prevent the transformation of neoplasms into malignant tumors. This group of funds is represented by various forms – tablets, injections, agents for external use. For the treatment of the 35 strain of the virus, the following are considered the most effective:
- Panavir .
- Isoprinosine.
- Epigen.
- Allokin.
- Groprinosin.
- Cycloferon , Viferon, Genferon and other interferon derivatives.

In addition, patients are prescribed vitamin complexes and drugs that stimulate an increase in immune defenses:
- Immunal.
- Polyoxidonium .
- Reaferon.
- Amiksin.
In order for the treatment of papillomavirus to be more effective, it is necessary to carry out complex therapy.
Prevention
The body of women is more susceptible to infection with the papillomavirus, in contrast to the body of men. Therefore, every girl who has reached puberty should know about the rules for preventing infection with this dangerous virus.
Prevention is quite simple:
- use barrier contraception during intimacy;
- do not engage in casual sex;
- treat genital tract infections in time;
- completely give up smoking and alcohol abuse;
- carefully observe personal hygiene;
- do not use other people’s means and hygiene items;
- avoid abortion;
- strengthen immunity.
However, these preventive measures cannot guarantee 100% protection against the papillomavirus. Given its wide distribution and easy human-to-human transmission, vaccination is recommended. Vaccination against papillomavirus is the only reliable preventive measure that will prevent the virus from entering the body for 15–20 years.
But vaccination is possible only if the papilloma virus is absent in the body, otherwise it will be completely useless. In this regard, doctors recommend vaccinating girls 11-15 years old who have not yet had sexual intercourse.
The vaccination procedure consists of three stages :
- initial administration of the drug;
- re-injection after 2 months;
- final vaccination after 4 months.
If one of the steps is skipped, the vaccine will not be effective.
The papilloma virus is a very insidious, but, unfortunately, ubiquitous infection. Strains with a high and medium risk of oncogenicity can lead to serious and sometimes incurable diseases, so suppression of the virus is necessary. As for strains with a low oncogenic risk, they should not be considered safe, since they can provoke various complications in the genitourinary system.