The development of medical science has created many research centers that deal with the same problems of diseases.
As a result, various interpretations of the same ailments began to appear. This group includes various types of papilloma. The ambiguity of interpretations required streamlining the research.
The goal is to include the disease in the unified global classification of diseases of the ICD, which helps to simplify the orientation in the disease due to the unambiguous interpretation of the described symptoms, signs, conditions, clinical indications. The ICD is updated periodically. And if new achievements in the study of the disease are clarified, then these data appear in the classifier.
Содержание:
Grouping papilloma
Scientific developments unequivocally confirmed the fact that all varieties of papilloma that can be located on the skin of the body, mucous membranes, internal organs, are of a viral nature. The cause of the formations was HPV. Classes according to the classifier have their own sub-items, sorting neoplasms by type, type, localization.
It happens that the virus belongs to the class of pathology of internal organs or systems. Then papillomavirus does not dominate in the prognosis of development and treatment methods, but the place of localization and the type of manifestation are more important:
- unspecified localization;
- area of the hip joint, legs;
- areas of the shoulder joints, hands;
- lip area;
- Spike, eyelid;
- ears with external auditory meatus;
- facial areas: chin, cheeks, cheekbones, nose;
- neck, head;
- chest area, dorsal area, abdomen.
Genital warts , genital warts , having a common location on the internal organs, including the genital tract, anogenital zone, are distinguished into separate groups . This is a tumor formation that has grown in the epithelium infected with some type of virus.
They are called genital warts in the literature . Favorite places of manifestations are the urogenital tract, anus. Rarely found on other parts of the body.
Formations in the form of polyps belong to the classification where such a pathology is indicated, but can be described in the HPV group, for example, the formation of outgrowths of the mouth, pharynx, tongue. But such redundancy is not terrible in the diagnosis of the disease.
Groups of internal organs affected by HPV:
- benign formations in the anus , large, rectum;
- respiratory system;
- papillomas of the mammary gland;
- neoplasms of the uterus, which are benign in nature;
- formations in the genitourinary system: pyelocaliceal apparatus of the kidneys, urethra, ureters, bladder.
A small overview of the structure of papillomavirus
HPV is found in keratocytes of the cells of the upper stratum corneum of the epidermis in the form of an episome, the essence of which is the genetic elements of bacteria, i.e. DNA. The genome of the form virus is created by:
- Early genes that are responsible for the replication of the HPV genome.
- Late genes are responsible for the synthesis of the protein shell.
Papillomaviruses have antigens: species-specific, type-specific. An antigen is any element that the body considers foreign or potentially dangerous, requiring the production of its own antibodies that can mount an immune response.
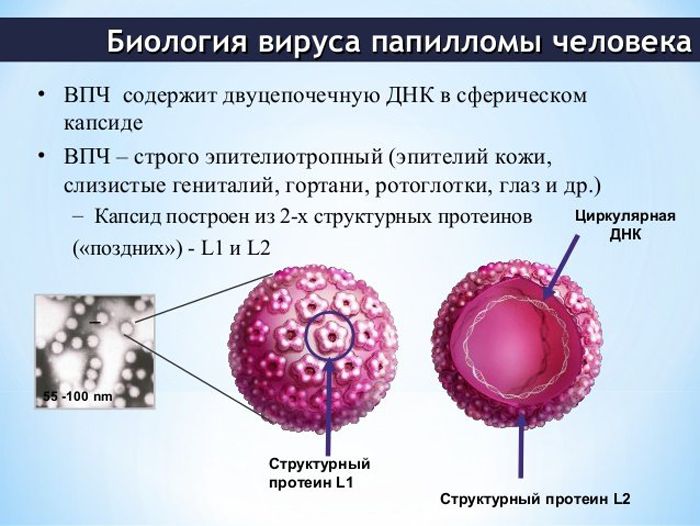
The formed virus does not have its own cell and waits for conditions for penetration into the body. Once in the environment, it finds a host cell and penetrates into it with its DNA, leaving its protein on the surface, which serves as a signal for the immune system to act to destroy it. And if rashes appeared on the skin, then the immune system failed, and the papillomavirus activated.
Overview of types of papilloma
The papilloma virus has up to 100 stamps. The type of stamp that acts at the site of penetration forms various papillomas that differ in appearance, growth rate, and localization on the body. It is important to determine the type of papilloma for the selection of effective treatment, to determine the risk of degeneration of the formation from a benign growth into a malignant tumor.
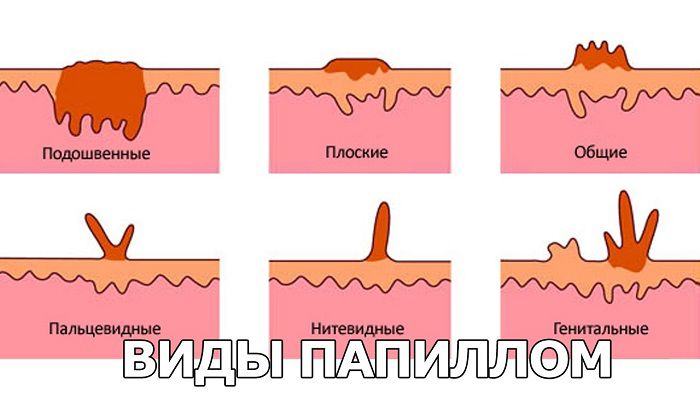
What are papillomas:
- simple or vulgar;
- plantar;
- flat;
- filiform;
- pointed.
Plain or vulgar
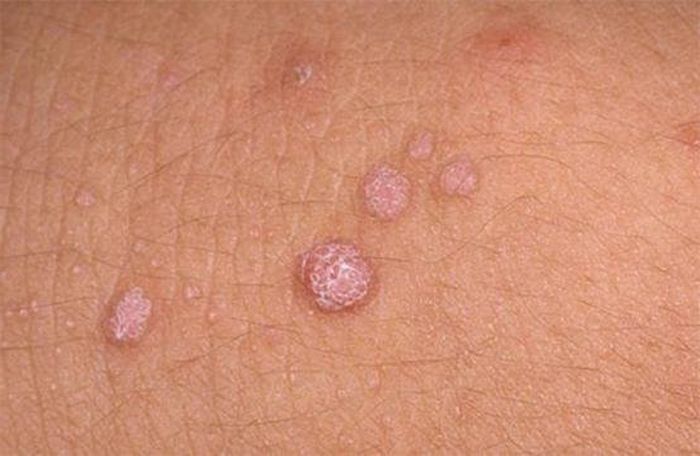
Such formations occur when several stamps from the list 26-29,41,63,77 enter the body. There is a high probability of a benign nature of such growths. The development process begins with a slight burning sensation and tingling in the area of \u200b\u200bthe body where the virus has penetrated.
Then, in this focus, a spherical growth of the tumor begins. After a certain period, the surface of the build-up becomes rough, changes to a dark color. The growth of a simple papilloma is from 1 mm to 1 cm in diameter.
Foci of papilloma species in adults on the body of the limbs of the hands: fingers and spaces between them, palms on the back. Frequent cases of vulgar papillomas in children, localization on the knees. Moving by crawling, the child injures the knees, and there are enough microcracks on the skin to become infected.
A simple papilloma begins with one formation. Without treatment, daughter growths grow next to it, acquiring a multiple character.
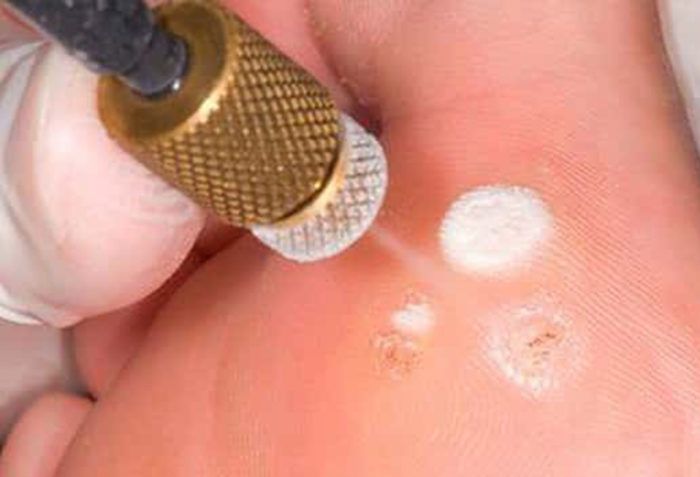
plantar
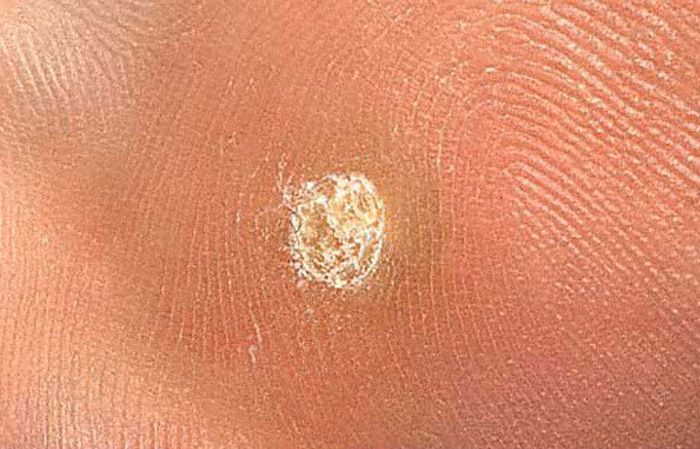
People who have picked up an infection of HPV 1,2,4 stamps will see their external manifestation on the feet, or rather the soles of the feet. They can be mistaken for a corn. But papilloma has symptoms, according to which identification is inevitable:
- the neoplasm on the sole has symptoms characteristic of papilloma vulgaris;
- pain syndrome;
- unlike corns that have a skin pattern, there is no pattern on papillomas.
In babies, blisters develop on the sole near the first growth, developing into papillomas. This development of events is called mosaic papillomatosis.
flat
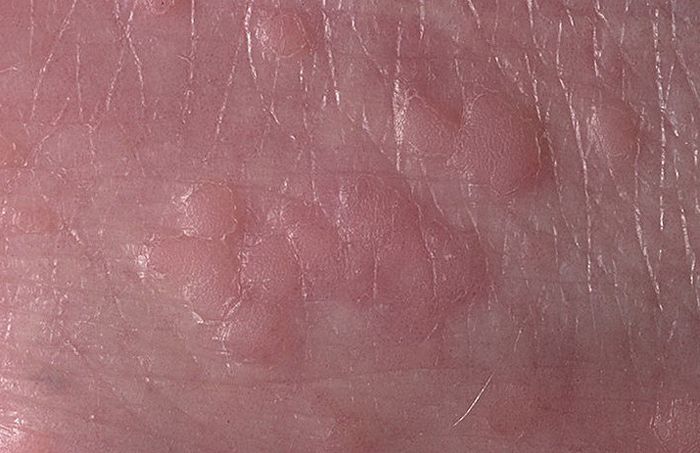
A formation that protrudes above the skin focus no more than a couple of millimeters is called a flat papilloma. Its shape is simply slightly elongated, oval. Places of manifestation are the area of the lips on the face, upper chest, external genitalia. In the female, they are found during diagnosis in the internal genitalia.
Multiple rashes are clearly visible on the body, although the colors of the growths differ little from the skin tone, or are slightly darker than the skin tone.
filiform
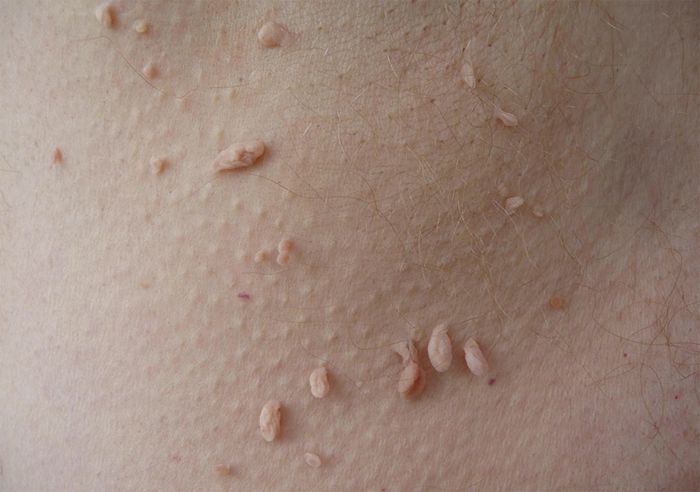
A formation that grows from a thin stem into an elongated narrow shape is called filiform papillomas or acrochords. Such species cause stamps of types 2 and 7. At the beginning of the manifestation, a small tubercle appears on the focus, which, in the process of growth, more and more stretches down and hangs down, resembling a thread.
These are papillomas that appear in both men and women after 40–45 years, that is, with increasing age. Filamentous papillomas more often than other types can be injured due to a special location on the body. The area of their distribution under the armpits, neck, upper eyelids, inguinal region, chest. Clothing or careless movement can hook on the base of the papilloma, its thin leg.
pointed
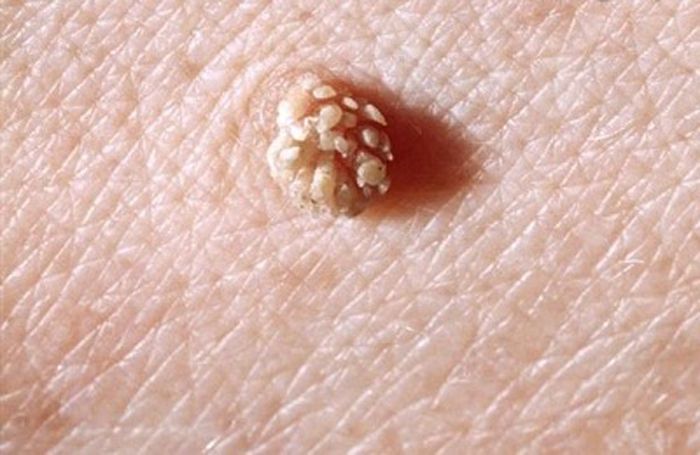
Formations in the form of papillae, which are arranged one by one or merge into groups, are called pointed papillomas, the second name of condylomas. Formations like a cockscomb in appearance. Coloring in skin tone, there are other tones, they reach pronounced pink shades.
Provoke infection HPV stamps, which can only be transmitted sexually. Therefore, the places of dislocation of such papillomas are the genital organs of both sexes, the perineum, groin, anus.
The disease has a high transience. In a few days, more and more healthy tissue is captured by rashes, single or multiple. The disease is poorly treated, giving relapses, other infections are often found in the diagnosis: chlamydia, mycoplasmosis.
So, we have considered what types of papilloma are according to the classifier. But this is not yet complete information about papillomas. The types of papilloma on the body include all of the above, with the exception of pointed ones. Although the location of the genitals is also on the body. Therefore, the conclusion is that papillomas and their types still depend on the types of virus stamps and have their favorite places of localization. In addition to species, papillomas are divided into types
Danger types of viruses
HPV stamps are grouped according to the risk of possible oncological complications. Allocate:
- high, HPV stamps – 16,18,36, 45;
- medium, HPV stamps 31 , 35, 33, 58 . 51, 52;
- low, stamps 11, 44, 43, 42, 6;
- non-oncogenic types.
Benign growths of non-oncogenic types most often cause papillomas on the skin.
It is impossible to delude yourself, even having a conclusion of non-oncogenicity. A simple type of papilloma on the face suddenly degenerates into oncological melanoma, which is almost impossible to escape from and death will occur in a couple of months. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent the development of the disease in the bud, that is, at its first manifestations in the form of papilloma, one must begin to be treated.
Neoplasms are especially dangerous if they capture internal organs. Internal papilloma is detected as a result of special medical research.
This type of disease is not well understood, but it is she who poses a huge risk of growth of oncological tumors. The cause of oncology is caused by stamps 7, 11, 32, 57, 72. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material: papilloma ICD 10 .
General principles of therapy
The healing of various formations that are caused by a stamp is paramount to depend on the location. Treatment is carried out in combination with the use of antiviral drugs, immunostimulants.
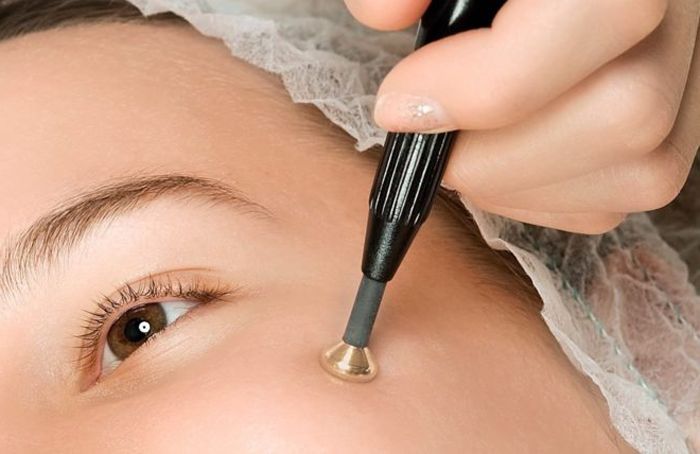
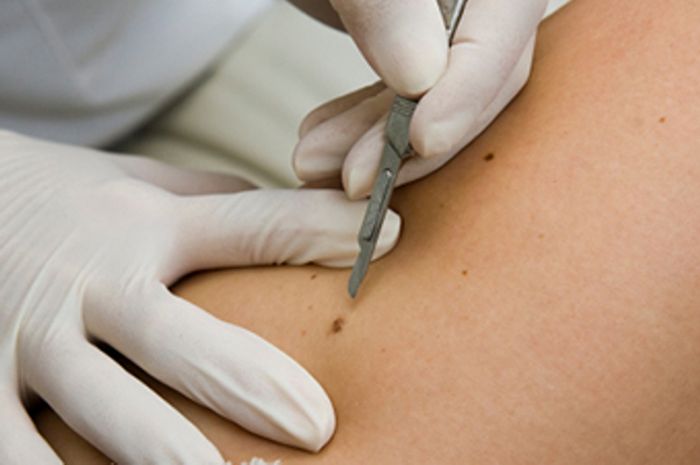
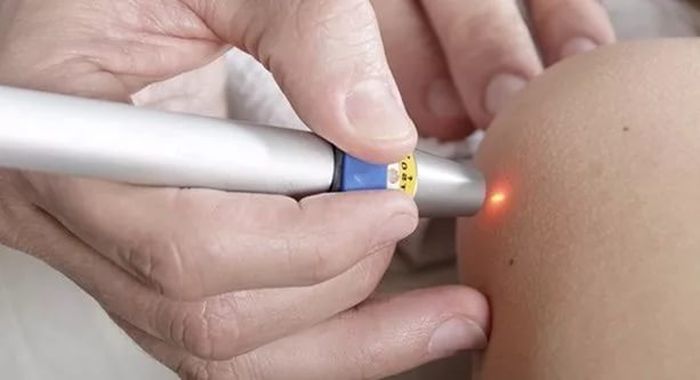
There are growths, according to the ICD-10 classifier, passing like papillomas of the eyelid, skin, which use standard treatment methods:
- freezing;
- burning out;
- laser removal.
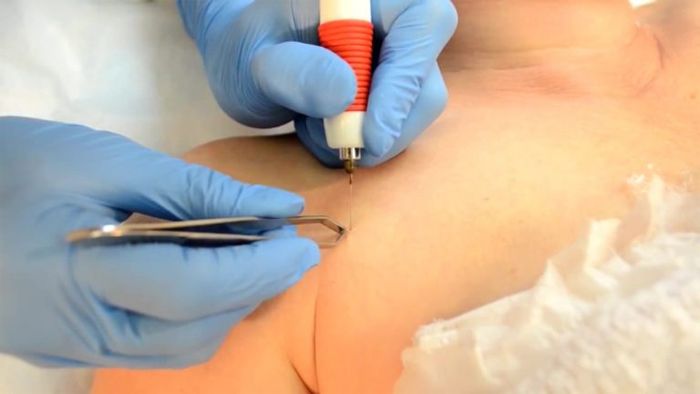
ICD-10 formations: mouth, nasal cavity, pharynx, eyelids, larynx, internal breast papilloma fall into treatment protocols that require approximately the same nature according to the methods of minimally invasive surgery. Conventional methods in these areas are associated with difficulties.
When papillomas are found in the internal organs, a quick reaction is needed. Only surgery in the shortest possible time will help to avoid oncology. Histological analysis of the removed formation diagnoses its type: benign or malignant.
All of the above proves the need for the treatment of papilloma, despite their simplicity. After all, cancer does not spare either the young or the elderly. Doctors are puzzling over the cause of cancer in humans. And having a papilloma, you obviously carry a bomb, when it explodes it is not known and whether it will happen at all. But why take the risk once again, in the early stages of papillomatosis, they achieve good results that will not fail in the future.