Benign neoplasms are quite widespread. People do not attach great importance to these formations and do not go to doctors, which can eventually lead to malignancy.
At annual preventive examinations, the individual should talk about everything that brings him discomfort and pain. Early diagnosis will lead to effective treatment.

Содержание:
- 1 General information, types of growths
- 2 How to distinguish HPV from a polyp?
- 3 Causes of the appearance of pathology
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 Do I need to see a doctor?
- 6 Diagnosis of the disease and examination of the intestines
- 7 Therapy of papillomatosis
- 8 Features of the treatment of papillomatosis in the rectum
- 9 Prevention and prognosis
General information, types of growths
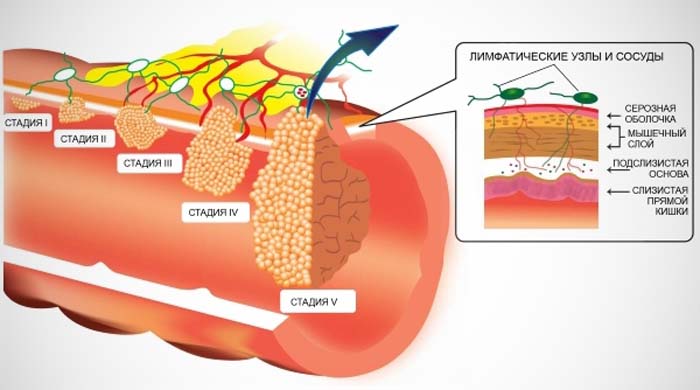
Intestinal papillomas are benign neoplasms that result from the active action of the human papillomavirus (HPV). Every sixth person has HPV, but not everyone has it. Most people are just a carrier of this virus without even knowing it.
Some are less fortunate and have HPV manifested by outgrowths on the skin and mucous membranes. HPV infection is highly specific to humans. HPV is a group of viruses that belongs to the papillomavirus family and includes 27 species, 5 genera and more than 600 species.
The main types of growths:
- flat;
- pointed;
- filiform.
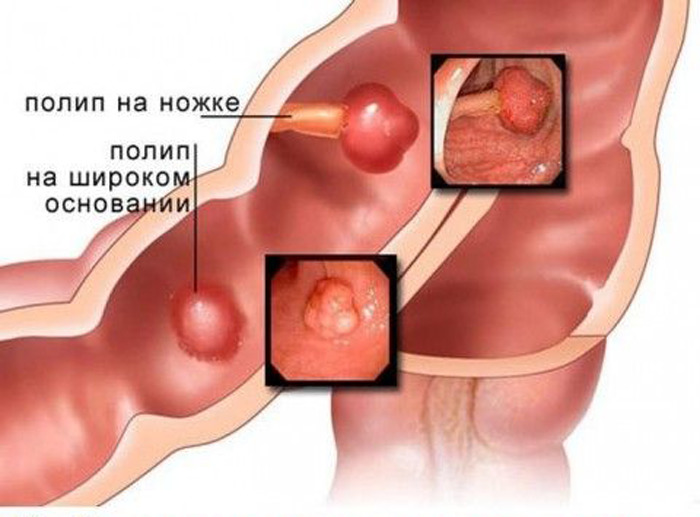
How to distinguish HPV from a polyp?
Many do not see the difference between papilloma and polyp, but it is still there. They have, at first glance, insignificant differences, which are not given much importance. These neoplasms have only one common feature – they are benign.
A polyp is formed on the intestinal mucosa, colon, rectum and stomach as a result of hormonal disorders, as well as against the background of reduced immunity.
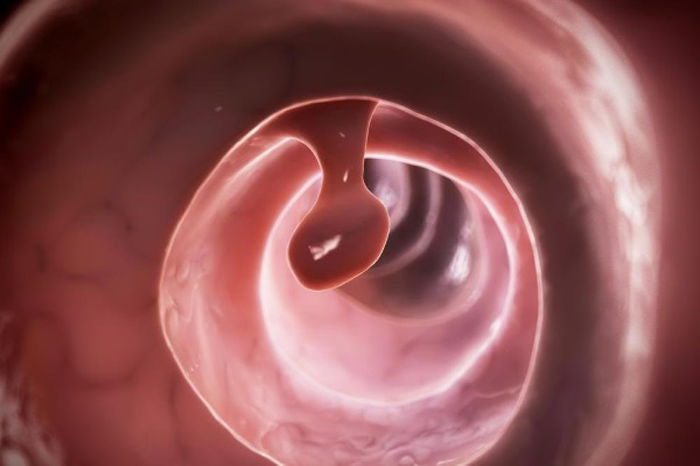
Outwardly, the polyp looks like a mucous formation on a stalk with a smooth surface, ranging in size from 1 to 5 cm. Polyps have many types and are often malignant.
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm that most often affects the outer part of the rectum, but can also form on the intestinal mucosa, as a result of the penetration of the human papillomavirus into the body.
Outwardly, papilloma looks like a formation with a wide base with a striated surface, ranging in size from 0.1 to 2 cm. Unlike a polyp, papillomas do not have a wide variety and are less likely to become malizable.
Causes of the appearance of pathology
Against the background of a decrease in the activity of the body’s immune system, the human papillomavirus is activated, which previously entered the body in the following ways:
- Sexual (the most common route of transmission).
- Transplacental (from mother to child).
- Contact (when touching household appliances, through abrasions and scratches).
- Autoinoculation (self-infection).
Due to the following reasons:
- Promiscuous sex, and unprotected sex.
- The presence of bad habits (alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction).
- Presence of inflammatory bowel disease.
- Emotional overstrain.
- Failure to follow the rules of personal hygiene in the presence of cracks, microtraumas, cuts, which can lead to HPV infection.
- Non-compliance with the regimen and balance in nutrition, excessive consumption of fried, spicy, salty.
- Uncontrolled intake of potent drugs.
There are 2 opinions, one of them is that papillomatosis is congenital, and the other is acquired.
Symptoms
The disease can be asymptomatic for a long time due to the small size of the neoplasms. Therefore, patients are treated already at an advanced stage of the disease, when symptoms appear.
- Detection, in feces, bloody streaks.
- Stool disorders (constipation and diarrhea, which either replace each other or appear separately).
- Isolation of blood after the act of defecation.
- Pain of varying intensity, can be both aching and cramping. Increases before the act of defecation, and then subsides.
- Dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, heaviness in the abdomen).
- Anemia occurs as a result of prolonged bleeding (weakness, headache, dizziness).
- An increase in body temperature, as a result of the development of the inflammatory process.
- With the localization of papillomas in the anus, the patient may be disturbed by the sensation of the presence of a foreign body and an increase in humidity in the anus.
- Increased salivation.
Do I need to see a doctor?
The pressing question is, is it worth going to the doctor? Definitely worth it!
Although intestinal papillomatosis has a lower risk of malignancy than with polyposis, early diagnosis and treatment will not lead to a disastrous outcome, but on the contrary, the outcome will be favorable and without consequences.
Diagnosis of the disease and examination of the intestines
For diagnosis, objective examination data (often uninformative), laboratory and instrumental research methods are used.
Laboratory research methods:
- KLA (decrease in the level of erythrocytes and hemoglobin, with inflammation, an increase in ESR, leukocytes with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left).
- Analysis of feces for occult blood.
- Blood chemistry.
- PCR method (HPV detection).
Instrumental research methods:
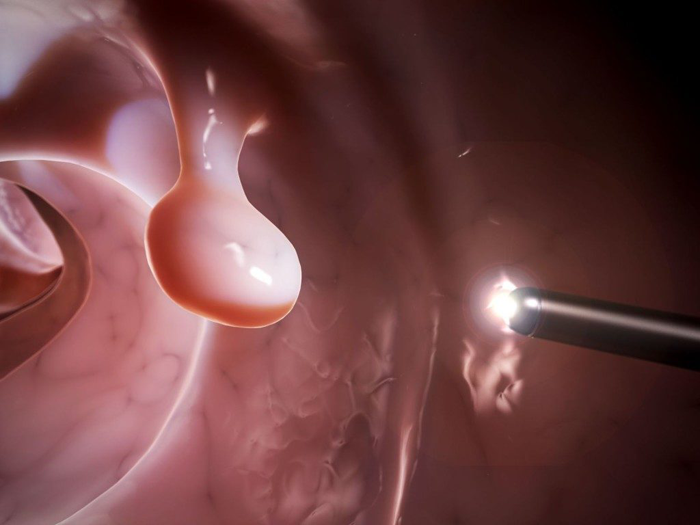
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination method that allows you to evaluate the mucous membrane of the colon using an endoscope.
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray method for examining the colon by filling it with a suspension of barium (contrast agent).
- Sigmoidoscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the lower part of the sigmoid colon and rectum using a special tube.
- ultrasound.
- Taking a biopsy for histological examination.
- CT and MRI.
Therapy of papillomatosis
In the treatment of intestinal papillomatosis, I single out: conservative and surgical treatment.
Conservative treatment
Antiviral drugs , which are aimed at suppressing the reproduction of HPV. Immunomodulating and restorative drugs. As well as symptomatic therapy.
- Isoprinazine is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. It is taken 1000 mg 3 times a day for 2 weeks. After a month break, you can repeat the course of treatment.
- Groprinosin is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. It is taken 500 mg 3-8 times a day for 14-30 days.
- Genferon is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. Available in the form of suppositories. 1 suppository 1 time per day for 10 days.
- Viferon – has a high antiviral and immunomodulatory activity. 1 suppository 2 times a day for 5-10 days.
- Panavir is an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. It is taken in 3 doses during the first week with an interval of 2 days, during the second week in 2 doses with an interval of 3 days.
- Likopid is an immunostimulating drug. It is taken 10 mg 1 time per day for 10 days.
Surgical therapy
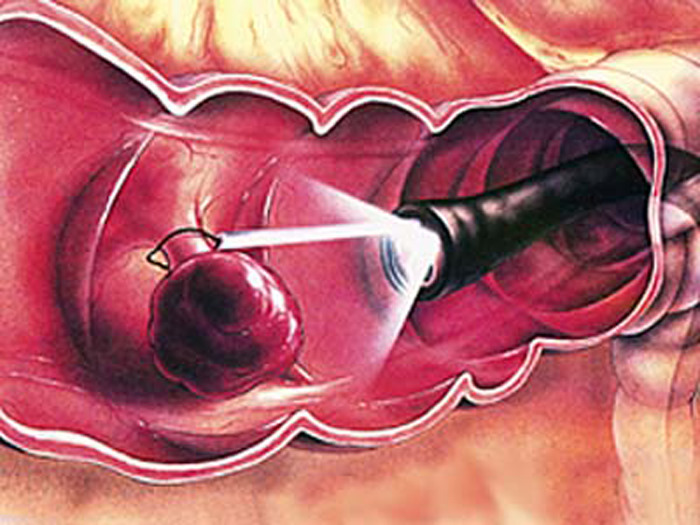
The optimal treatment for papillomatosis is still a surgical method of treatment. Methods of surgical treatment:
- Removal of papillomas with a laser.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction .
- Radio wave therapy.
- Removal of papilloma with a scalpel. The most traumatic method.
Folk remedies and recipes
In some cases, alternative therapy has a beneficial effect on the treatment of papillomatosis. They have an immunostimulating, anti-inflammatory effect on the patient’s body.
- Enemas with infusion of celandine. Preparation of infusion: pour 50 g of celandine with boiling water (50 ml), leave for 1 hour and strain.
- Baking soda solution. Acts as an antiseptic and disinfectant.
- Baths from such plants as: chamomile, St. John’s wort, sage. With papillomas of the anus.
Features of the treatment of papillomatosis in the rectum
In the treatment of papillomatosis of the rectum, medicinal, hardware and folk methods are used.
medicinal method. Removal of papillomas with the help of drugs: cryopharm, ferezol, wartner cryo , super celandine.
Hardware methods:
- With the help of a laser.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Surgical intervention (cutting with a scalpel).
About folk methods mentioned above.
Prevention and prognosis
With timely treatment, the prognosis of papillomatosis is favorable. If timely treatment is not started, complications may occur (bleeding, intestinal obstruction, etc.), and even worse is malignancy.
Prevention plays a big role in reducing the risk of disease. Firstly, there must be a constant sexual partner, and it is also necessary to avoid promiscuity.
Secondly, compliance with the rules of personal hygiene. Do not use other people’s razor, towels to avoid the contact method of HPV infection. Thirdly, it is necessary to observe the diet, as well as to monitor its balance.
Fourthly, to eliminate the harmful effects of alcohol, cigarettes and drugs, which lead to the development of many diseases. Thus, they suppress the protective processes of the body.
Some experts advise to resort to vaccination against several types of HPV.
Papillomas are not rare diseases, but people treat them with some negligence, which can eventually lead to papillomatosis of the intestines and other organs.
And in the future, and to an unfavorable outcome of the disease. Therefore, each person should take care of his own health and seek medical help in a timely manner.