Throughout the history of its existence, people share the planet with many other species and microorganisms. As a result of contact with some of them, they become an environment for reproduction and development. For example, the human papillomavirus is perceived as a harmless skin growth, usually without pain when touched.
This makes it dangerous, because the threat of developing harmful tumors or the rapid defeat of large areas, blood poisoning is almost asymptomatic. It is necessary to get rid of such unexpected guests in your body in order to feel healthy and protected.

Содержание:
What is papillomavirus?
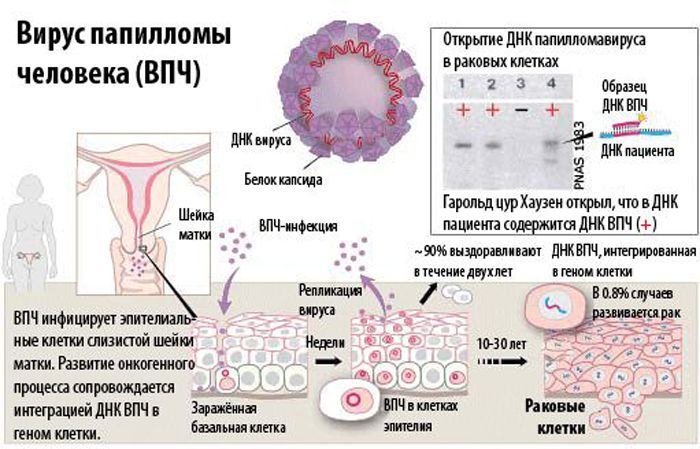
The human papillomavirus is understood as an infection that affects the tissues of the epithelium, causing the appearance of warts and other skin growths, including on the mucous membranes. The danger of the virus was discovered by Harold zur Hausen in 2008, who, as a result of his research, identified two oncogenic types. For modern medicine, over 100 varieties of HPV pathogens with genetic differences are known, see which HPVs of the oncogenic type in women . Approximately 40 species are capable of affecting the human genital organs.
The virus is usually attributed to latent sexual infections with the greatest distribution among these diseases. The risk group includes up to 50% of the adult population who are sexually active. Among other types of infection – vertical – from mother to child in the birth process and domestic – through contact with mucous membranes and blood.
Depending on the aggressiveness of the virus, it can develop as a benign or malignant formation. In the first case, getting to the site of unprotected epithelium, for example, a wound or mucous membrane, the virus cells begin to rapidly divide and “occupy” new positions.
Our skin, in order to somehow limit the movement of the pathogen, tries to create a barrier of keratinized cells. So, there are growths and warts. All the same, the virus enters the bloodstream, spreading throughout the body, it can appear on any other part of the epithelial tissue.

If the pathogen behaves very aggressively, then, along with its rapid spread, it is able to infect cell chromosomes, causing the formation of dysplasia or carcinoma. It is impossible to guess in what way and nature of development HPV that has entered the human body will differ.
Here, the condition of the skin and mucous membranes, immunity, predisposition and heredity at the genetic level play an important role. Stress makes the virus more aggressive, so women are more likely to suffer from this disease than men.
The most common factors that increase the body’s sensitivity to the papilloma virus are :
- Post-transplant – A temporary decrease in immunity makes the body more susceptible with less defense against pathogenic organisms.
- Direct contact with infected HPV.
- Unbalanced diet with frequent stressful situations.
- Conducting a promiscuous sexual life, the presence of several partners in one period.
- Predisposition due to genetics.
- Pregnancy – a woman’s immunity temporarily falls against the background of a change in the intensity of the release of certain hormones.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- The presence in the course of treatment of steroid hormones that disrupt the mechanism of formation of epithelial fibers.
- Diabetes.
- Obesity – the skin can be injured during movement at the points of contact of the folds of the epithelium, opening up access for pathogens.
Approximately about 90% of those infected in the first year are able to recover from the disease on their own. In the rest, HPV turns into a recurrent, chronic, long-term form with a probable degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
Symptoms of papillomavirus infection in men and women
HPV can live in the human body for a long time without revealing itself. This is achieved through a long incubation period of several weeks or even years. In the presence of strong immunity, the body independently blocks the pathogen, preventing it from multiplying and spreading throughout the body. However, any malfunction of the immune system can provoke the manifestation of symptoms of papillomavirus.
Development with external symptoms is not always very obvious, with a pronounced and rapid course. Most often, a sharp proliferation of skin formations is characteristic of infection through micro-wounds on the epithelial cover of the fingers, knees, feet or palms. Then the neoplasms are localized around the point of entry into the body, with subsequent location even in distant skin areas from the site of infection due to entry into the bloodstream. The clinical picture depends on the type of HPV that has affected the person.
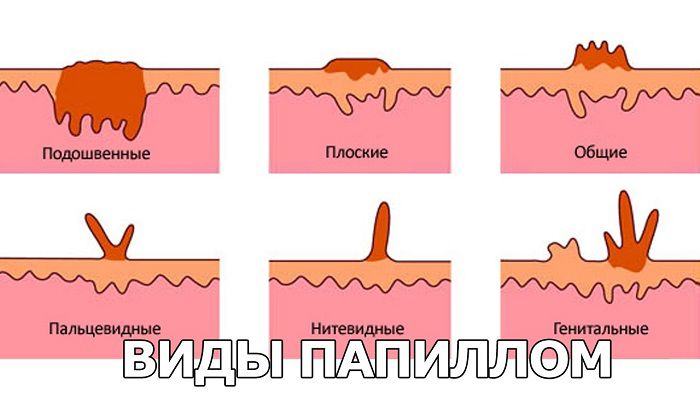
There are five main types of papillomavirus:
- Ordinary, vulgar or simple papillomas . The size is from a couple of millimeters to 1 cm, the back of the hand, soles, toes and hands are chosen as the localization site. Most often, they are not treated, but resolve on their own in a few months or years.
- Juvenile or flat warts . They are up to 5 mm in diameter, accumulate on the shins, palms, neck, face. They appear most often in boys of adolescence or youth, whence the name is taken. Differ in invisibility and weak distinction in color, degree of keratinization.
- Plantar and palmar growths . Sometimes they are called corns, thornsbecause they appear in those places where the skin of the hands or feet is most often subjected to friction or pressure. They reach 1 cm in diameter. They are the most difficult to cure, they are painful.
- Acrochords or filiform papillomas . In appearance, they resemble a thin short hair of skin, the length of which reaches 1 cm. They are collected in the folds of the epithelium, armpits, on the chin, lips, eyelids and other parts of the face, neck. They do not resolve on their own and require treatment or removal.
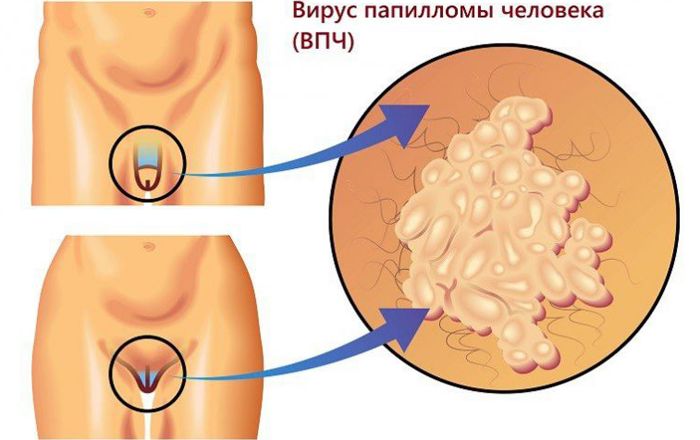
- Warts or pointed growths . The most dangerous type, which is localized on the skin of the genital organs of both sexes. It can spread to the mucous membrane of the larynx, to the anus, in the bladder. Increase the risk of transformation into malignant tumors.
What is the threat from papillomavirus?
Regardless of the state of health of a person and his genetic predisposition, if the virus enters the body, the consequences can be unpredictable. On the one hand, there are many cases when a person independently fought without any medicines or other means with a pathogen. However, it is not always possible to achieve such a result, often growths and warts spoil the aesthetic appearance, being localized on open areas of the skin or even on the face.
Some of the species are able to “capture” large areas, forming a “map” on the human epithelial cover. Even if there are no painful sensations, the sensitivity in the affected areas is significantly reduced, which leads to a decrease in the reaction to the effects of the outside world. Reproduction in large numbers has another form – the formation of whole clusters, hanging skin plexuses.
Sometimes, if they are large, they can be painful. When changing clothes or doing normal daily activities, warts and skin growths can be injured. This causes them to grow even more and increase in size. When the body ceases to cope, it is necessary to help it get rid of the invasion of infectious agents.
Another danger factor is the ability to transform from a benign formation into a malignant tumor. This is common for HPV on the genitals that affects the cervix. It is possible to identify the “enemy” only when examined in the doctor’s chair, because almost all skin growths do not have innervation, therefore they do not signal pain as a result of contact with solid objects.
The danger of existing varieties of viruses is classified by numbers from 1 to 81. The danger rating is presented in the following form:
Группа Номера штаммов Неонкогенные 1–5, 10, 28,49 Низкоонкогенные 6, 11, 42–44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81 Среднеонкогенные 26, 53, 65 Высокоонкогенные 16, 18, 31–35, 39, 45, 52–56, 58, 59, 66, 68
Among HPVs from a highly oncogenic group for strains 16 and 18, according to statistics, the greatest danger, in 70% of infected women, the disease ends with oncology. The first is more dangerous, because up to 54% of cases, the appearance of squamous cell carcinoma is on his “conscience”.
For women
HPV pathogens that most often affect women are classified into the following groups:
- Not causing the development of oncology.
- Causing cancer in rare cases.
- Causing oncological neoplasms with a high probability.
The greatest danger is in the third group of pathogens, since, in addition to the ability to cause cancerous tumors, they are characterized by rapid development.
Most often, women are at risk of reduced immunity. This happens as a reaction to stress, pregnancy, hormonal changes in transitional cycles, the transfer of serious illnesses, etc. Promiscuity in sexual intercourse, unhealthy lifestyles, bad habits and other factors that adversely affect the body’s defenses become a favorable environment.
The detection of HPV in a woman’s body does not mean the presence of cancer or its imminent appearance. However, the following factors contribute to this:
- The use of products that are harmful to the body in any form and form, which fill the tissues and systems of the body with toxins and toxins.
- Hard strenuous work.
- Hormonal disruptions, diabetes and other diseases that cause metabolic disorders.
- Rare contact with sunlight and fresh air.
- Decreased immune defense.
- Frequent use of nicotine.
- The presence of a high concentration in the body of free radicals that can damage the DNA structure at the molecular level.
For men
According to statistics, approximately 25-70% of men who come into contact with an HPV-infected woman also become infected. In most cases, those who do not show the virus become its carrier. Even in the absence of manifestations on the genitals, in the anal area or other skin, HPV is able to spread to new partners, mercilessly infecting them.
If skin growths form on the genitals, then men should seek medical help, as this creates discomfort for their usual lifestyle, hygiene and may threaten the development of atypical epithelial cells. The latter is the initial stage of the formation of cancerous tumors .
It is believed that the defeat of sexual types of papilloma of men of the epithelium of the anus and genital organs with an equal measure of probability can turn into cancer, like HPV of the cervix of women. In men, the risk group includes those who :
- Started having sex early.
- Changes sexual partners frequently, allows unprotected contacts.
- Allows the presence of inflammatory processes on the epithelium of the genital organs in the advanced stage.
- Has a weak immune system.
- Neglects personal hygiene.
- Smokes and drinks excessively.
During pregnancy
The peculiarity of fetal nutrition lies in the presence of the placenta, which, on the one hand, supplies all the necessary substances and oxygen to the child, and on the other hand, is a reliable protective barrier against almost all harmful pathogens that live in the mother’s body. Therefore, direct infection does not occur. However, during childbirth, there is a high probability of infection of the baby with laryngeal or genital growths, anal papillomas.
With the location of skin formations on the skin of the genital organs, the risk of rash, bleeding and damage to papillomas accelerates. Otherwise, when localization is a different epithelium of the body, the virus does not pose any danger to the child.

Papillomas contribute to an increase in vaginal discharge, which, in turn, becomes just an ideal environment for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. This leads to hormonal disruptions and a drop in the immune functions of the body of pregnant women.
Diagnostics
The essence of the diagnosis is a preliminary examination of the detected skin growths. Scrapings are taken from these neoplasms and clinical studies are carried out to identify the type of virus. The principles and methods of diagnosis in men differ from those in women. However, for all assigned:
- PCR diagnostics . Based on its results, the amount of HPV in the scraping from the affected area is determined and other STDs are detected.
- Dijin test . Helps to identify the type of virus.
- Anoscopy . The perianal area is examined under magnification.
- Histological and cytological examination reveals the risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor and the stage of the disease.
- Immunoassay . Determines the presence of HPV antibodies.
- Colposcopy . Appointed for women. It consists of a biopsy of the material from the cervix, passing the PAP test.
In addition to biopsy for women, when HPV affects the cervix, if necessary, biopsies can be ordered for other infected people to collect more accurate data.

How to treat
The treatment is based on an integrated approach based on the physical elimination of warts and growths, as well as increasing immunity, and suppressing a viral infection.
To date, there are no drugs that can purposefully destroy HPV. The most common means today are :
- Preparations based on iodine for local control of growths on the epithelium.
- Immunal.
- Immichimod is available in the form of a cream to stimulate cellular immunity.
- Viferon and cycloferon in ointments for topical external use after the physical removal of papillomas.
- Interferon is administered through subcutaneous injections, eliminating growths in a few days of therapy.
Removal methods
To eliminate epithelial growths on the body, the following methods are used:
- Radioknife . As a method of physical elimination, high-frequency waves are used, which allows painless removal of the growth with minimal damage. Often used to combat papillomas on the nasolabial folds, eyelids and other open areas of the body. The most popular device is the Surgitron apparatus.
- Laser . The technique of burning the epithelium is used. It is an effective method without the risk of bleeding.
- Cryodestruction . A preparation with liquid nitrogen is applied to the surface of the growth. Warts and growths are literally frozen and destroyed, which is what the name of the procedure means.
- Electrocoagulation . The oldest method, which is based on the impact on the HPV-affected area of the skin with electricity. Rarely used today for facial surgery, as the result can be scar tissue of the epithelium.
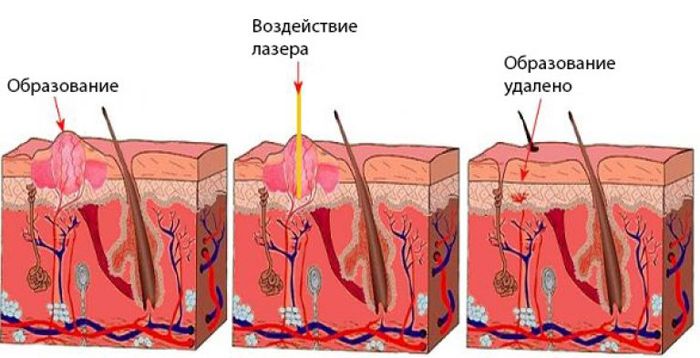
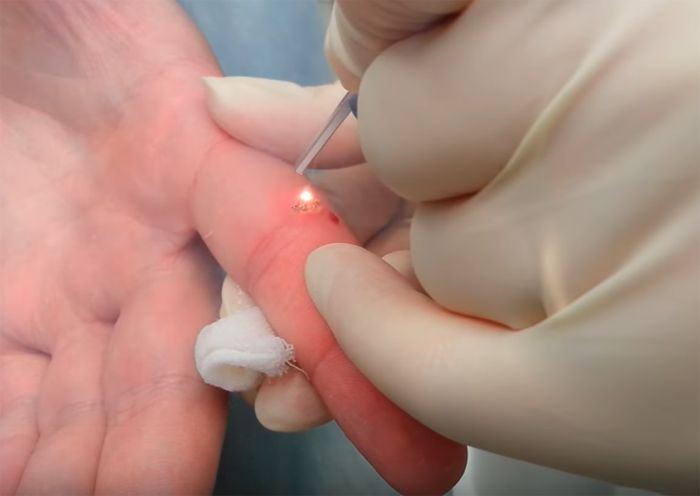
Folk methods based on the juice of garlic, dandelions, celandine, etc. are also widely used. In order to prevent repeated growths, after removing primary warts and papillomas, regular monitoring and control by a doctor should be carried out.
Prevention
In order to prevent infection with papillomavirus, you must adhere to the following rules :
- Undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist for women, contact a dermatovenereologist in a timely manner for men as soon as growths are found on the genitals.
- After receiving an injury, immediately disinfect the wound and close it from the external environment with a band-aid.
- When visiting public places, adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, constantly wash your hands upon returning home.
- Avoid contact with people who are infected with HPV.
- Limit sexual contact to one regular partner.
- Exclude from life bad habits that lead to a decrease in immunity.
- Provide good nutritious food.
- To increase immunity, to be more often in the fresh air, to take sunbaths.

A Pap smear or PAP test in women does not detect papillomavirus, however, it signals cellular shifts towards oncology. One of the causes of which may be the human papillomavirus. An increased number of cells with an atypical structure in a scraping indicates a risk of developing cancer. This method helps to identify oncological diseases in the earliest stages of manifestation.
Vaccination
Today, only two drugs are used for vaccination :
They do not cure an infected person, but they increase the body’s resistance to harmful influences and generally protect against various types of infections. Vaccination is effective only for a “clean” organism aged no more than 26 years. Therefore, children should be vaccinated against this infection.
Conclusion
Papillomas on the human skin most often cause discomfort due to an unpleasant appearance, painful sensations when in contact with clothing, and the center of increased attention of outsiders. Few people think that HPV in the body during periods of weakened immunity is able to develop and affect large areas or even turn into a malignant formation.
Therefore, children and young people under 26 should be vaccinated against papillomavirus, adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, and at the first detection of an unfamiliar growth on the epithelium, look for safe methods of treatment.
During pregnancy, papilloma is not dangerous for a child if its place of growth is not the mother’s genitals. Otherwise, the risk of infection of the baby during childbirth increases. This threatens with complex formations of growths on the vocal cords, the mucous membrane of the larynx, and the skin of the genital organs.