Papillomas are characteristic small growths on the skin or mucous membranes that result from the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Moreover, the virus can be inside the body for years and not make itself felt until the immune system is weakened for some reason.

Often, soft neoplasms appear in the genital area, but papillomas on the face , armpits and other parts of the body should not be ignored.
Содержание:
What is HPV and what does it look like?
Papillomas are benign formations on the surface of the skin or mucous membrane, which appear as a result of the growth of epithelial tissue.
This is preceded by active reproduction of the human papillomavirus, which divides very quickly in favorable conditions for it.
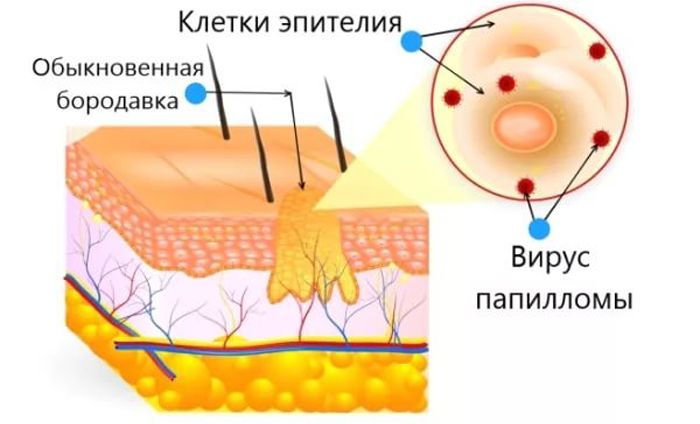
The formations are soft, often convex, can appear on any part of the body. They can be of any color and any size, but tend to grow very quickly.
Papilloma consists of multiple small nodules formed into a single growth, it can look like an allergic rash, a mole, a pimple, so many are in no hurry to see a doctor.
In addition, the formation can be almost flat, or it can protrude significantly above the skin and cause noticeable discomfort. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material: papilloma ICD 10 .
What is neoplasm made of?
Outwardly, papilloma resembles papillary growth.
Structurally, the outgrowth is formed by connective tissue penetrated by the thinnest vessels and covered with epithelial tissue. Neoplasm tissues can be loose or dense, soft or prone to keratinization.
Varieties of formations
Papillomas are any benign growths on the skin or mucous membranes caused by HPV activity. Therefore, there are several types of classification of growths according to various criteria.
By type of growth :
- Exophytic, which protrude above the surface of the skin.
- Endophytic, which germinate inside the epithelial layer.
Appearance and location :
- Ordinary (simple, vulgar).
- Flat.
- Plantar.
- Filamentous (acrochords).
- Pointed (warts).
Simple papillomas resemble small protruding moles of a rounded shape, often rough, rough. Can be single or multiple, rarely cause discomfort.
Flat neoplasms are difficult to notice on the skin, since they practically do not rise above the surface. They are more often oval or round, less often – polygonal or irregular in shape, can have any color.
Papillomas that appear on the soles are called plantar warts. They have a clear border, outwardly resemble a corn. It is impossible not to notice plantar papillomas, since they cause severe discomfort when walking.
Filamentous papillomas (acrochords) are the most common. They resemble a wide, rounded, convex papillary formation on a thin thread-like stalk. Acrochord tissue is always elastic, growths are often multiple.
Genital warts are often compared with cauliflower inflorescences: they have this form. Places of localization: genital area, anus.
The nature of localization
Papillomas can appear on any part of the body or mucous membrane, however, there are so-called favorite places for neoplasms, and there are quite unusual ones. The latter will be discussed further.
Breast papillomatosis
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is a formation inside the mammary duct. Outwardly, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, profuse discharge from the nipple (white, greenish, brown with bloody impurities) causes anxiety.
The main risk factor for the disease is hormonal failure (perimenopause, obesity, ovarian dysfunction).
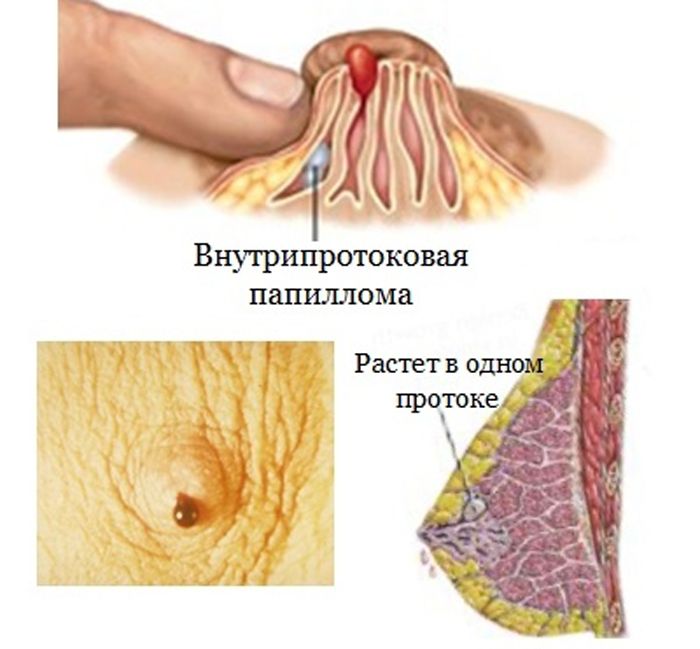
Diagnosis is carried out by ductography, ultrasound, MRI, mammography. Treatment is surgical only.
In the throat
Papilloma in the throat is a small papillary formation that develops from epithelial tissue. As a rule, with papillomatosis of the throat, there are several growths in the tonsils .
This disease is more common in childhood, up to 5 years, and infection occurs from an infected mother during childbirth.
Symptoms of the disease include a change in voice (hoarseness), difficulty breathing, coughing, shortness of breath, and in severe cases, asthma attacks.
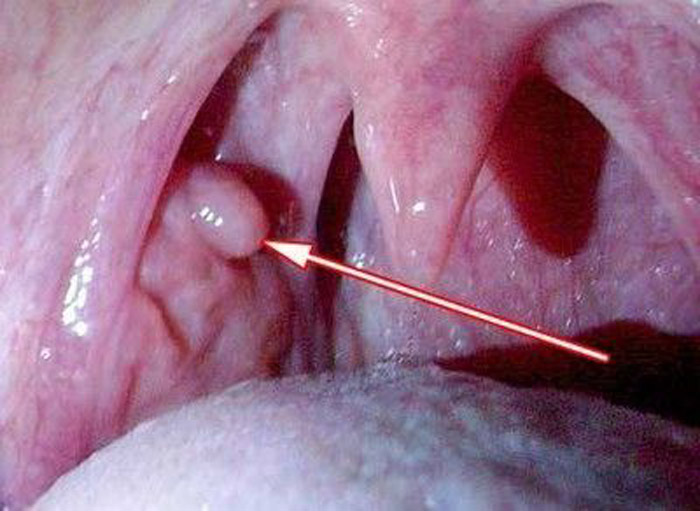
After the diagnosis is made, the type of virus is determined, then the most optimal method of treatment (surgical or medical).
With extensive damage and severe course, it is not advisable to remove neoplasms by the surgical method. Doctors also try to avoid surgical removal of papillomas in childhood.
With a non-surgical method, interferons are prescribed, as well as drugs that promote the production of their own interferons, antiviral drugs, cytostatics, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Among the surgical methods used:
- Electrocoagulation (removal by electric current).
- Cryodestruction (exposure to low temperatures).
- Ultrasonic disintegration (destruction by ultrasound).
- Argon plasma or laser coagulation (laser exposure).
Sometimes a child goes through up to 2 dozen operations to remove papillomas on the throat, but it is the operation that allows you to return to normal breathing and speech.
The paradox is that multiple operations lead to the formation of scars that interfere with normal breathing and talking.
Papillomatosis of the cervix
Since HPV is most often transmitted sexually, cervical papilloma is not uncommon. The danger of the disease is a high risk of degeneration into cervical cancer.
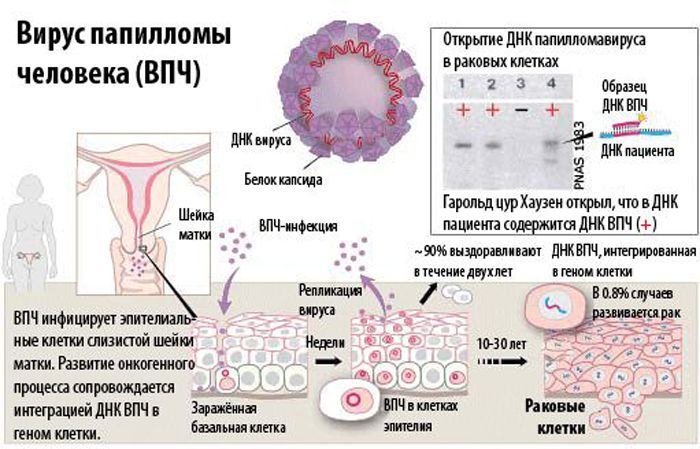
The specificity of cervical papilloma is the absence of clinical signs. Detection of a neoplasm is possible only during a gynecological examination, and some types of growths are not even visually visible. Then a special histological examination and biopsy is required.
Papillomatosis of the cervix is treated with medication (immunostimulants, antiviral drugs) and surgical (high-frequency coagulation, freezing, laser removal ) ways. The likelihood of recurrence is quite high even after the removal of the build-up.
If the formation was detected during pregnancy, treatment is carried out by cryodestruction and laser therapy.
On the tongue
Papillomas on the tongue are rare and always require treatment. Usually the first symptoms are a white coating on the tongue and a feeling of discomfort while chewing and swallowing food, talking, at rest.
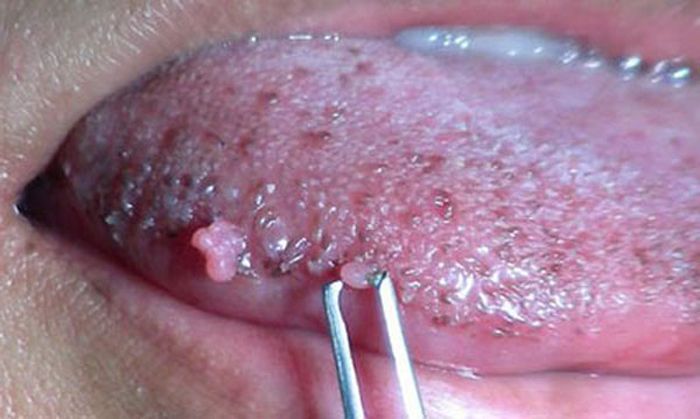
Genital warts often form under the tongue, flat ones on the sides or back.
Diagnostic methods: PCR.
Treatment of outgrowths in the tongue includes antiviral therapy, strengthening the immune system, antiseptics, and taking vitamins. Methods for removing papillomas in the tongue are also used : cryodestruction, radio wave method, laser removal.
The longer the disease is ignored, the more difficult speech becomes and the higher the risk of developing malignant tumors.
Ways of infection
The main route of infection is sexual. The virus is transmitted through contact not only with an infected person, but also with a carrier, that is, a person may not even know that HPV is present in his body. Infection occurs through any contact (oral, vaginal, anal) and even petting.
Also, the virus can be transmitted by household contact when using common hygiene products (comb, razor, toothbrush, towel, clothes and shoes).
It is possible to transmit the virus from mother to child during fetal development or during childbirth.
What factors provoke pathology
HPV carriers are, according to various sources, up to 70-80% of the population. At the same time, many live with the virus for decades, and it does not make itself felt. For example, transmission of the virus can occur during adolescence, and infection by the age of 50-60.
However, some people become not only carriers of the virus, but also the owners of a small outgrowth on the skin or mucous membrane – papillomas.
There is always one factor that provokes pathology – weakening of the immune system. With exacerbation of chronic diseases, the development of infections and inflammations of various nature, pregnancy, hypothermia, frequent stress, the risk of virus activation increases.
Promiscuous sex and poor personal hygiene increase the likelihood of infection.
What is dangerous for humans?
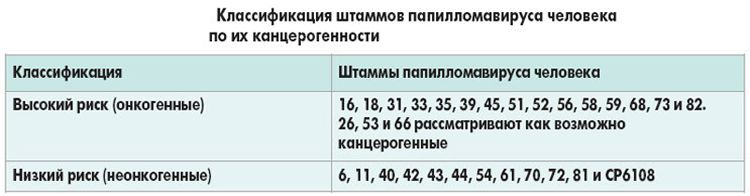
The danger of papilloma lies in the fact that there is a possibility of degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant one. Of the 190 known strains of the virus, at least 13 have a high degree of oncogenicity.
In addition, when the papilloma is injured, an open wound appears, into which the infection easily penetrates. At the same time, the virus itself can come to the surface of the skin and infect neighboring areas, as a result of which several papilloma appears instead of one.
Even if the papilloma disappears as a result of drug therapy or surgical removal, the virus still remains in the human body. It persists throughout life and is able to be reborn and periodically disturb the patient.
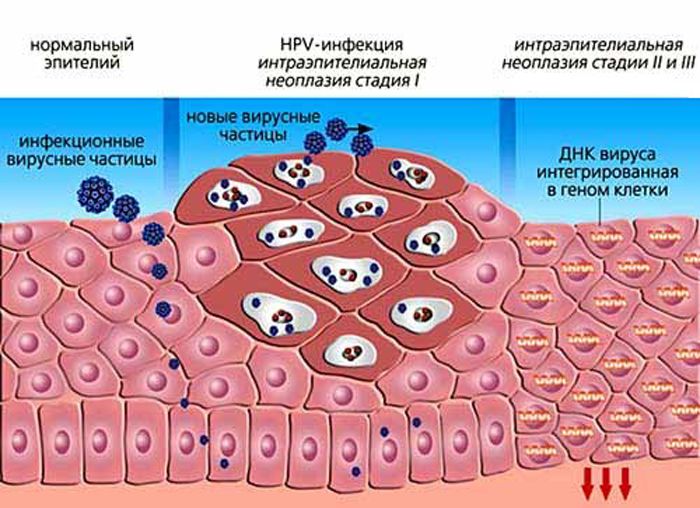
How the disease progresses
Papillomavirus penetrates the human epithelium, the basal layer of the skin, and settles there. The incubation period can take from several weeks to several months. Then, if a person’s immunity is strong, the body is able to heal itself, which happens especially often at a young age.
If the immune system has not been able to overcome the virus on its own, with any weakening of the immune system (infection, inflammation, pregnancy), it begins to actively divide, forming these very growths on the skin and mucous membranes – papillomas.
Papillomatosis appears only in the form of genital warts and warts, which a person is forced to periodically remove or undergo a course of treatment.
In the worst case, the disease degenerates into cancer.
Nuances of treatment and prevention
A complete cure for papillomavirus never occurs, except in those cases when the immune system copes with it without the help of medications and surgical methods. In 60% of people, the virus remains for life.
Treatment is carried out only after a complete examination, as a result of which the degree of oncogenicity of the virus is determined. For example, if a virus has a high chance of degenerating into cancer, you need to be very careful with treatment and constantly visit a doctor to monitor the condition.

Drug treatment involves taking antiviral drugs and drugs that strengthen the immune system. As a rule, doctors recommend approaching the treatment of papilloma in a complex way: for example, removing a growth with a laser is accompanied by a course of taking immunomodulators, as well as making lotions from herbal infusions for the speedy healing of a wound.
Prevention measures include simple rules:
- Refusal of promiscuity.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Regular visits to the doctor for preventive examinations.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Compliance with personal hygiene.
Most of the population is infected with papillomavirus, but not everyone is faced with the clinical manifestation of the disease. Papillomas – soft benign growths on the skin or mucous membranes – are dangerous, firstly, with a high risk of injury, and secondly, with the likelihood of degeneration into cancer.
There is no vaccine for HPV, and there is no cure. Papillomas can only be removed surgically or medically to slow down the course of the disease.







