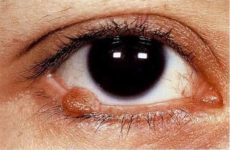
Papillomas are small neoplasms that grow from epithelial tissue. The size of this growth can be from two to three millimeters to a couple of centimeters.
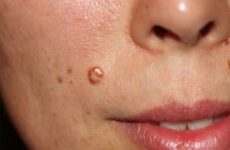
They look like a papilla that rises above the surface of the skin on a special stalk at the base of the tumor. The surface of such neoplasms has uneven edges.

Содержание:
Human papillomavirus in women on the cervix: what is it?
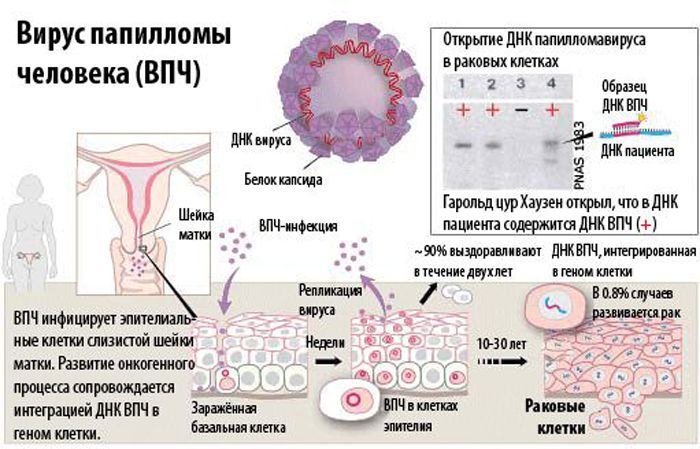
Papillomatosis is a disease caused by the human papillomavirus. It manifests itself in the form of multiple neoplasms. In women, papillomatosis of the cervix is quite common .
Symptoms are not always visually visible. Often the virus is located deep in the layers of the epidermis, where it multiplies and grows. With a deterioration in immunity and other provoking factors, clinical symptoms appear, then the disease becomes contagious .
Scientists know a large number (more than a hundred) strains of this microorganism. They do not have separate names, but are serial numbers.
According to the oncogenic type, papillomaviruses are conditionally divided into 3 categories:
- non-oncogenic – under no circumstances can provoke the development of a malignant tumor;
- low oncogenic risk – in certain conditions there is a small chance of developing a tumor;
- oncogenic – in certain circumstances provoke oncological diseases, are a proven cause of cervical cancer. These include strains from the 15th to the 20th, the most dangerous are the 16th and 18th types. However, the presence of these types of papillomas in the body does not at all guarantee that the patient will soon develop cancer. Certain conditions are necessary for the transformation into oncology. With timely detection and treatment, the disease goes away.
Transmission routes
HPV infection most often occurs through sexual contact with a carrier of the virus. In some situations, infection can occur in a domestic way – through visiting a bath, pool, sauna, etc. The possibility of self-infection during depilation, scratching the genitals is also not ruled out.
A newborn can become infected through passage through the mother’s birth canal. All women who are sexually active are at risk of contracting this disease.
Risk factors
The following adverse factors increase the risk of cervical HPV:
- the presence of bad habits;
- therapy with drugs of the cytostatic group;
- pregnancy;
- promiscuous sex life;
- early onset of sexual activity, when in adolescents the immune system is not yet fully formed;
- decreased immunity, lack of vitamins in the body;
- atopic dermatitis;
- the presence of papillomatosis in history;
- violation of the microflora in the intestines and in the vagina;
- sexually transmitted infections, sexually transmitted diseases.
Locations of flat papilloma
Flat papillomas can appear on the face, on the body most often, on the palms, forearms and legs, on the external and internal genital organs (on the labia minora, in the vaginal cavity and on the cervix).
Varieties of cervical papillomavirus in women
Doctors divide cervical papillomavirus into the following types:
- Pointed papillomas . They are characterized by the growth of the epithelium and connective tissue on the surface of the cervix. They look like small folds, vessels and connective tissue grow into these folds. In appearance, they resemble cauliflower.
- Squamous cell papillomas – these neoplasms rise above the surface of the epithelium, contribute to the deformation of the uterus as it grows. Outwardly, they look like warts.
- Inverted papillomas on the cervix . Such growths are able to penetrate deep into the tissues, destroying the cervix. This species refers to a precancerous condition. Adiagn
Symptoms of uterine papillomatosis
In most cases of HPV on the cervix, there are no symptoms at all. That is why, if a woman does not regularly undergo medical examinations by a gynecologist, it is very difficult to diagnose him in time. At a later stage, the following symptoms may appear:
- a noticeable increase in inguinal lymph nodes;
- burning sensations in the genitals;
- specific vaginal discharge that was not there before.
Symptoms may vary depending on the type of microorganism that caused the disease. In the acute course of the disease, genital warts occur, and squamous cell papillomas of the cervix indicate a chronic stage. The latter cause serious damage to the structure of the epithelium.
The absence of external manifestations for a long time is due to the strong immunity of the patient. Thanks to the effective functioning of the immune system, it does not allow infections to develop.
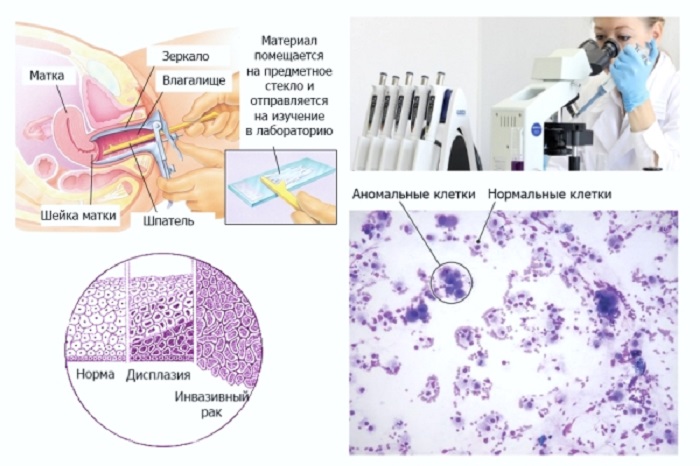
Papillomas on the cervix can be seen by the doctor during the examination. During a gynecological examination, the following manifestations may indicate HPV:
- formations in the form of warts;
- tuberosity – appears due to changes in the epithelial tissue in the neck. It can be seen visually, as well as groped. The bumpy surface is a sign of the presence of genital warts on the cervix, they can be single or multiple. The appearance of these neoplasms is usually observed in the acute form of infection;
- leukoplakia, dysplasia – the formation of areas of epithelial tissue with atypical cells.
What are dangerous?
Human papillomavirus dysplasia is a very dangerous condition.
The human papillomavirus is a scientifically proven cause of a malignant tumor of the cervix, these two concepts are inextricably linked. Treatment of dysplasia is most effective in the early stages of the development of the disease.
If this condition is not detected in time, the disease will progress and may turn into cancer. That is why all women need to regularly undergo preventive examinations by a gynecologist.