Papillomavirus is one of the most common viruses that infect humans. There are many varieties of this microorganism – scientists number about 600. According to statistics, most of the world’s population is infected and is a carrier of this virus, but not everyone knows about it, because quite often there are no manifestations of the virus.

Содержание:
General characteristics of the human papillomavirus, what kind of disease is it
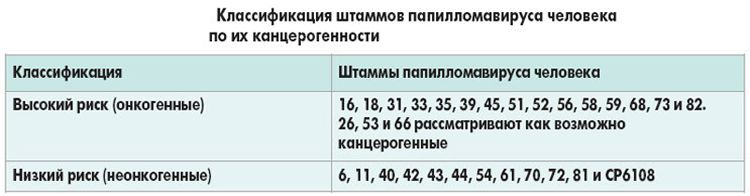
All types of papillomavirus can be divided into three groups – strains with low oncogenic risk, strains with medium oncogenic risk and strains with high oncogenic risk.
The papillomavirus 56 strain has an average level of oncogenicity, which means that in some cases it can provoke oncological ailments.
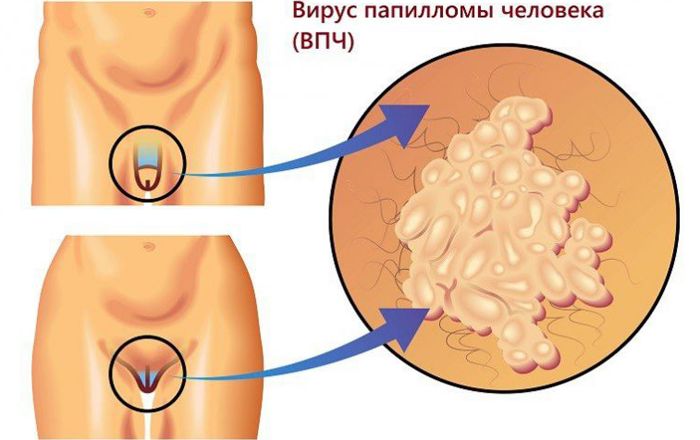
This type of virus provokes the appearance of growths, which can be localized not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. Most often, pathological growths appear in the intimate area. The development and growth of warts must be monitored in order not to miss the degeneration into a cancerous disease.
Scientists very carefully studied the 56 strain of papillomavirus, and came to the conclusion that this strain is more dangerous for women. Of course, genital growths can also be observed in men, but, firstly, they are much less common in men, and secondly, this strain of the virus can transform into oncological processes in the cervical region of the uterus, which, by definition, does not threaten men. But this does not at all indicate the safety of papillomavirus for the male half of humanity, and men can develop complications when the virus is activated.
Provoking factors
Once in the body, the papilloma virus remains in it forever, but may never be activated throughout life. In order for the virus to show its activity, the following factors are necessary:
- low immunity;
- hormonal disorders;
- lack of folic acid;
- pathology of the urinary tract;
- stress, depression, prolonged emotional overstrain;
- a large number of sexual partners;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- HIV infection;
- avitaminosis;
- violations of metabolic processes;
- childbearing period.
In addition, there are external provocateurs of virus activation:
- smoking;
- drug addict;
- frequent visits to areas with high humidity – baths, saunas.
Ways of transmission of papillomavirus
The papilloma virus has received its wide distribution due to the fact that it is transmitted during intimacy. Moreover, the form of sexual contact does not matter – infection occurs during vaginal, oral, and anal sex. It is believed that this is a disseminated virus that during life can appear in the body of any person who has an active sex life.
However, you can get infected with a dangerous virus in other ways:
- by contact – the virus penetrates through skin lesions;
- The virus is transmitted from a pregnant woman to her fetus.

Symptoms in women and men
In men, the development of any type of papillomavirus occurs in most cases without clinical signs. Rarely, the appearance of growths can be observed on the genitals. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, and the activity of the pathological microorganism is not blunted, the virus can enter the urethra or urethra. But in this case, the symptoms usually do not appear.
As for the clinical picture of papillomavirus infection in women, growths on the skin and mucous membranes are most often observed. If the immune system is working normally, there may be no symptoms for a long time. In addition to the appearance of warts, a woman may experience:
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during intimacy;
- bleeding that is not related to the menstrual cycle;
- discomfort when urinating.
These clinical signs appear as a result of trauma to the growths that are inside the genitals. The clinical picture becomes more pronounced after a secondary infection joins the pathological process.
However, based on these symptoms, it is impossible to conclude that the papillomavirus is present in the body. Exactly the same signs accompany erosion, cystic formations, cystitis and other pathologies. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a qualified specialist.
Diagnostics
The most informative way to determine the presence of a virus is a PCR test.
In the course of diagnostic measures, the following is revealed :
- visual manifestations of the virus – warts and condylomas, which have a sharp tip;
- the presence in the blood of antibodies to an infectious agent;
- dysplasia in the cervical region of the reproductive organ.
However, despite the fact that laboratory tests are quite accurate, the diagnosis of the virus does not always give positive results. This is due to the peculiarities of the development of infection.
The diagnosis of the papillomavirus must be carried out several times. Studies have shown that the course of the disease is unstable, and correct diagnosis the first time is not always possible.
So, to identify the papilloma virus, the following studies are carried out :
- visual inspection;
- colposcopy;
- PCR analysis;
- cytological smear ;
- molecular biochemical test;
- histological analysis, biopsy.
Treatment
Treatment of the papillomavirus is impossible. As already mentioned, it will not work to eliminate it from the body, however, it is possible to suspend its development and achieve a latent form that is more significant than a pathogenic microorganism. For this, the following drugs are used :
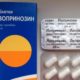
- Antiviral . This group of drugs does not allow the virus to multiply, as it prevents the division of DNA. In addition, the drugs have an immunostimulating effect and eliminate the visual manifestations of pathology. Assign Acyclovir , Panavir , Isoprinosine.
- Immunomodulators . These medicines help to increase the natural protective functions of the body, which leads to the deactivation of the virus. Most often, doctors prescribe Likopid , Neovir.
- Chemotherapy . Since one of the consequences of papillomavirus is oncological processes in the cervix, chemotherapeutic methods are used, which are carried out in several stages.
- Cytostatics . Bleomycin, Podophyllotoxin, Podophyllin are prescribed. These drugs have an antitumor effect, prevent the growth of neoplasms, and inhibit the development of malignant processes.

With minor manifestations of the virus, the doctor may advise using traditional medicine recipes. But we must understand that this is only an auxiliary therapy that cannot be used as an independent treatment of pathology.
There are many folk ways to deal with the visible manifestations of the papillomavirus, here are some of them:
- Celandine . It is recommended to steam the growth well, and then grease it with celandine juice. The procedure is carried out several times a day until the build-up disappears completely. Effective for small single growths. The celandine plant is poisonous, so all precautions must be observed.
- Egg white . They lubricate the warts and leave for several hours. It is recommended to carry out this procedure several times a day.
- Walnuts . Green walnuts are ground and poured with kerosene in a ratio of 2:1. Insist for three weeks, then filter, and the resulting slurry is treated with growths twice a day.
- Aloe . A fresh cut of the sheet is applied and fixed with a plaster. Leave for several hours. The course of treatment is two weeks.
- A good effect is the use of lemon oil and tea tree oil . It is recommended to lubricate the growths twice a day for 2 weeks.

If conservative methods remain ineffective, and the growths do not disappear, surgical treatment is prescribed. It is based on the following methods:
- cryosurgery;
- laser therapy;
- chemodestruction;
- radio wave surgery;
- electrocoagulation;
- amputation of the cervix is a radical method of treatment.
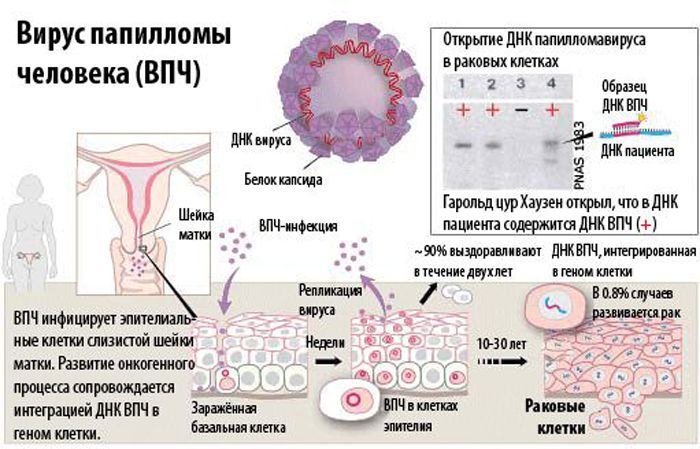
With the help of these funds, the focus of the affected tissue is removed, however, in 50% of cases, a relapse of the disease is noted, which is associated with the inability to control the complete removal of infected tissue.
It is most effective to treat human papillomavirus infection in a complex manner, in which case significant results can be achieved.
Prevention
In order to prevent infection with the virus and reduce the risk of possible complications later, the following preventive methods are necessary:
- Vaccination . It is carried out for girls aged 13–15 years, but if there is already a papillomavirus in the blood, the vaccine is useless.
- Compliance with intimate hygiene , especially in public places.
- Having only one verified sexual partner .
- Timely treatment of all diseases of an infectious nature , and in particular infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Leading a healthy lifestyle .
- Regular preventive examinations at the gynecologist .
Consequences and danger
The fact that the 56th strain of papillomavirus can lead to oncological processes has already been said, but since this type of virus has an average oncogenic index, this phenomenon is rarely observed. However, in addition to the formation of a malignant tumor, women may experience the following complications of the papilloma virus :
- infertility;
- impotence;
- decrease or complete loss of sexual desire;
- hearing and vision impairments;
- negative manifestations from the central nervous system.
In addition, papillomavirus increases the risk of contracting other infections, including HIV. This is due to a decrease in the body’s defenses, which leads to its greater vulnerability.
The 56th strain of the papillomavirus is a serious threat to a woman’s health, but if it is detected in a timely manner and all the necessary measures to deactivate it are taken, it can exist in the body in a latent state for a long time and not provoke negative consequences. You should not neglect your health, because in order for the virus already in the body not to be activated, you just need to take care of the immune system and lead a proper lifestyle.