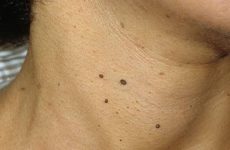
The presence of papilloma on the tonsil can not only cause discomfort, but also pose a serious health hazard, especially for children.
And although the formation is benign, it warns of the presence of the human papillomavirus in the body, as well as the need for prompt treatment.
Содержание:
Features of the disease
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common group of viruses that has oncogenic potential . HPV can have a productive or transformative effect on the epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes. As a result of the first, a benign formation appears – papilloma, the second can lead to cancer.
Thus, papilloma is an external manifestation of HPV. According to statistics, of all formations in the oropharynx, 40% are papillomas. The tonsils, their arches, and the soft palate are the most common sites of occurrence.
In appearance, papilloma is a nodule with a papilla. It is attached to the mucosa with a short or long stem. Outgrowths can be located singly or in a group. The most susceptible to the disease are small children under 5 years old, as well as women during periods of hormonal imbalance, for example, during pregnancy or menopause.
Causes of papillomatosis
The appearance of papillomas on the mucous membrane is a consequence of the penetration of HPV into the body. If the disease affects the tonsils, then, as a rule, the virus belongs to types 6 and 11.
HPV can be in the human body and not harm him as long as the immune system performs its protective functions. When it is weakened, microorganisms are activated, the epithelium grows, papillomas appear .
The reasons why immunity is reduced may be as follows:
- the presence of chronic diseases of the ENT organs (tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, otitis media);
- use for a long time of antibiotics and hormonal drugs;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disturbances in the work of the endocrine glands;
- stress, malnutrition, lack of vitamins.
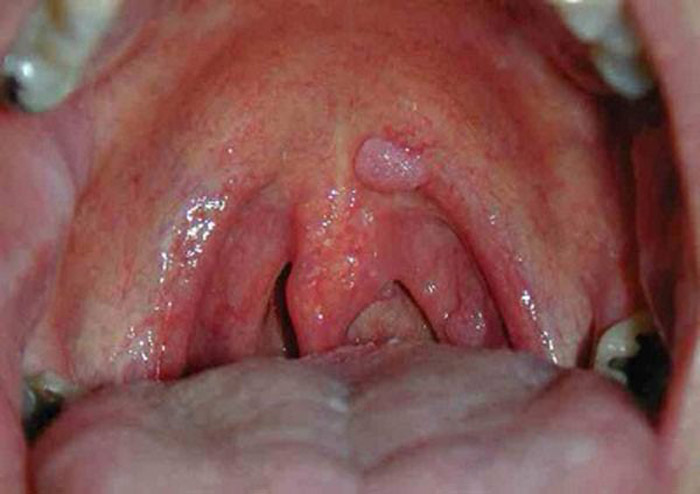
In addition, factors such as:
- smoking, addiction to alcohol;
- regular consumption of food that burns the mucous membrane;
- hormonal imbalance;
- acceptance by women of OK; heredity;
- bad ecology;
- the presence of dental diseases and ineffective oral hygiene.
Ways of infection
The papilloma itself is not transmitted from person to person, but HPV infection occurs. However, it is impossible to predict how he will behave, whether papilloma will appear or not, since this is due to many factors.
You can get HPV regardless of age and in the following ways:
- Sexual contact is the most common form of infection in adults. Sexual contact can cause infection. Even the presence of a condom can only reduce the risk of infection, but not completely eliminate it.
- At home . The transmission is carried out through common household items or hygiene products – a towel, washcloth, razor. This route of infection is most common in children, because they often play with the same toys, eat with the same appliances, drink from the same glasses. You can also get infected in public places – these are baths, saunas, pools. Intranatal. During passage through the birth canal, the virus is transmitted from mother to baby. With this method of infection, the pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi of the baby are most often affected.
- HPV poses the greatest danger to people with a suppressed immune system as a result of chemotherapy , transplantation, as well as in the presence of HIV, AIDS, and oncological diseases in the body. In addition, if a person has sexually transmitted diseases, such as ureaplasmosis, candidiasis, gonorrhea, they increase the risk of infection.
Varieties of growths on the tonsils
In order to choose an effective treatment in the future, one should take into account the varieties of papillomas. The following types are distinguished depending on:
Lifetime:
- Congenital.
- Acquired.
- Children’s.
- Recurrent.
- Adult.
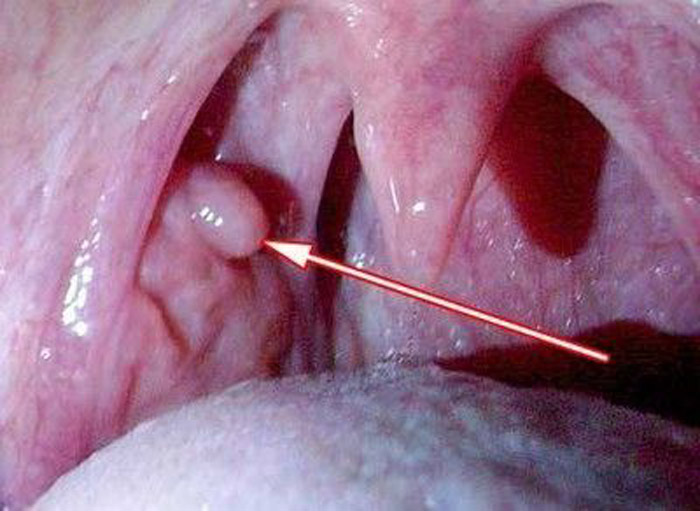
Affected area:
- Limited, concentrated in one place.
- Widespread, occupying many areas.
- Obturating, making it difficult to breathe.
Effects on the respiratory tract and their changes:
- First degree. It is characterized by a slight difficulty in the respiratory process, hoarseness and noise.
- Second degree. Manifested in a feeling of anxiety, shortness of breath, lack of oxygen.
- Third degree. Causes loss of consciousness and asphyxia.
Cancer risk levels:
- Benign.
- Malignant.
Symptoms of HPV
If the papilloma on the tonsil is small, then, as a rule, it does not manifest itself in any way. Only with its growth appear shortness of breath and hoarseness. In the future, the disease may be complicated:
- unpleasant sensations, reminiscent of the presence of a foreign object;
- discomfort and perspiration;
- difficult breathing;
- cough;
- violation of the swallowing reflex;
- in rare cases, pain radiating to the neck and submandibular region.
As a rule, the growth of papillomas in adulthood occurs on one side of the throat, while in children it is characteristic that both halves are affected. As a result, babies are more difficult to tolerate the disease, and the symptoms may be as follows:
- heavy breathing after exercise, and then at rest;
- outdoor games or running are accompanied by a paroxysmal cough;
- asthma attack, blue lips and nasolabial triangle.
After diseases of the ENT organs suffered by the child, the formation of papillomas on the tonsils is possible. Parents can see it on their own by examining the oral cavity. It is very important to contact an otolaryngologist in a timely manner, since the disease is more dangerous, the younger the baby is.
Diagnostic methods
If you suspect the presence of papilloma, you must visit an otolaryngologist who will visually examine the mucous membrane and establish the presence of education, its location, size, and the degree of damage to the organs surrounding it. In order not to confuse papilloma with other diseases, additional methods are used.
Diagnosis can be made using:
- Laryngoscopy , when the doctor visually examines the larynx using a laryngoscope. There are two types – direct and indirect.
- Microlaryngoscopy . It is performed under general anesthesia using an operating microscope.
- Laryngastroboscopy and electroglottography , which allow to identify violations in the work of the vocal cords.
- Computed tomography . It consists in a layer-by-layer study, which allows obtaining three-dimensional images.
- Autofluorescent study to clarify the boundaries of the growth and reveal hidden papillomas.
- Biopsy , which is performed in the presence of bleeding or a large formation. To do this, a piece of papilloma is taken with a needle and studied under a microscope.
- PCR , which helps to accurately distinguish papilloma from other formations, as well as to identify its type, since each has its own risk of oncogenicity.
- Histology . This study is carried out after removal for the presence of cancer cells in the formation.
Methods of treatment
Only a doctor can decide on the methods of treatment for a particular patient. As a rule, it includes the removal of papilloma in combination with the use of medications.
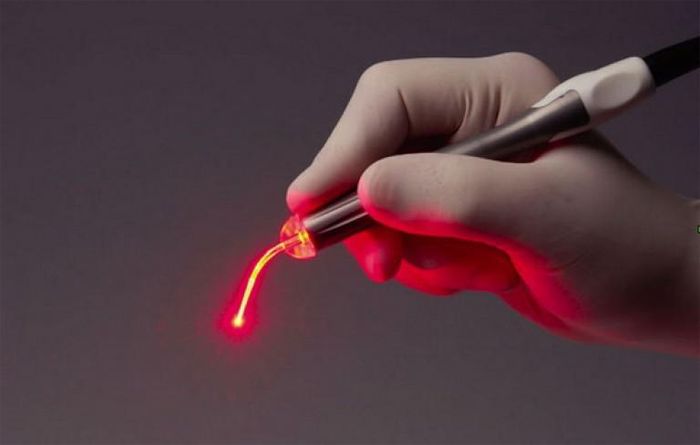

The following methods can be used to remove papilloma:
- Surgical removal with a scalpel . It is carried out under local anesthesia and can be: Extralaryngeal is used in severe cases of the disease, when there is a risk of asphyxia. The patient’s larynx is dissected and growths are removed through the incision. Intralaryngeal is used for patients older than 8 years. Special tools help to remove papillomas, and control is carried out using a laryngeal mirror.
- Laser removal is the safest and most painless method. It is also the most effective, because after its use the risk of relapse is the lowest. There are no scars and scars after treatment.
- Radiotherapy lasts 20 minutes. Papillomas and affected areas are removed with a radio wave scalpel, after which a crust appears at the site of intervention. After complete healing of the wound, it departs. This method is the second most popular after the laser.
- Cryodestruction is the cauterization of growths with liquid nitrogen. The whole operation takes a few minutes, and after 2-3 days the tissues die off and move away along with the papilloma.
- Electrocoagulation – removal of papillomas with a high-frequency electric current. This allows the blood vessels that feed the growths to stick together. After that, after a few days, the formation will die and disappear.
- Ultrasound removal means applying an applicator of hydrogen peroxide to the affected tonsil. Then, under the action of ultrasonic waves, oxygen molecules penetrate the tissues, causing the death of the virus.
- Chemical cauterization involves the impact on education with the help of: Potassium permanganate; silver nitrate or lead; perhydrol.
Medicines are one of the components of treatment for HPV. The doctor may prescribe:
- antiviral agents ;
- preparations containing interferon;
- immunomodulators ;
- chemotherapy drugs;
- hormonal agents.
In adults
The attending physician chooses one of the removal methods, taking into account contraindications for a particular case.
So, pregnant women should not use:
- radio wave destruction;
- removal with ultrasound;
- burning with chemicals.
The radiofrequency method is not used in patients:
- with disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- in the stages of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- in the presence of cancer.

Electrocoagulation should not be additionally used in patients with blood clotting disorders and intolerance to electroprocedures.
In children
Operation in children is possible only under local anesthesia. The methods that are used to remove papillomas in a child are as follows:
- cryogenic;
- electrocoagulation;
- ultrasonic.
They are less traumatic, painless, effective, as well as an easier process of restoring damaged areas.
Contraindications are cases when the child:
- there are open wounds in the oral cavity;
- elevated temperature;
- cold intolerance;
- blood diseases.
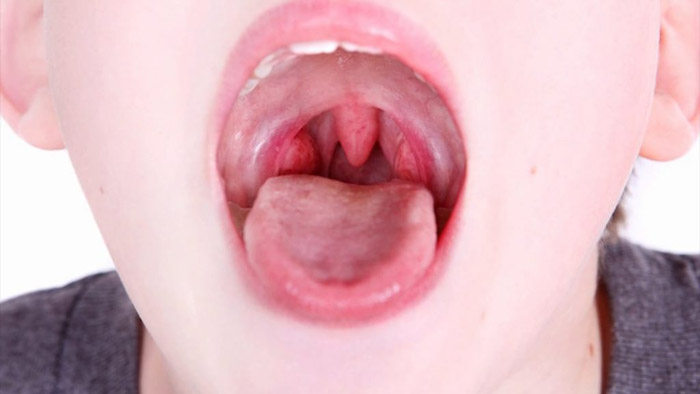
Possible Complications of HPV
The most dangerous papillomas on the tonsils in childhood due to the narrower lumen of the larynx in babies. Education can grow into the palate and palatine arches, which further reduces the respiratory lumen. Respiratory failure develops.
In the absence of emergency medical care, asphyxia can occur. Therefore, if a growth on the tonsil is found in a child, it is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible.
For adults, papillomas are less dangerous, however, complications can occur. One of the most dangerous is the degeneration into a malignant formation.
Growing on the trachea, lungs and bronchi, papillomas can lead to respiratory failure. Another possible complication is cicatricial stenosis of the larynx, which appears with frequent relapses and subsequent treatment.
Neoplasm prevention
No preventive measures can guarantee that a person will not become infected with HPV. As already noted, the carriers of the virus are most people, many of whom are not even aware of its presence. However, it may not manifest itself in any way. To do this, you need to maintain a good immune system. This will help:
- hardening and exercise;
- walks in the open air;
- a varied diet rich in vitamins and minerals;
- lack of hypothermia;
- rejection of bad habits.
Finally
If HPV has entered the body, then it will not be possible to get rid of it. The presence of papillomas on the tonsils can pose a serious threat to both the health and life of the patient, especially if the immune system is weakened.
Therefore, the main task is to remove the formation in a timely manner, without waiting for complications. In the future, adhering to a healthy lifestyle, you can completely avoid relapses.