Содержание:
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is important to know first about the human papillomavirus?
- 3 Risk factors
- 4 How does papillomavirus most often manifest itself?
- 5 Methods of transmission and activation of the virus
- 6 Symptoms and features of the development of the disease
- 7 Features of the activation of the virus in the male body
- 8 Whether it is necessary to hand over analyzes and with what frequency?
- 9 Diagnosis of diseases
- 10 How to treat?
- 11 Surgical excision of formations
- 12 conservative methods
- 13 Prevention
- 14 Conclusion
Introduction
There are many types of human papillomavirus. Among them there are especially dangerous for women , which can provoke times of the cervix – this is type 31 virus .
It is sexually transmitted, has its own DNA structure and personal genotype . The symptoms of this disease may not appear for quite a long time, but as soon as the immune system weakens, HPV will show all its manifestations.

What is important to know first about the human papillomavirus?
The 31st genotype belongs to the group of increased risk of oncological diseases. The virus enters the body and begins to rapidly change human cells, which leads to the development of cancer of the genital organs (both women and men).
HPV can stay in the human body for a long time, without making itself felt, and waiting for the body’s immune defenses to decrease. This virus enters the body during unprotected intercourse, from mother to child during childbirth, as well as through household items (by contact with the blood of an infected person).
Risk factors
There are several risk factors for the activation of HPV 31 in the human body:
- unhealthy lifestyle and unhealthy diet;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- stress;
- debilitating diets;
- the presence of bad habits;
- promiscuous sex life;
- hormonal disbalance;
- genetic predisposition;
- insufficient observance of hygiene rules;
- diseases of the intestines and stomach;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
How does papillomavirus most often manifest itself?
Papillomas are benign neoplasms that can become malignant. Bovenoid papulosis is one of the main manifestations of type 31 virus, it is a genital rash that is localized on the genitals (in women on the labia and vaginal walls, in men – on the head of the penis). They look like plaques that rise slightly above the skin, they can be from pinkish to yellow.
Methods of transmission and activation of the virus
Virus 31 genotype is most often transmitted sexually during unprotected intercourse. But there are also recorded cases of domestic transmission (by contact with the mucous membranes of the carrier of the virus).
Using a condom greatly reduces the chance of infection, but does not prevent it with 100% certainty. Activation of HPV occurs in parallel with a decrease in the protection of the body’s immune system.

Symptoms and features of the development of the disease
HPV 31 after entering the human body can be in a “sleep” mode for a long time. But as soon as the immune system gives way, the virus begins to show its presence with the following symptoms:
- the appearance of warts and papillomas on the genitals;
- vaginal bleeding and increased discharge;
- the appearance of bowenoid papules on the inner side of the thighs;
- pain and discomfort during and after intercourse.
Women are more likely to be exposed to this type of virus due to their hormonal levels and the structure of the reproductive system. Therefore, treatment should be timely, because papillomas may well be transformed into malignant neoplasms and cause cancer. The complete extermination of this virus in the body is impossible, treatment implies a reduction in manifestations and excision of growths.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body is most vulnerable, because the level of hormones increases at the speed of light. As a rule, in the early stages of gestation, treatment is aimed at reducing external manifestations, because antiviral drugs are especially dangerous for the development of the unborn baby.
Therapy involves laser excision or freezing of genital warts. Genotype 31 is especially dangerous for expectant mothers, because it is able to cross the placenta, and also infect the child during childbirth. It also appears in the form of yellowish scales.
Features of the activation of the virus in the male body
The virus enters the male body in the same way as the female body – through microdamages in the skin of the penis during intercourse (without a condom). External manifestations affect the coronal sulcus and frenulum of the penis.
These parts are covered with rashes – plaques with a yellow crust, which can itch and cause tolerable pain. Rarely, the urethra and the head of the penis are exposed to rashes, but in this case there is a strong pain syndrome.
Whether it is necessary to hand over analyzes and with what frequency?
Women are advised to take a smear for cytology and HPV tests in order not to miss the development of the 31st genotype before its visible manifestations begin. Until the age of 30, it is necessary to take an HPV test every 3-5 years. From 30 to 60 years of age, this procedure should be performed every three years in the absence of the virus, and every 9 months for an initial positive result.

If a positive test is confirmed, a colposcopy and smear analysis for cytology should be performed. After the age of 60, the development of the virus is not noticed in women, so periodic tests are not required.
Who orders a virus test?
A referral for analysis is issued by a dermatologist, urologist and gynecologist when dealing with complaints of rashes in the genital area.
Diagnosis of diseases
If any symptoms appear (whether it be rashes or pain in the genitals), you should immediately contact a specialist who will refer you to the necessary tests and carry out diagnostic measures. An experienced gynecologist can even visually distinguish HPV 31, but the diagnosis is confirmed after several procedures: PCR, colposcopy, biopsy and a cytology smear.
polymerase chain reaction
This is the collection of a small amount of biological material from a patient, for example, vaginal secretions or saliva. After that, a special substance is added to the biomaterial, which copies viral DNA cells along the chain. In large numbers, it is easier to recognize dysplasia.
Pap smear
This is a time-consuming and completely painless analysis for a woman. A swab is taken from the patient’s cervix and vaginal walls, after which the material in a test tube is sent to the laboratory. There it is stained and examined under a microscope. This helps to consider the slightest deviations from the norm.
Biopsy
This is the removal of a small piece of tissue (infected with a virus) for detailed study. Biopsy is the most common method for suspected tissue degeneration into malignant.
Colposcopy
In the case when, after taking a smear, the doctor has doubts about the diagnosis, a gynecological examination of the female genital organs is performed using a colposcope. In its course, dysplasia is easily considered.
How to treat?
In the treatment of HPV, an integrated approach is important, which includes drug therapy, topical drugs, as well as some physical. procedures. Also in recovery, hygiene, protection during sexual contact and a measured lifestyle play a huge role.
First of all, it is worth curing chronic diseases (if any) and putting your immunity in order. For this, immunomodulators and immunostimulants are used. Folk remedies in the treatment of this disease are powerless and their only benefit is that some of them strengthen the immune system. Antiviral treatment is aimed at combating the virus that causes the disease.
In most cases, drugs such as Cycloferon , Poludan are prescribed. In the case when conservative therapy does not help get rid of the virus, and the risk of papilloma developing into malignant tumors increases, a surgical method for excising the growths may be indicated. Removal is carried out using cryodestruction (freezing of tissues), or excised with a laser.
Surgical excision of formations
This is the only effective method in the fight against the human papillomavirus. Excision of neoplasms is carried out with a small capture of neighboring tissues (with a low risk of malignancy of the growths). Otherwise, most of the tissue surrounding the papilloma is removed. There are several techniques for removing growths:
- laser surgery. One of the best techniques in which the neoplasm is burned out with a laser beam. The procedure does not entail infection during its implementation, as it is non-contact. In tandem with the evaporation of papilloma, vessels are soldered, which minimizes blood loss. At the site of manipulation, only a small crust remains – a scab, which itself disappears.
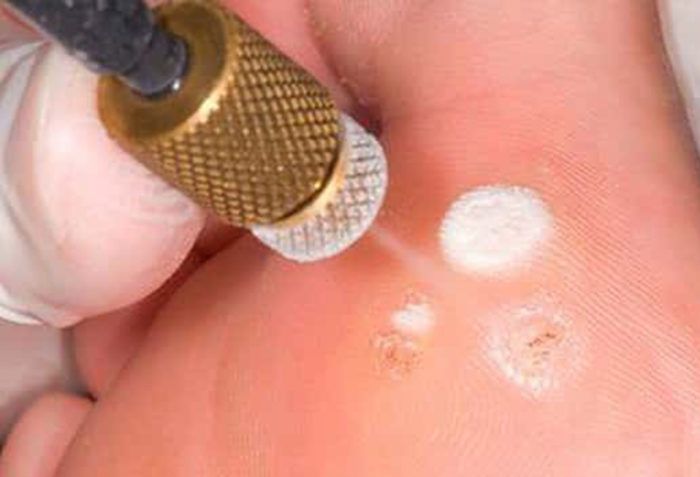
- Cryodestruction. This is freezing warts with liquid nitrogen. After it, the growths darken and fall off after a few days.
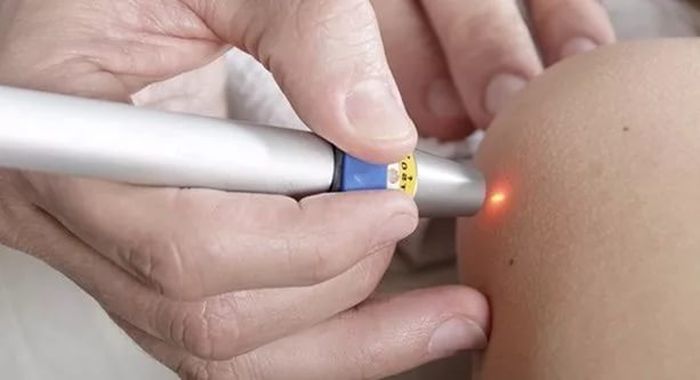
- radio wave surgery. Exposure to high-frequency radio wave radiation, the technique is similar to laser.

- The classical excision of growths and electrocoagulation are extremely rarely used in our time, since they have a rather high risk of injury, because cutting off the growth provokes bleeding.
conservative methods
Conservative therapy involves taking antiviral, as well as immunostimulating agents. These drugs cannot completely eliminate the virus from the body, but they prevent it from spreading further and increase the body’s ability to resist the virus. The most famous drugs for suppressing papillomavirus type 31 include:
- Cycloferon (the drug has an antiviral effect, helps the body fight pathological bacteria).
- Derinat (an immunomodulator that targets the immune system, enhancing its anti-inflammatory properties).
- Isoprinosine (an antiviral drug that is used both for conservative treatment and after papilloma removal).
- Likopid (a potent remedy for chronic and sluggish infectious processes).
- Panavir (immunostimulant and antiviral drug). Available in the form of solutions for injection, rectal suppositories, as well as a gel.
- Interferon (protein immunomodulator). Available in the form of suppositories, powders and injections.
- Cordyceps (immune system regulator, eliminates genetic failures).
- Transfer Factor (the most powerful and safe immunomodulator, has no side effects).
Prevention
The most significant and main factor is protected sex. It includes not only the use of good quality condoms, but also a reasonable approach to the number of partners.
After all, promiscuous sex life can serve not only as a source of infection with HPV, but also with chlamydia, syphilis, and HIV. It is also worth considering your sexual preferences, because in recent years cases of anal cancer have become much more frequent.
Other preventive measures include:
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
- Strengthening the body through sports, hardening.
- Stick to a proper balanced diet.
- Timely treatment of chronic and infectious diseases.
Conclusion
Do not despair if you find suspicious rashes on your genitals, you should immediately run to a gynecologist or urologist for help. After all, the earlier the diagnosis is made, the greater the chances for a speedy recovery.
Even with the confirmation of the diagnosis of HPV type 31, there is a successful outcome of treatment and minimization of the degeneration of benign neoplasms into malignant ones. All that is needed from the patient is to undergo a diagnosis, take tests and strictly follow the recommendations of your doctor.