Human papillomavirus is rightly considered one of the most common infectious agents. Medical statistics show that up to 90% of all people are infected with it, and all over the world.
The virus strikes with its survivability in the human body, and cutting-edge drugs cannot guarantee getting rid of the infection.
Its numerous varieties cause a variety of lesions of varying degrees of danger – from small warts to oncology, which HPV of the oncogenic type in women exist in women. The risk of severe consequences makes you take this infection seriously and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Содержание:
Types of the virus and their manifestations
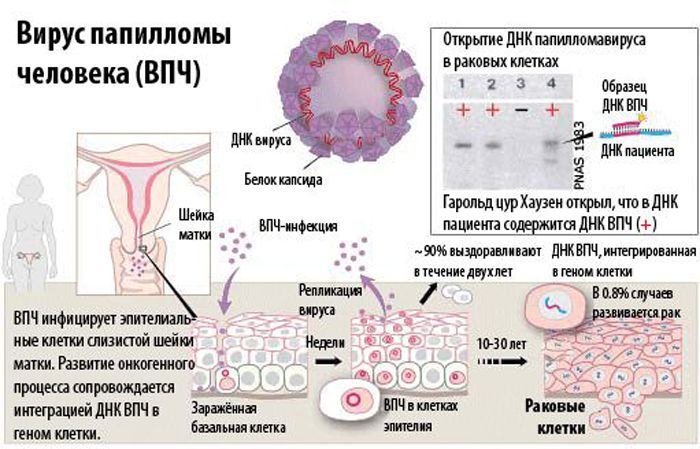
Human papillomavirus (HPV) or Human papilloma virus (HPV) is a highly contagious, DNA-containing virus that causes the development of benign lesions on the skin and mucous membranes (papillomatosis).
Formations of a warty type grow from epithelial cells and can affect both the skin and internal organs of a person. In this case, people of both sexes and different ages, including children, are affected.
Currently, more than 160 different strains of the virus have been identified that have a certain localization and specific manifestation. The following characteristic options are distinguished.
Skin lesions:
- HPV 1, 2 and 4 – plantar formations of a warty appearance.
- HPV 2, 4, 26, 27, 29, 57 – typical (common) warts on the skin.
- HPV 3, 10, 28 and 49 are flat warts.
- HPV 7 – butcher’s warts.
- HPV 2, 3, 5, 8–10, 14, 15, 19, 20, 36, 47, 50 – epidermodysplasia of the verciform type.
Damage to the genitals:
- HPV 6, 11, 42, 54 – genital warts.
- HPV 6, 11, 16, 18, 30–33, 39–43, 51 , 52, 55, 61–64, 67 – dysplasia and flat warts with a high probability of malignancy.
- HPV 16 , 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 54, 66 , 68 – malignant tumors, including in the vagina, on the vulva, anal area, cervical cancer.
Non-genital lesions:
- HPV 13 and 32 – hyperplasia of the oral mucosa.
- HPV 6, 11, 30 – papillomas in the respiratory tract of a recurrent type.
- HPV 1, 6, 11, 16, 18, 30 – lung oncology, malignant tumors in the neck and head.
Oncogenic types of HPV
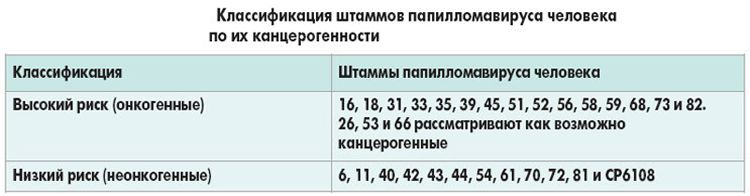
HPV leads to the development of benign formations. However, it has been established that in some cases they have a tendency to malignancy (malignancy). Although the probability of such an irreversible transformation of cells does not exceed 1.5-2 percent, it cannot be discounted. The degree of risk is largely determined by the type of HPV, which have different oncogenicity.
According to this indicator, the most common HPVs can be divided into 3 groups:
- Viruses incapable of malignancy – HPV 1-3 and 5 . The formations provoked by these strains of viruses are not dangerous to humans and often disappear on their own.
- Low-oncogenic viruses – HPV 6, 11, 42-44 , 53-55 . Their transformation occurs extremely rarely and only in particularly unfavorable conditions. Most often they cause condylomatosis.
- Highly oncogenic viruses (HPV-9 group) tend to transform, and the risk of oncology increases significantly. These viruses include HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 56, 59, 68, 66 , 82, 73. A precancerous condition is often associated with papillomatosis caused by HPV 30, 40, 43, 57 , 62, 67, 69.
HPV 16 and 18 are considered the most common and dangerous. The defeat of strain 18 ends with cancer in 12-15% of cases, and HPV 16 – almost half.
Ways of infection
The papilloma virus is highly contagious. It is able to exist and develop for a long time only in the human body. At the same time, HPV is very tenacious and, even after effective treatment, remains viable, invading cell chromosomes and passing into a latent state. As a result, almost 15% of all people are carriers of the virus without being aware of it at all.
The most common way of infection is sexual contact, both traditional and non-traditional. It should be borne in mind that at the age of 20–32, almost half of all people leading an active sex life become carriers of various types of HPV.
During sexual contact with an infected partner, the probability of infection exceeds 60%, and with genital warts approaches 100%. Barrier contraception significantly reduces the risk of infection, but does not give a complete guarantee.

Infection with HPV is also possible through contact and household contact. The risk increases in the presence of damage to the skin (scratches, abrasions, burns, etc.). The size of viruses is extremely small, which allows them to easily penetrate through microcracks in the skin. Infection can occur through direct contact with an infected person (shaking hands, kissing, wrestling, etc.).
The probability of HPV penetration in such public places as a bathhouse, swimming pool, toilet is quite high. In a humid, warm environment, the infection can persist for some time outside the human body.
You can get infected through shared objects. Cases of infection during medical procedures and surgical operations are noted. Babies become infected during childbirth if the mother has an infection in the vagina or uterus.
Risk factors affecting infection
The likelihood of contracting HPV largely depends on a person’s lifestyle. People at increased risk include people who start sexual intercourse at too early an age, are sexually active with casual, unprotected sex.
At the same time, even contact with an infected person does not always lead to infection. A good immune system is able to deal with the infection on its own.

The introduction of HPV into the body occurs with a decrease in immune defenses and the appearance of other favorable conditions. There are the following factors that can affect the infection:
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency, especially HIV infection;
- weakened female body in the postpartum period;
- chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system, as well as venereal diseases;
- endocrine disorders, diabetes mellitus;
- treatment with immunosuppressants;
- repeated abortions, prolonged and uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives;
- excessive physical activity leading to exhaustion of the body;
- severe general intoxication, significant hormonal imbalance;
- some drugs – cytostatics, a number of antibiotics.
The risk of a virus infection increases with a passive lifestyle, improper and insufficient nutrition, passion for starvation diets, and the presence of bad habits (alcohol, drugs). The lack of vitamins in the body contributes to the development of papillomatosis.
Symptoms
In most cases, HPV is in the body in a latent state and does not manifest itself in any way. When favorable conditions appear, abnormal division of epithelial cells begins, leading to the appearance of peculiar formations visible to the naked eye.
Such manifestations can appear anywhere on the body, but are most often found at the site of the initial introduction of the virus. This explains the frequent localization of formations on the genitals. However, papillomas or condylomas can appear in the oral cavity, near the anus, on the larynx, in the respiratory tract, intestines and some internal organs.
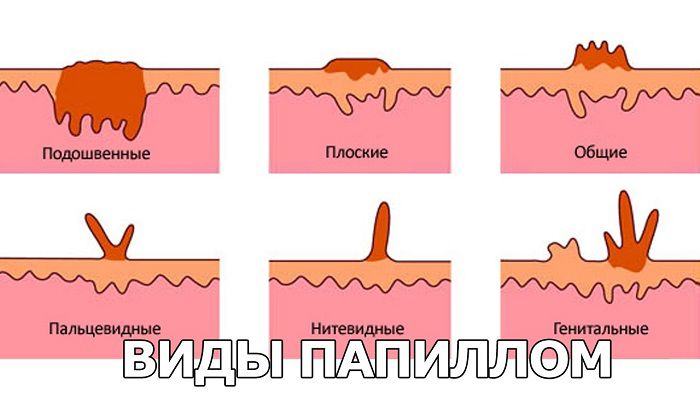
The main symptom of HPV infection is a growth, a bulge on the skin or mucous membrane. The following main forms of papillomatous formations can be distinguished:
- Typical warts (papillomas) . Papillomatous warts differ from similar growths of a different genesis in their inconstancy. Depending on the state of immune protection, they can periodically appear and disappear on their own. The color of the formation differs little from the skin. Such varieties are distinguished – juvenile (youthful) warts of a flat type, spines or plantar warts, vulgar warts on the upper limbs.
- Pointed warts . They germinate in the form of papillae on the genitals, near the anus, in the mouth, on the lips, larynx, on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. Single or multiple formations may be found. A characteristic variety is a merged condyloma. Several pointed formations merge into one growth resembling a cauliflower. If a weak solution of acetic acid is dropped onto such an outgrowth, then it acquires a pearly white color.
- Flat papillomas . These masses are small in height but can be quite large in diameter, indicating a large number of abnormal cells and a chronic infection. There are such specific varieties – laryngeal papillomas that affect the vocal cords and have a multiple appearance; bowenoid papulosis, characterized by pink, flat papillomas on the genitals.
- Bowen’s disease . These are rounded plaques with clear boundaries and a velvety surface. Most often they are found on the genitals.
The course of the disease
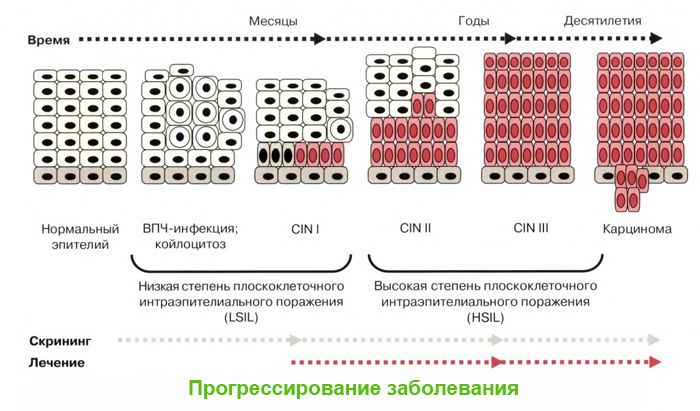
As a result of HPV infection, papillomatosis (condylomatosis) develops. The pathogenesis of the disease is associated with the growth of benign formations from epithelial tissues. With a weakened immune system, HPV penetrates the skin or mucous membrane and reaches the basal layer.
Here, the virus, which has its own DNA, penetrates the cell chromosomes, disrupting their structure. The cell is modified so that HPV receives the most comfortable conditions for reproduction.
The course of the disease is caused by the active division of modified cells. As a result of this process, a benign formation is formed. If the virus has an increased oncogenicity, then malignancy of the formation gradually occurs.
The specifics of the course in men
It is believed that the course of the disease in men is less dangerous than the effect of HPV on women. However, men’s health can also be seriously damaged. The following characteristic male problems are distinguished:
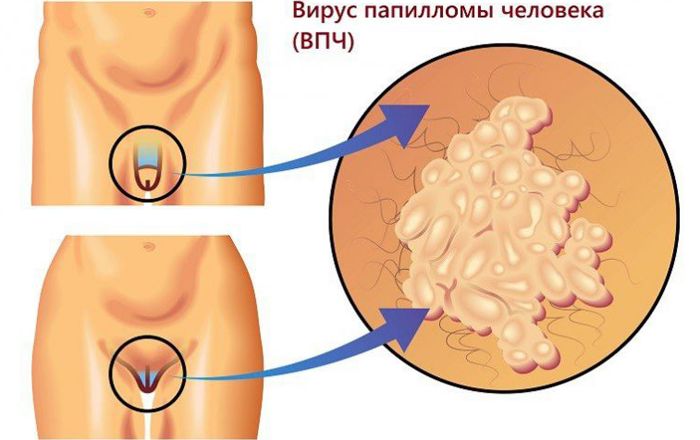
- Condylomatosis , represented by genital warts. At the first stage, small seals appear on the penis or scrotum, urethra, in the rectum, around the anus. Gradually, these formations acquire a typical shape and size, after which growth stops. During the formation of growths, itching may be felt. Nearby condylomas can join together with the appearance of a formation resembling a cockscomb.
- Bowenoid papulosis . It is considered a precancerous condition and occurs in men aged 25–35 years. The most characteristic manifestation is brown, pink or purple papules in the form of a rash on the body of the penis.
- Bowen’s disease . It is characterized by single formations in the form of a plaque covered with scales that hide the weeping focus. They are round or oval in shape. The growth of the formation occurs at the edges, which allows them to increase to 9–12 cm in diameter. With this disease, there is a risk of provoking squamous cell cancer.
The specific localization of HPV lesions in men is the penis and scrotum. In addition to the fact that this causes discomfort during sexual intercourse, there is a risk of mechanical damage and bleeding, as well as psychological stress from thoughts about how such defects will be perceived by a partner.
The specifics of the defeat of women
Papillomas in women are more dangerous, and there are objective prerequisites for this. Formations inside the vagina or on the cervix are invisible with a simple examination, which delays the visit to the doctor. In addition, constant hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle create the basis for the growth of formations, and estrogen contributes to their malignancy.
The female body quite often affects more than 30 varieties of HPV, and some of them are highly oncogenic. The most common HPV 16 and 18, when affected by the cervix, can cause cell degeneration and cancer development. At the first stage, dysplasia develops, which can still be stopped, but further malignancy becomes an irreversible process.
Even benign formations in women can cause serious consequences. This is due to constant stress when even simple cosmetic defects are found in the neck or décolleté area.
Genital warts in the vagina interfere with sex, and sometimes become a source of an unpleasant odor. All this can lead to serious mental disorders.
The specifics of the defeat of children
The manifestation of CHD infection in children is usually observed 5–10 months after the virus has entered. Warts in a child should be looked for in hidden places – in the armpit, between the fingers, and other skin folds.
Frequent localization in babies – sole, hands, face. Often, growths are found in the mouth and nose, in the larynx and bronchi. In newborns, the upper respiratory tract is often affected, and papillomas also appear on the eyelids, ears, face, and throat (tonsils).
In newborns, laryngeal papillomatosis with growths in the glottis is of particular danger. This can cause serious breathing problems. A special variety is hyperplasia of the epithelium in the oral cavity with damage to the tongue, palate and the formation of pointed forms.
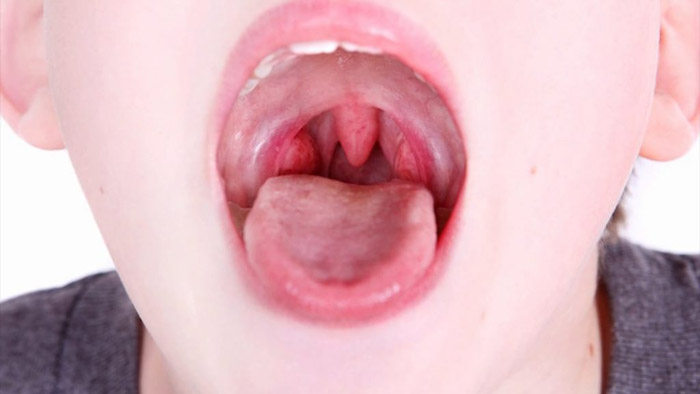
Dysplasia lesions (reddish or brownish, rough spots) on the feet and hands are prone to malignancy. The danger of childhood papillomatosis is increased by the lack of a stable immune system. Treatment of these manifestations should be started as early as possible, without leading to severe consequences.
HPV and pregnancy
Pregnant women are at particular risk of HPV. The virus has practically no effect on the course of pregnancy. Sharp hormonal changes lead to an increase in the number of lesions and their size, including the appearance of large warts in the birth canal.
This phenomenon increases the risk of bleeding and can disrupt the passage of the fetus. In the case of multiple accumulation of formations, the question arises of the admissibility of natural childbirth and caesarean section. In addition, in the presence of genital HPV lesions, a woman is more likely to infect a child during childbirth.
Diseases caused by a virus
The incubation period of diseases provoked by HPV can range from 20 days to 3–4 years (most often, 3.5–4 months). The lesion causes hyperplasia of almost all epithelial layers. The following main pathologies are distinguished:
- Typical diseases are plantar, simple and flat warts; genital warts; verruciform epidermodysplasia
- Precancerous and oncological pathologies – dysplasia of varying severity; erythroplasia of Queyra; Bowen’s disease bowenoid papulosis; laryngeal papillomatosis; Heck’s disease; conjunctival papillomas; cervical cancer and oncology of other localization (squamous cell carcinoma of the genital organs, anal canal, vagina, vulva, etc.).
The development of a particular disease depends on the strain of HPV. Diseases can be limited only to a cosmetic defect that is not dangerous to health, but there can be serious consequences. Find out also what HPV is, deciphering the results of the analysis
Which doctor to contact
Papillomatosis requires a serious attitude. There is a risk of severe complications, which means that if pronounced signs of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor.
This problem is dealt with by doctors of the following specializations – gynecologist, andrologist, urologist, proctologist, depending on the location of the lesion.

Diagnostics
The very fact of the presence of the disease is easily established by external examination by the nature of the manifestation. To identify the type of HPV and the characteristics of the course of the disease, diagnostic studies are carried out:
- Colposcopy using a special device (colposcope), which allows you to determine the depth of the lesion, the size and localization of the focus.
- Biopsy with sampling of affected tissues for cytology and histology.
- PRC . This method allows you to refine the viral strain and barks a complete picture of the lesion.
See also material on the topic: HPV type 16, quantitative analysis, decoding .
Treatment of papillomavirus infection
Depending on the complexity of the disease and the risk of complications, the doctor prescribes treatment:
Conservative treatment. It helps at the initial stage in the absence of complicating factors. Antiviral drugs are considered basic – Interferon, Cycloferon , Reaferon, Viferon, Leukinferon. A modern remedy, Alpizarip, has a direct effect on the virus.
Suppression of HPV activity is also achieved by interferon synthesis inducers – Neovir, Ridostin, Tamerite, Immunofan. An important role is given to increasing immune protection with the help of immunostimulants – Derinat, Wobenzym, Likopid .
Medical removal of papillomas. The drugs provide a blockade of the nutrition of abnormal tissues or chemical burning of growths. The drugs Kondilin, Solcoderm, Fluorouracil, Imiquamod are used.
Operative treatment. It can be based on the following technologies:
- Cryogenic exposure , which ensures the removal of formations by deep freezing with liquid nitrogen.
- Radio wave surgery . The function of the scalpel is performed by a radio knife – a narrowly directed, radio frequency wave generated by a special device (for example, the Surgitron generator).
- Electrical coagulation . It is provided with an electric knife – high-frequency current.
- laser removal . Burning formation is provided by a laser beam.
With a large size of the lesion and a high risk of oncology, a surgical operation is performed. The surgeon uses a scalpel to remove the affected tissue and the surrounding area.
Prevention and vaccination of papillomavirus
Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. As a prevention of papillomatosis, 2 main directions are distinguished – streamlining sexual life and strengthening immunity. It is important to ensure a normal lifestyle, nutrition with enough vitamins, and treat infectious and chronic diseases in a timely manner.
There is currently no universal vaccine for all types of HPV. With this in mind, it is customary to provide protection against the most oncogenic strains.
Thus, the Gardasil vaccine is directed against HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18. With a triple vaccination of adolescents, the necessary immunity is provided. Against HPV 16 and 18, the Cervarix vaccine is intended . Vaccination is carried out from the age of 10.
Human papillomavirus is one of the most common infections. In most cases, it is unable to significantly undermine health, but the likelihood of serious complications exists. To exclude the growth of malignancy of formations, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner to determine the viral strain.



Папилломавирусная инфекция относится к папулезным вирусным заболевания. Ее незамедлительно лечат. Потому, что она вызывает онкологический процесс. Типы имеет “высокий риск” и “низкий риск”. Берегите себя!