Warts that occur on the skin can only be a cosmetic defect, and do not cause any discomfort to a person. But when it comes to genital warts, it’s much more serious.
This type of neoplasm can not only cause pain, but also significantly threaten human health. In addition, genital warts are highly contagious and can be passed on to a sexual partner.

Содержание:
- 1 What types of HPV cause them?
- 2 Differences from other formations on the genitals
- 3 Causes and factors for the appearance of growths
- 4 Methods of transmission of the virus
- 5 Locations and symptoms
- 6 Possible complications and dangerous consequences
- 7 Which doctor should I contact with this type of HPV?
- 8 Diagnostics
- 9 How to treat them?
- 10 Prevention and vaccination
What types of HPV cause them?
The human papillomavirus is special, it provokes various problems. The genital wart is the most dangerous manifestation of this pathology.
Anogenital warts are caused by approximately 20 different strains of HPV. Visible growths – 6 and 11 strains, anogenital – 16, 18, 33, 35 . Genital warts can be represented by papillomas and condylomas.
Papillomas
These anogenital warts appear on areas of the genital organs that have skin. They are round and smooth, slightly raised above the skin and do not have a leg.
There are also keratic papillomas. They appear relatively rarely and are characterized by a thicker surface. Most often affect areas of dry skin.
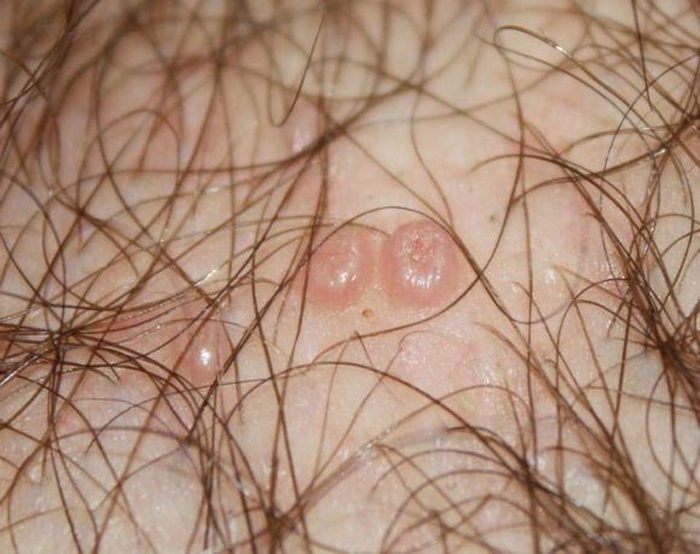
warts
These are fibroepithelial neoplasms that appear on mucous surfaces. Warts have a thin stalk or a wide base, they can be single or merge into groups. In appearance, warts resemble a cockscomb or cauliflower.
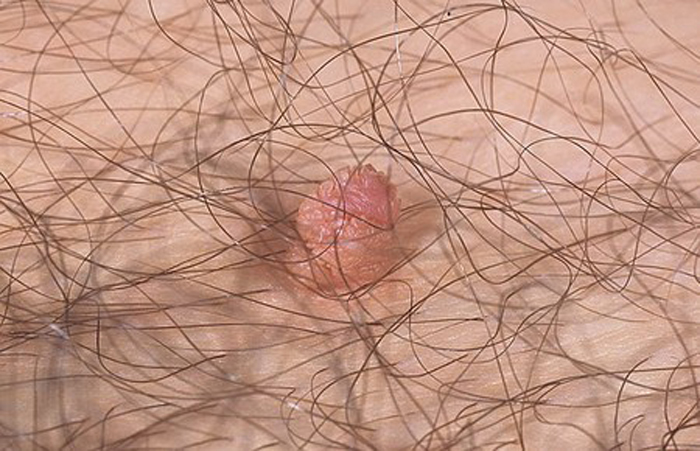
Differences from other formations on the genitals
Genital warts should be differentiated from Buschke-Levenshtein tumor, moles, genital herpes, molluscum contagiosum.
Genital herpes is a group of vesicular neoplasms that have transparent contents. This ailment, unlike genital warts, has a vivid clinical picture – the patient has itching and burning, and when the bubbles burst, it is possible that large erosive foci form.
Molluscum contagiosum is similar to an ordinary pimple, having a slight depression in the center. Inside the bubble is a mass in which there are rounded bodies, resembling molluscs in appearance.
Moles are most often small, dark in color and do not protrude above the surface of the skin. Easily confused with papilloma – hanging nevus, which can be flesh-colored. Moles in intimate places are observed from birth.
Bushke-Levenshtein condyloma is a type of pointed papilloma. At the initial stage, several papillomas are formed, which subsequently merge into very large foci.
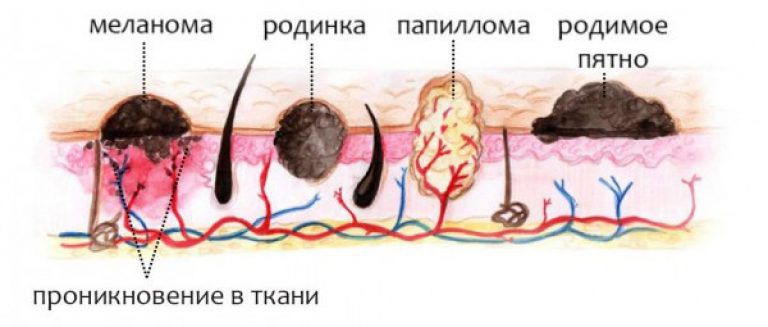
Over time, the growth becomes covered with scales and becomes rough. The neoplasm is separated by grooves, in which liquid contents with an unpleasant odor accumulate.
Causes and factors for the appearance of growths
The reason for the appearance of genital warts lies in the penetration of the papillomavirus into the human body. The aggressiveness of this infection is enhanced by the following factors:
- excessive sexual activity;
- the sexual partner has anogenital warts or has cervical cancer;
- low immunity;
- the presence of venereal pathologies;
- tobacco smoking and drug addiction;
- alcoholism;
- pregnancy;
- avitaminosis;
- endometriosis and other diseases of the uterus.

Methods of transmission of the virus
The papilloma virus is mainly transmitted sexually – through vaginal, anal or oral sexual contact. In addition, infection is possible when a newborn passes through the birth canal of an infected mother. Less common is the contact-household way of transmission of the virus.
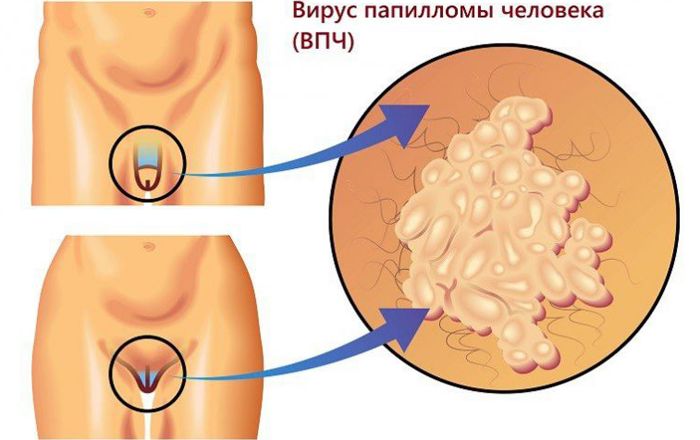
Locations and symptoms
According to doctors, most often genital warts occur in places of maceration. These are areas of the mucous membrane or skin in contact with moisture.
On the genitals of women
Possible areas for the appearance of genital warts:
- vagina;
- labia (small);
- Cervix;
- the mouth of the urethra;
- anus area.
On the genitals of men
Men have the following risk areas:
- anal area;
- the head of the penis;
- foreskin.
Also find out how warts appear on the penis , diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Possible complications and dangerous consequences
It must be understood that almost always the appearance of anogenital warts is associated with the penetration of low-oncogenic strains of the papilloma virus into the body, but the presence of oncogenic viruses is not excluded. According to statistics, with the appearance of genital warts in women, the risk of developing cervical cancer increases significantly.
In addition, there is an increased risk of developing:
- cancer of the vagina, vulva, anus;
- formations of a malignant nature of the bladder, liver, lungs, head and neck;
- lymphomas.
Quite often, genital warts become inflamed and suppurate, especially if they are subjected to frequent mechanical impact.
Which doctor should I contact with this type of HPV?
Urologists, gynecologists and dermatovenereologists deal with the problem of genital warts. If necessary, they give referral to highly specialized doctors.

Diagnostics
Diagnosis of neoplasms on the genitals is as follows:
- visual examination using gynecological mirrors, otoscope or anoscope;
- carrying out tests with a solution of acetic acid;
- histological examination;
- tissue biopsy.
The last analysis is carried out in the following cases:
- difficult to establish a diagnosis;
- lack of improvement after treatment;
- atypical lesions of the genitals;
- the patient is diagnosed with immunodeficiency;
- neoplasms are strangely colored, strongly fixed, rough;
- warts are ulcerated or bleeding.
How to treat them?
Medicine does not yet know how to destroy the papillomavirus in the human body. All treatment is aimed only at suppressing the activity of the virus and eliminating existing warts.
Treatment can be conservative or surgical, depending on the prevalence of neoplasms, their localization and morphological features. See also: wart on the penis , effective treatments

The use of medicines
The following medications are used on an outpatient basis:
- Podophyllotoxin . Lubricate the formation with a solution or cream for 3 days. You need several courses with breaks of 5-7 days. The cream is prescribed for neoplasms located on the skin, and the solution is used to treat the mucous membranes.
- Imiquimod . This is a cream that is used 3 times a week for 8-12 weeks.
- Preparations based on ascorbic acid and interferon – ointments Viferon, Altevir , Reaferon A. These funds enhance local immunity, are used several times a day for 1-2 months.
This treatment is prescribed for the treatment of genital warts at home, provided there are no signs of transformation into a malignant pathology, as well as in the presence of small lesions.
More severe forms of the disease are treated only in stationary conditions:
- 80% triacetic acid solution . Applied once. The acid acts on the growth, and its tissues become necrotic. After some time, education is rejected. Independent use of this tool is prohibited, since if it enters healthy areas, it causes severe burns.
- Solcoderm . The drug contains oxalic, lactic and nitric acids, as well as copper nitrate. Removal of the neoplasm is achieved by burning the growth. Several procedures are possible.
Together with local treatment, the patient is prescribed an injection of interferon into the vein, which has a blocking effect on the virus.
Chemical or surgical intervention
With extensive damage, methods of hardware destruction are used:
- Radio wave treatment – neoplasm tissues are destroyed using a device that emits special ions. It is used to remove growths that are dangerous for their transformation into oncology.
- Laser removal – CO2 laser vaporization is considered the most painless and safest operation to remove genital warts located in the cervix and urethra. This method reduces the possibility of re-developed pathology.
- Electrocoagulation – removal of a neoplasm with an electric current passing through a metal loop.
Folk methods of therapy
Modern medicine treats folk remedies differently, but it would be wrong to categorically deny the benefits of such therapy. Of course, you need to use folk recipes only after consulting a doctor, and it is better to use them as an additional therapy.

The most popular folk remedies for genital warts are:
- Celandine . Celandine juice is extremely poisonous, so it must be used very carefully, and only if the neoplasm is located on the skin. For a delicate mucous membrane, this remedy is quite aggressive. It is easy to use – you just need to apply the juice of the plant to the wart. This must be done every day until the neoplasm disappears. Serious studies on the safety of using celandine to remove warts have not been conducted, and it is impossible to exclude the provocation of the transformation of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
- Garlic . Garlic has antimicrobial and antiviral activity. To prepare a remedy, you need to chop the head of garlic and soak the mass in vodka. Insist in a dark place for 2 days, and then use for compresses.
- Rowan . It is necessary to cut the rowan berry in half, and apply to the papilloma until it disappears.
- Aloe . Cut along the aloe leaf, you need to tie to the neoplasm 2-3 times a day.
Also, warts can be treated with decoctions and infusions of the following medicinal plants, they must be taken orally:
- burdock;
- Melissa;
- St. John’s wort;
- sage;
- calendula;
- blueberry leaves;
- burdock.

It is important to understand that treating malignant neoplasms with folk remedies is not only impractical, but also very dangerous.
Prevention and vaccination
To minimize the risk of genital warts, the following rules should be followed:
- Avoid casual sex and have only one verified sexual partner. Use barrier contraception if there is no confidence in the safety of intimacy.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Completely rest.
- Eat right and balanced.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Strengthen the immune system, and in case of any failure, seek advice from an immunologist.
- Regular check-ups with a urologist and gynecologist.
When a papillomavirus is detected in the body, it is necessary to carry out antiviral therapy, remove neoplasms, and monitor the dynamics of the pathology.
With regard to vaccination, today there are two vaccines that prevent the appearance of the virus in the human body. However, it is advisable to vaccinate only before the virus enters the body.
Given the high contagiousness of HPV and the fact that 90% of the inhabitants of our planet are infected with one or another strain of this virus, vaccinations should be done before the first sexual contact. The optimal age is 12-14 years. If the virus is already in the body, the vaccine will be useless.
Every person should know about the danger of genital warts, if suspicious growths are found in the intimate area, you should immediately contact a specialist, find out the etiology of the neoplasm and carry out appropriate treatment. Also, we must not forget that the presence of genital warts is a danger to the sexual partner.