Human papillomavirus disease requires accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Deciphering tests for HPV infection is an important step in the examination and subsequent therapy.
Studying the norms and deviations of diagnostic indicators, as well as understanding the results of the tests, will help not only prepare for the trip to the doctor, but also approximately plan your next steps.
Содержание:
Tables for decoding the results: norms and deviations
To diagnose HPV and prescribe the necessary treatment, you need to submit biological material for analysis.
There are more methods for screening the human papillomavirus. The results of the most basic diagnostic methods will be discussed in detail in this article.
PCR results
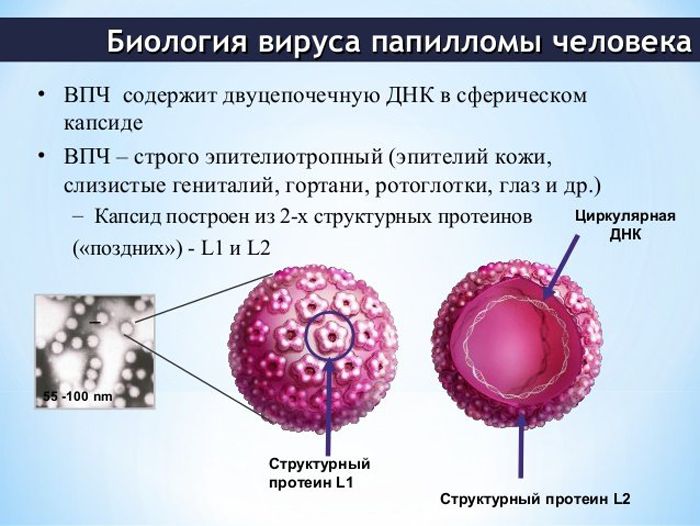
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method helps to identify DNA and RNA of pathogens of infectious diseases in any fragments and cells of tissues of the human body.
In the table you can find general information about the possible results based on PCR analysis .
Вирусная нагрузка ВПЧ Предварительный результат Расшифровка 0-3 Lg Отрицательно Норма. Вирус в организме отсутствует. 3-5 Lg Не определено Концентрация инфекции находится на границе с нормальным значением. Требуется провести дополнительное исследование. Присутствует риск развития дисплазии. Больше 5 Lg Положительно Превышена концентрация инфекции. Высока вероятность присутствия дисплазии.
quantitative research
Quantitative analysis (another name is Digene-test) allows you to capture viral DNA with a special RNA probe. Then count the genetic material.
The normal values of the analysis results can be seen in the table.
Группы ВПЧ Типы ВПЧ Предполагаемые результаты Низкий онкогенный риск 6, 11, 42, 43, 44 Более 1 относительной единицы – положительный результат (концентрация вирусов клинически значимая).
Если меньше 1 – «Не обнаружен» — результат отрицательный.
Высокий онкогенный риск 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68 Более 1 относительной единицы – положительный результат (концентрация вирусов клинически значимая).
Если меньше 1 – «Не обнаружен» — результат отрицательный.
ELISA
ELISA reveals the qualitative and quantitative content of three classes of antibodies in biological material:
- IgM.
- IgA.
- IgG.
These antibodies are produced at different stages of the disease.
For example:
- IgM – is produced at the very beginning of the disease. A healthy person should not have these antibodies in the body.
- The presence of IgG indicates that a person is either a carrier of the infection, or has already had it.
- If IgA antibodies are found in the blood, a person needs intensive care. The infection is chronic. The absence of IgA indicates that the infection has been eradicated.
Traditionally, venous blood is donated for this analysis.
For a more convenient interpretation of the results, the table shows combinations of the absence or presence of these three classes of antibodies in the body.
IgM IgG IgG Результат нет нет нет У человека отсутствует иммунитет к инфекции нет есть нет У человека имеется постинфекционный иммунитет есть нет/есть нет/есть Острая инфекция есть есть есть Состояние хронической инфекции находится в стадии обострения нет нет/есть нет/есть В организме присутствует хроническая инфекция
When deciphering the results, (yes) indicates a positive result, and (no) indicates a negative one.
General blood sampling study
A complete blood count is not intended to determine the presence of human papillomavirus in the body. This method is used to identify concomitant sexually transmitted diseases.
These include:
- Hepatitis.
- Chlamydia.
- HIV.
- mycoplasmosis, etc.

If the complete blood count showed a negative result for concomitant infections, then treatment will be directed exclusively to HPV.
What the results mean
Briefly, we will describe each below.
false positive
A positive test result for HPV infection does not always mean the presence of the disease. There are also false positive results that need to be rechecked.
Reference value
The reference results of the analysis cannot be considered as the only true ones. These indicators imply the total value obtained by the laboratory during the study of a certain sample of the population.
For example:
- pregnant women;
- young people aged 20-35;
- nulliparous girls, etc.
The results of the analyzes of these categories of citizens are necessary in order to obtain an average total indicator of the relative norm.
Thus, a quantitative analysis for HPV is performed. An average value of 3–5 Lg implies questionable results. They are collected by evaluating a specific sample of carriers of the HPV virus.
Most often, it is necessary to betray only the qualitative outcome of the study, which shows the presence of the virus. If a non-oncogenic type of HPV is detected, its concentration should be considered insignificant.

If the study is positive?
If the HPV test is positive, then the virus is present in the body. Don’t worry.
Many do not even know about their disease and live happily for many years. Symptoms of pathology are activated only during the weakening of the immune system.
Depending on the general clinical picture of the disease and the type of pathogen identified, the doctor prescribes treatment. Most often it includes:
- antiviral therapy;
- methods of destruction of neoplasms;
- therapy to strengthen the immune system.
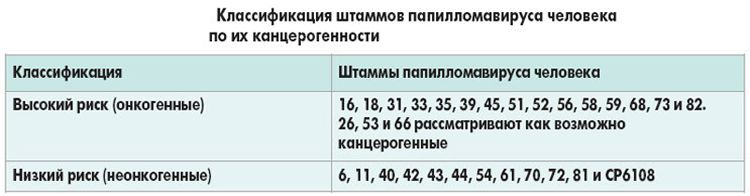
At 56, 16, 31, 18 and other oncogenic strains
If strains of infection with an increased oncogenic risk are detected, treatment should be started immediately. Therapy should be aimed at restoring immunity and eliminating formations.
Therefore, it is imperative to undergo an additional diagnostic study for the presence of dysplasia or erosion. To detect malignant changes in cells, a histological examination of tissues should be performed.
For benign strains
Non-oncogenic HPV types do not cause cell mutation. They can pose a threat only if the papillomas are damaged or combed with clothing details.
An infection can get into the wound, which will cause a secondary inflammatory process. Damaged cells of the neoplasm will begin to rapidly spread to healthy “neighbors”.
Benign strains of HPV can manifest as:
- warts of various forms and types;
- warts;
- “Butcher’s warts” – neoplasms of red color, similar to open wounds.
It happens that the analysis for HPV is positive, but there are no clinical manifestations of the virus (warts, genital warts, etc.). This may indicate that the person is only a carrier of the infection.
If papillomavirus DNA is not found
If the results of the analysis showed that the DNA of the human papillomavirus was not detected, then there is no infection in the patient’s body.
If there is a small concentration of infection in the body, then the human immune system is able to independently suppress its activity.
But with a weakened immune system, the virus can begin to “act”. Therefore, do not neglect repeated examinations. Often they are the ones who detect the presence of the disease.
What can affect performance
So that the HPV test is not false, doctors recommend adhering to certain rules. If patients violate them, the results of the study are distorted.
False positive results may be diagnosed if:
- the person ignored the recommendations of the doctor and violated the rules for preparing for the diagnosis;
- shortly before the analysis, the patient was treated;
- the material was taken incorrectly;
- the biological sample was contaminated.
To ensure that the results of the HPV analysis are not false, you need to consider several rules:
- it is forbidden to use antimicrobial, antibacterial and antiviral drugs for 12 hours before taking material for analysis;
- 72 hours before the smear, you need to refrain from sexual intercourse;
- a few hours before collecting the material, it is advisable to refrain from urinating;
- before going to a specialist to take the material, you need to take a bath;
- a smear should not be taken during critical days, as well as two days before their start, and within two days after.
In the event that the patient is going to take a blood test, it is better to do this on an empty stomach.
Proper preparation for the examination, compliance with the doctor’s clear recommendations will allow not only to identify the disease, but also to rebuff it in time.






Самые опасные онкогенные ВПЧ — это 16, 18, 30, 31, 33, 39, 40, 42, 43, 52, 55, 57-59, 61, 62, 67-70 типы — их называют ВПЧ высокого онкогенного риска.
В этом году хоть дело с мертвой точки сдвинулось. Государство озаботилось здоровьем женщин. Статистика по раку шейки матки неуклонно растёт. Вот и дали возможность женщинам 30-65 лет пройти анализ впч в рамках скрининга РШМ по ОМС, 1 раз в 5 лет. Если клиника отказывается делать бесплатно, то нужно жаловаться в Минздрав.