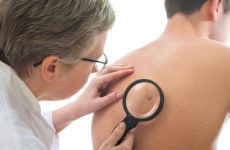
HPV (human papillomavirus) used to be considered “guilty” only in the development of cervical cancer in women. But today it has “changed” its orientation and causes the development of tumor neoplasms of a malignant nature in the penis of a man.
The virus is most often sexually transmitted and causes damage to the mucous membranes and skin not only on the penis , but also in the anus. But still, not everything is as scary as it might seem at first glance. Today, HPV can be successfully treated.
Содержание:
Human papillomavirus: what is it?
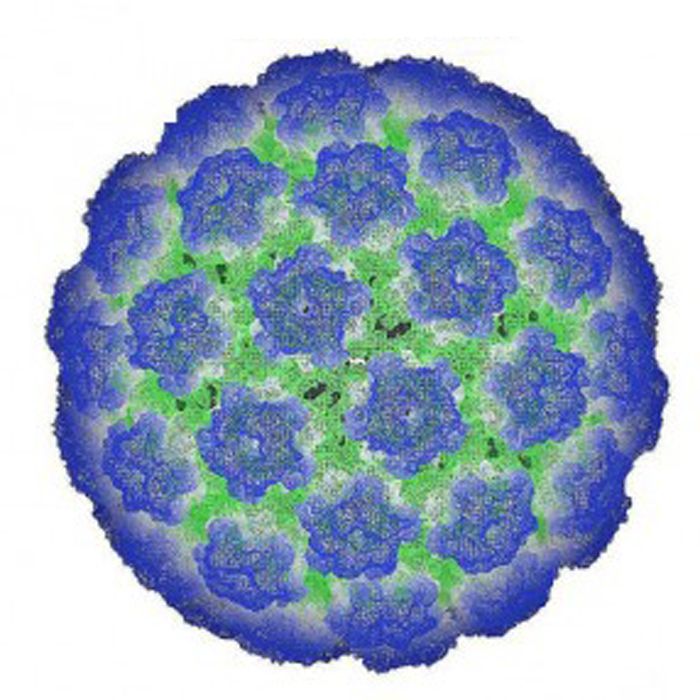
HPV-16 type in men (Human papillomavirus 16) is a virus that is included in the category of dangerous oncogenic risk, which has about 120 varieties. Depending on the DNA, each virus is assigned a specific number.
It is HPV-16 that provokes the development of malignant neoplasms in the body, as it is embedded in sections of human DNA and reduces antitumor immunity, as a result of which outgrowths appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
Genetic cells affected by the virus undergo a process of division uncontrolled by the body, which leads to the appearance of cancerous tumors.
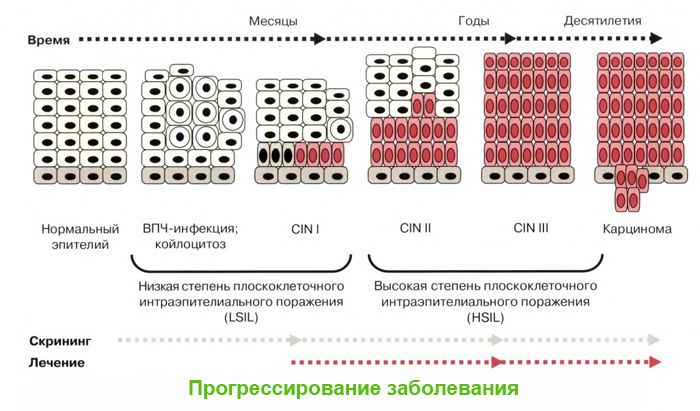
Papillomavirus lives in human blood, the incubation period for such a virus is quite long – from several weeks to several years, so diagnosing the pathological process caused by the virus is somewhat difficult.
HPV may, in general, not manifest itself in any way in the human body – it all depends on the immunity of the “carrier”, which does not even know about the presence of pathology, but, nevertheless, is its distributor. On average, about 90% of all people on the planet are infected with HPV, and the period from infection to the development of cancer takes about 10 years.
Once again, it should be repeated – the development of the pathological process depends entirely on the state of human immunity and the influence of adverse factors.
Sources of infection and risk factors
Attention: HPV most often enters the body of a man through domestic routes, while a woman becomes infected only through sexual contact. HPV-16 is very rarely transmitted through warts or bedding.
To increase the risk of HPV infection, just a few factors are enough: smoking, reduced immunity, constant stressful situations and, of course, genetic predisposition. The above factors also have a significant impact on the manifestation of clinical symptoms of pathology.
Ways of transmission of the virus
Infection usually occurs sexually, while sexual contact does not have to be completed – viruses get from a sick person to a healthy person simply from contact of mucous membranes with frank caresses.
Frequent change of sexual partners significantly increases the risk of HPV infection. In some cases, you can get infected in public places (baths, saunas, pools or toilets), especially if there are wounds or microcracks on the skin.
Symptoms of pathology
Most often, the activity of HPV in the human body causes the development of skin pathology – Bowen’s disease. A symptom of such a disease is a small red spot that transforms into a plaque. Papules form on it, eventually developing into cancerous neoplasms.
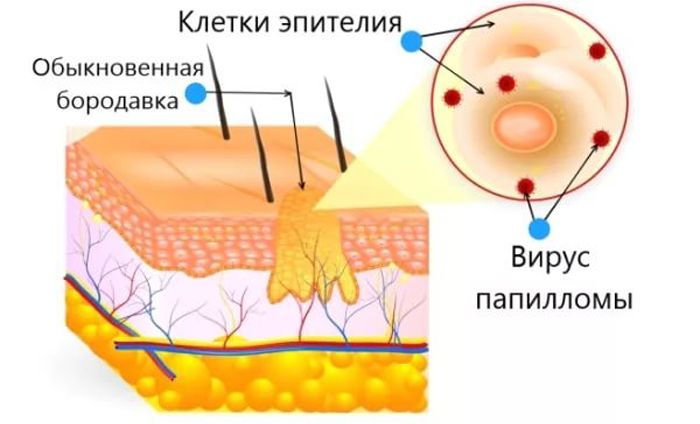
The skin in the affected area often peels off, causing discomfort, which is the first sign of pathology. Such neoplasms are most often localized in the armpit, perineal area, on the neck and the inner surface of the hands, without affecting the genitals.
In men, it is HPV-16 that can appear on the skin of the penis, the mucous membrane of the foreskin, the scrotum, the area around the anus or the perineum in the form of warts. They can be either single or multiple and are small flesh-colored tubercles on a small stem, quite soft to the touch.
Such warts are called genital warts , which grow and take on the shape of a cauliflower. Often their appearance does not disturb the man in any way, but sometimes the process of development of neoplasms is accompanied by irritation of the skin next to them, itching and even a burning sensation.
In some cases, the growth of genital warts can be painful, especially when such formations occur in the urethra or urethra.
The danger of HPV-16 in men is that healthy cells of the genitals and anus are affected, which leads to the rapid development of the oncological process. But the presence of a virus in a representative of the stronger sex is also dangerous for his sexual partners. HPV infection in women causes the risk of developing cervical cancer, so the presence of the virus in men must be diagnosed in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of papillomavirus
To diagnose a pathological process, a dermatologist sometimes needs an examination of the lesion site – neoplasms have a characteristic appearance and structure, which makes them easily recognizable. But to choose a method of treatment, it is necessary to identify exactly the type of HPV.
To determine HPV-16 in a man, a specific DNA is performed – a blood test (PCR polymerase chain reaction method), which determines not only the presence of the virus, but also its amount in the body, and also takes a smear from the urethra for cytology.
Sometimes such a diagnosis is not enough, since it only determines the status of the virus: simple or oncogenic. For a more detailed study, a biopsy of neoplasm cells is used, special attention is paid to specific neoplasms on the penis.
Treatment of the disease
For the treatment of pathology today, there are several methods, the timely use of which allows you to avoid the serious consequences of the disease:
- Instrumental techniques (surgery, laser surgery, cryotherapy, electrocoagulation and exposure to radio waves) involve the removal of neoplasms. For the use of such methods, several indications are necessary: aesthetic discomfort, frequent traumatization of neoplasms and a high level of tumorigenicity of the growth. But surgical removal of the neoplasm cannot eliminate HPV from the body, so they only cope with its manifestations.
- Drug treatment includes individually selected immunomodulatory drugs and antiviral drugs, as well as ointments for external use.
- Complex therapy is the most effective way, therefore, along with medicines, treatment with folk remedies can also be used . Alternative medicine helps to quickly strengthen the immune system and dry out rashes on the skin until the neoplasms disappear completely, as well as prevent further development of infection throughout the body. But folk advice should only complement traditional treatment and must be agreed with the attending physician.
See also how HPV is treated in men, drugs, scheme .
Infection prevention
Today, there is no specific treatment for pathology, the virus is practically not excreted from the body, despite the treatment. Therefore, HPV-16 prevention methods are becoming increasingly important. One of these methods is preventive vaccination, which is advisable to carry out before the onset of sexual activity.
The optimal age for the procedure is adolescents of both sexes 9-17 years old and young women aged 18-25 years.
The consequences of ignoring the disease
In women, HPV has more serious and obvious signs, while a man, being a carrier of the virus for a long time, may not be aware of his problem. Therefore, all representatives of the stronger sex, leading an active sex life, always need to remember a few rules:
- use condoms (condoms) during sexual intercourse to prevent the transmission of HPV to a partner;
- is attentive to the state of his health, strengthening and maintaining immunity;
- independently examine the genitals and anus – if neoplasms are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor – this way you can significantly reduce the risk of developing a pathological process.
If the manifestations of pathology are ignored and there is no timely treatment, the risk of degeneration of small neoplasms into cancerous tumors increases several times. With timely examination and well-conducted treatment, the development of cancerous neoplasms with HPV-16 is significantly reduced.
A large number of people, especially men, after discovering that they have HPV-16, are wondering: how to live on? In the case when the virus has firmly “settled” in the body, it is still not necessary to be nervous and “sound the alarm”.
To prevent the development of a pathological process, it is enough to carefully and regularly monitor your health – to avoid accidental sexual intercourse; treat diseases that depress the immune system in time; maintain the immune system at a certain level; give up bad habits and spend more time outdoors.
Then, perhaps, the virus will “doze” for a long time without being activated. These guidelines should be followed by both men and women. But the fair sex needs to be much more careful: men naturally have stronger immunity, so most often they are carriers of pathology than suffer from its manifestations.