Cervical papillomas are small tumor formations that grow from squamous epithelial tissue. Treatment of this pathology should be carried out without fail, as this is a rather dangerous phenomenon.

Содержание:
Why is HPV dangerous?
Scientist Harald Hausen proved that papillomas can provoke the development of cancer. The insidiousness of the pathology is that for a long time it may not manifest itself clinically in any way, and it is impossible to detect a dangerous growth on its own. Therefore, all women, without exception, are advised to regularly undergo examinations by a gynecologist.
It has already been proven that a long stay of the papillomavirus in a woman’s body (10–15) years leads to the development of oncology, and in patients with immunodeficiency, a dangerous disease occurs after 5 years.
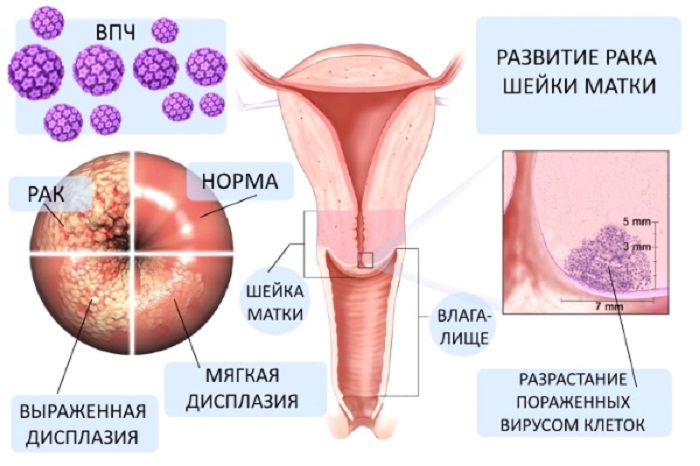
Quite often, cervical papilloma is combined with an equally dangerous female disease – erosion, and it is erosive changes that create favorable conditions for the development of papillomatosis – multiple papillomas. The presence of erosion at times increases the likelihood of a malignant neoplasm.
Methods of transmission of the virus
The papillomavirus is a microorganism that, when it enters the human body, remains there forever, the ways of transmission of this pathological agent are as follows:
- Sexual . Most often, the virus is transmitted during normal sexual intercourse, but it is possible that it enters the body during oral or anal sex. In addition, the virus can live in the saliva of the host, so kissing can also be a way to transmit it.
- Household . A virus can remain viable in the environment for a long time, provided it has a favorable microclimate – it needs humidity and elevated temperature. Therefore, using someone else’s towels, wearing someone else’s underwear, etc., can lead to infection with the virus. Very often the virus is transmitted in public baths, swimming pools, solariums.
- Vertical . This way of transmission of the virus is to infect the child from the mother, this occurs during childbirth, when the baby passes through the birth canal.

There are cases when the infection with the virus occurred in medical institutions or in beauty salons – when tools were used that did not undergo proper disinfection.
Factors provoking infection
Predisposing factors that provoke infection:
- disruption of the immune system;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- frequent stressful situations and nervous strain;
- severe colds;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- the presence of untreated infections that are sexually transmitted;
- cervical erosion;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene measures;
- smoking and alcohol abuse.
Types of HPV
The following types of papilloma can develop on the cervix:
- Pointed – they look like folds ingrown into vessels or connective tissue. With progression, they begin to resemble cauliflower.
- Squamous – similar to a common growth – a wart, such neoplasms often lead to deformation of the cervix and the reproductive organ itself.
- Inverted – in the course of development they go deep into the tissues and destroy the organ. In the presence of papilloma data, doctors speak of a precancerous condition.
How does HPV infection lead to uterine cancer?
There are different strains of the papillomavirus, and some of them have a high oncological index, for example, HPV 16 and 18 strains initially provoke the development of a cancerous process.
Viruses of other strains can also cause cervical cancer, but not in a short time. In addition to the fact that this takes time, certain factors are still needed that will provoke oncology. Namely:
- lack of adequate therapy;
- the patient’s reluctance to remove existing papillomas on the cervix;
- self- treatment of papilloma by folk methods – without the advice and control of a doctor, these methods can accelerate the degeneration of a neoplasm into a malignant one;
- poor immunity;
- bad habits;
- stress.
How does vaginal HPV develop?
After the papilloma virus enters the body of a woman, its development can proceed according to the following scenarios:
- The infection is destroyed within a few months by the immune system. Occurs in 15-17% of cases.
- A woman becomes a carrier – the virus does not manifest itself in any way, and can remain latent for many years, but a woman can infect her sexual partners all this time.
- There are signs of the presence of HPV in the body – condylomas, papillomas, warts appear on the genitals, and the worse a woman’s immunity is, the more likely it is that the infection will progress and give rise to erosion or a malignant process.
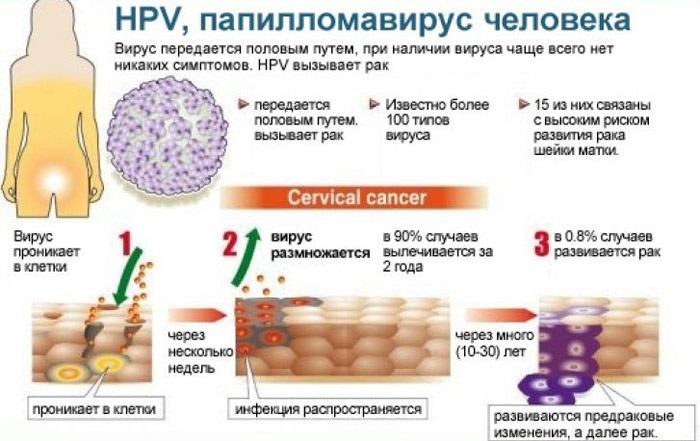
How to cure papillomavirus?
We must immediately make a reservation that it is not yet possible to cure the papilloma virus. There is no method or drug that could completely eliminate the virus in the human body.
All therapy that exists at the moment is aimed at suppressing the infection and stopping its manifestations. But at the same time, relapses are not excluded, since the virus muted by treatment can be activated again if conditions are favorable for it.
Treatment of manifestations of papillomavirus can be carried out by medication, chemical or surgical means. In some cases, doctors do not object to traditional medicine, but only if they are used as an additional therapy and supervised by a specialist.

Medical therapy
Treatment of cervical papilloma with medications is selected for each patient on an individual basis.
At the initial stage of the disease, antiviral drugs are prescribed that will suppress the activity of the infection, for example:
- Kripferon.
- Panavir .
- Raeferon.
- Alpyrazine.
- Vikferon.
- Cidofovir.
In addition, vitamin complexes and immunomodulatory therapy are prescribed.
Chemical Methods
Destructors are used to remove cervical papilloma chemically. These funds lead to the fact that pathological cells die, and the neoplasm disappears.
Since the cervix is a rather sensitive organ, not every destructor is suitable for the removal procedure. Most often, doctors use triacetic acid, Ferezol, Solcoderm.
Surgical method
Surgery is a classic way to remove papilloma. It is carried out with a scalpel, under anesthesia. It must be said that this method is significantly inferior to other modern methods of papilloma removal – it is more traumatic, and after it the woman will have a long rehabilitation period.
However, this is the only way that allows you to remove malignant cells, so only it is used in the late and advanced stages of papillomatosis.
Cryodestruction
Papilloma is frozen with liquid nitrogen, after which the neoplasm is rejected. It is important that after this exposure, the epithelium layer is restored, and healthy cells grow in place of the fallen off neoplasm.
As for the use of this method in the presence of atypical cellular structures, it is not always possible to remove them, and after some time a relapse of the pathology is possible.

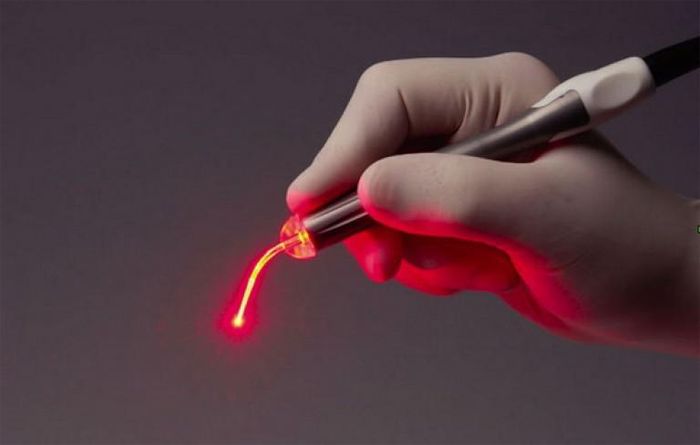
Laser vaporization
This is the most common way to remove papilloma on the neck of the genital organ, and most importantly, the most gentle. It is recommended for girls who plan to have a baby in the future. Laser removal is effective even in advanced cases.

Electrocoagulation
The essence of the method is cauterization of damaged areas with electricity. It is used for women who are no longer going to give birth. This is due to the fact that after the procedure, scars will remain on the cervix.
Radio wave method
Low-traumatic method of papilloma removal. For the procedure, an apparatus is used that generates radio waves, with their help, cellular fluids are heated, evaporated, which leads to the destruction of the neoplasm. After exposure, a scab forms on the cervix, which eventually disappears. Hospitalization of the woman is not required.
Traditional medicine
It is forbidden to use traditional medicine directly to remove papilloma on the cervix! Wrong actions can give impetus to the growth of the neoplasm.

The maximum that is allowed is the use of decoctions and infusions for oral administration. Recommended herbs that help boost immunity:
- aralia;
- radiola pink;
- eleutherococcus;
- ginseng;
- thyme;
- thyme;
- nettle;
- motherwort;
- dandelion root;
- rose hip;
- currant;
- St. John’s wort;
- lungwort and so on.
Nuances of HPV treatment during pregnancy
If papilloma on the cervix is diagnosed during pregnancy, drug treatment is undesirable, but if the use of drugs is required, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Inosine pranobex.
- Interferon and its inducers.
- Panavir.
- Dietary supplements that have a strengthening effect.
- Immunal.
- Polyoxidonium .
- Ferrovir.
- Alloferon.
- Allomedin.
- Spray Epigen .

The use of cytostatics, cryodestruction, laser therapy during pregnancy is prohibited. Treatment is recommended to start in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Prevention
At the moment, apart from vaccination, there is no other effective way to protect against the papillomavirus. However, vaccination is not mandatory and is not included in the National Vaccination Schedule. There are currently 2 vaccines in use – Gardasil and Cervarix .
The optimal time for vaccination is the period before the onset of sexual activity, since after the papillomavirus enters the body, it is useless to vaccinate.
But experts still recommend that all women under 45 be vaccinated in order to prevent infection with other strains of papilloma.
As a non-specific prophylaxis, it is recommended to observe the rules of intimate hygiene, to refuse casual sexual contacts and to strengthen the immune system by all means.







