The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common disease. It is transmitted quite easily, and the main therapy is aimed at removing papillomas, condylomas and warts, which are the result of infection, as well as maintaining immunity.
This disease occurs in both men and women. The difference is that in the representatives of the stronger sex, the incubation period lasts from three months to a year, and in women – 1-8 months.
Содержание:
Causes and ways of transmission
The disease is most susceptible to people aged 18-35 years. Most often, the virus is asymptomatic, which can be fraught with the appearance of malignant tumors.
The main mode of transmission is sexual. It is also possible to become infected by household means, for example, when using public baths, saunas and swimming pools.
Classification
HPV can affect the epithelium as warts, which are not dangerous, but it can also provoke malignant tumors. Papillomaviruses are divided into the following groups:
- Non-oncogenic HPV . These viruses are not malignant. They often go away on their own.
- Low oncogenic . Such viruses are extremely rare and, in the presence of certain factors, can provoke the development of an oncological process. Usually they are sexually transmitted and are manifested by warts.
- Highly oncogenic . Such viruses quite often provoke malignant genitourinary neoplasms. Types 16 and 18 can provoke penis cancer in a man or church cancer in a woman with whom he has sexual contact.
In the course of HPV is divided into the following forms:
- Latent (does not appear outwardly, concealment is characteristic, it is determined only in a laboratory study).
- Subclinical (the disease manifests itself erased).
- Clinical (characteristic symptoms of infection, manifested by neoplasms and dysplasia).
The latent form is the most common. A separate group includes people with severe immunodeficiency, debilitated patients – the treatment of infection in them is much more difficult.
Risk factors
Risk factors that increase the chance of contracting HPV include the following:
- Early onset of sexual life, a large number of sexual partners and their frequent change.
- Lack of barrier contraception during sexual intercourse.
- The presence of concomitant sexual infections.

Vitamin deficiency, weak immunity, and somatic diseases can also increase the likelihood of clinical manifestations.
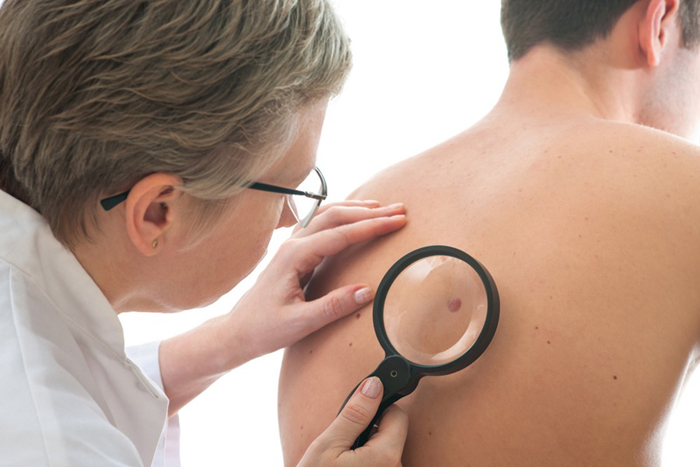
The main signs of papillomavirus, how papilloma manifests itself
During the incubation period, there are usually no symptoms of HPV in men . They occur only with reduced immunity. Penetrating into the tissues of the epithelium, the virus can grow in the form of the following neoplasms:
- Papilloma . A non-cancerous tumor that rises above the level of the skin. As a rule, it has the form of a pod.
- Wart . It is almost always a benign formation that looks like a small nodule. The color is white or flesh.
- Condyloma . A growth that looks like a cauliflower. The color can be green to brownish.
If you find such neoplasms, you need to contact a specialist. They are usually removed for prevention. HPV infection can have several scenarios:
- If a person has strong immunity, then he does not allow the disease to “take root” in the body and contributes to its self-destruction.
- The virus may “quiet” for a while. There will be no symptoms, but it can be passed on to other people.
- After any decrease in immunity, activation of the virus is possible. Various neoplasms may appear on the skin. In this case, you need to see a doctor.
- The worst option is the appearance of formations on the genitals or mucous membranes. This can lead to penile cancer. Other infections that can provoke impotence and problems with conception may also join.
Rare forms of human papillomavirus infection
There are several forms of pathologies, which include the following:
- Bowenoid papulosis . In this case, multiple papules appear, which may have a different diameter. They are characterized by a smooth surface, uneven edges on the head and body of the penis. Most often, this pathology is benign, but over time it can degenerate into oncology.
- Bowen’s disease . This form is characterized by the appearance of growths with uneven edges and a rough surface. On the skin, they have a gray-brown color, on the mucous membranes – a rich red. The size and number of neoplasms may vary. In men, such spots can appear on the hands, on the head , on the penny. Most often, the formations are in the skin, however, they can transform into invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
- Carcinoma . With high-gene types of HPV, dysplasia, malignant degeneration of the epithelium, and oncological diseases are possible. Genital warts in the genital area do not affect the reproductive functions of a man, but are contagioustherefore , when they appear, you need to consult a specialist.
Diagnostic methods
HPV is treated by a dermatovenereologist, urologist and andrologist. To establish the oncogenicity of a neoplasm, various examinations are used. First, the doctor examines the localization sites, then prescribes additional diagnostic measures, which may be as follows:
- Smear and scraping from the urethra.
- Biopsy. It involves the study of a tissue sample of the build-up, which is taken when it is removed.
- Dinege test. The most modern method that can determine the presence of the virus, the amount and its load on the body.
- This method allows to predict the course of the disease with the maximum probability.
- polymerase chain reaction. It makes it possible to determine the presence of HPV, the strain of the virus, as well as the level of oncogenic danger.
- Anal oncocytological smears. This analysis.

Treatment of papillomavirus infection
The human papillomavirus cannot be completely eliminated from the body. Treatment is aimed at removing neoplasms, preventing their transition to a malignant form, as well as strengthening the immune system. See also how HPV is treated in men, drugs, scheme . For this, the methods below are used.
Medical treatment
If during the diagnosis the HPV virus was diagnosed in the body, the following medicines can be prescribed:
- Immunomodulators . These drugs strengthen the protective resources of the body, preventing the development of formations. They are prescribed in two forms: tablets and rectal suppositories. These include such medicines as “Viferon”, “Genefron”, “Isoprinazine” and others.
- Cytotoxic drugs . Aimed at preventing the division of virus-affected cells (“Kondilin”, “Podofilin” and others). Most often, these are topical agents.
- Stimulants . Medicines that stimulate the body’s own synthesis of interferons (“Indinal”, “Cycloferon” and others).
Hardware treatment
Of the destructive methods aimed at removing papilloma, the following can be used:
- Cryodestruction . Application to the formation of liquid nitrogen to remove it.
- Electrocoagulation . Application for removal of electric current. In this case, the papilloma disappears, and a small wound remains, which heals for several weeks.
- laser removal . This is the most popular method now, which allows not only to eliminate the build-up, but also to prevent relapses.
- radio wave method . A special radioknife is used to eliminate neoplasms effectively and painlessly.
Removal
If growths with a high degree of oncogenicity have been identified, then their surgical excision with a scalpel may be indicated. After the operation, scars and scars may remain.
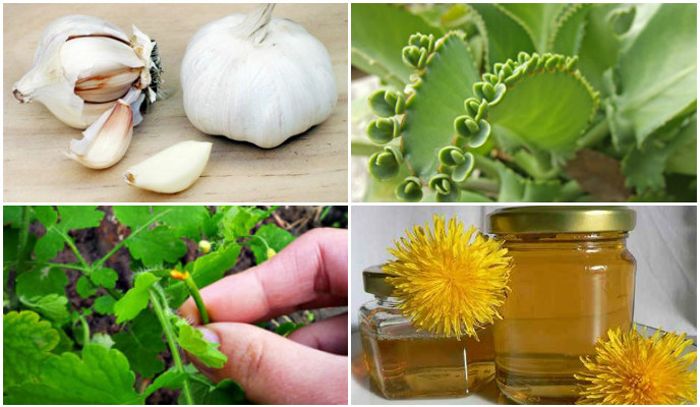
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine offers many recipes that help eliminate growths on the skin and strengthen the immune system. Medicinal plants, baths, decoctions based on them are usually used.
The following have worked well:
- Potato juice . It is recommended to drink fresh juice daily in the amount of 100 ml for 7-10 days. During this time, the body will receive the necessary trace elements, which will strengthen the immune system.
- Decoctions . For general strengthening of the body, you can use decoctions of plants such as chamomile, St. John’s wort, wild rose, dandelion. You can mix these herbs in equal proportions.
- Celandine juice . They are recommended to lubricate neoplasms. After a few weeks of regular procedures, they disappear on their own. This method is used for any formations provoked by the human papillomavirus.
- Egg white . It is recommended to rub papillomas with egg white (chicken and quail can be used) every two hours. Repeat until the swelling disappears completely.
- Garlic with baby cream . Grate the head of garlic and mix the resulting slurry with baby cream in equal proportions. Mix well and use to lubricate papilloma every day. Repeat 1-2 times a day.
- Aloe juice or banana . You can lubricate the formation with fresh aloe juice or banana peel. Use until completely gone.
- Essential oils . 1-2 drops of eucalyptus or tea tree oil can be applied to papilloma. You can also use lemon juice. These funds can be used alternately 2-3 times a day.

Disease prevention
To reduce the risk of infection, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Compliance with personal hygiene. It is important to use individual hygiene items: a toothbrush, a towel, and so on. You also need to be careful when visiting public saunas, swimming pools, etc.
- Caution in sexual life. Passing regular examinations for sexual infections, one sexual partner and using barrier contraception with new partners.
- Measures aimed at strengthening immunity, timely therapy of emerging diseases.
- Vaccination. There are special vaccines that protect against oncogenic strains of the human papillomavirus. For men, Gardaxil may be suitable. Information about the periods and schedule of vaccination can be obtained from a doctor.
Taking care of the body and following simple rules allows you to prevent infection or, as early as possible, identify this pathology and take the necessary measures. If characteristic neoplasms appear, you need to consult a doctor and follow all his recommendations in the future.