Warts are benign neoplasms on the human body, the appearance of which is provoked by the human papillomavirus.
Warts of any type and any localization are contagious, and the ways of transmission and influencing the activation of the virus are different.

Содержание:
- 1 Are they transferable or not?
- 2 Which of them can be infected?
- 3 Methods of transmission of infection
- 4 What factors contribute to the transmission and development of the disease
- 5 From what moment does a person become a carrier and when does he cease to be dangerous
- 6 Do relapses happen?
- 7 How to avoid infection
Are they transferable or not?
Because warts are a pathology of a viral nature, they can be transmitted from a virus carrier to a healthy person. Penetrating into the cells, the papillomavirus gives rise to their improper division, resulting in the formation of growths that rise above the surface of the skin.
When formations appear, we can talk about the transition of the virus into the active phase, which means that the virus has been in the body for a long time, and provoking factors have awakened it to activity.
The papilloma virus is quite resistant to the influence of the environment, and can be in it for quite a long period of time.
Which of them can be infected?
Warts can be:
- ordinary;
- genital warts;
- flat;
- keratomas;
- circumungual;
- plantar;
- filiform.
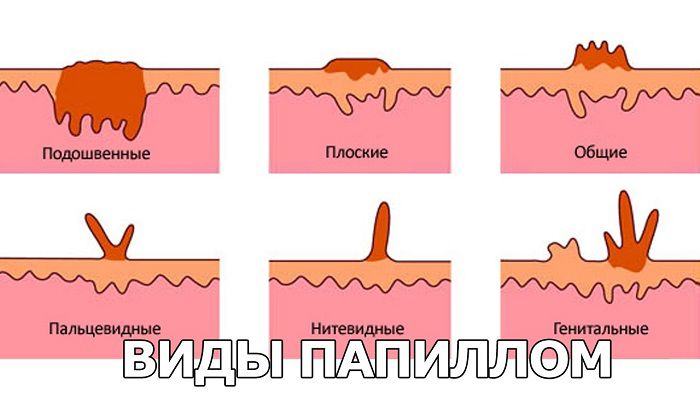
All types of warts , with the exception of keratomas, appear on the human body as a result of the vital activity of the papillomavirus of different strains, therefore, they can all be transmitted from person to person.
Ordinary
Common or vulgar warts make up about 70% of all skin warts. Most often they appear in children of school age.
These are sharply limited, dense, painless, bodily or white neoplasms that rise above the skin in the form of tuberous hemispherical nodules.
Sometimes their surface can be covered with papillae – growths resembling cauliflower. The usual places of localization are the face, the back of the hands, fingers.
If these neoplasms are not treated in a timely manner, they can change their shade to brown over time, and also spread significantly over the surface of the skin. Transmitted by close contact with a virus carrier – by contact-household.
Genital warts
Genital warts or genital warts appear on the epithelium of the genital organs. Most often, these formations are benign, but the risk of their degeneration into a malignant pathology cannot be ruled out.
In women, genital warts in most cases affect the clitoris, labia minora, urethra, vagina, and cervix. In men, the glans penis, frenulum, and foreskin are considered to be frequent places of localization of these neoplasms.
Genital warts can also be observed in the anus, and this may not always be the result of anal sex, the fact is that warts are able to capture the entire perineum.
Genital warts often experience mechanical stress, as a result of which they can be injured, inflamed and suppurated. The way of transmission is intimacy.
flat
The provoking factor in the occurrence of flat warts most often becomes a hormonal disorder, which is accompanied by a deterioration in immune defense.
It must be said that flat warts are not as contagious as, say, genital warts are. However, it is also possible to become infected with them through household contact, especially when the immune system is in poor condition.
Keratomas
Keratoma occurs when the cells of the stratum corneum of the epidermis thicken and keratinize. Most often, pathology is observed in people of the older age group – 50-65 years.
The cause of keratoma is age-related changes in cells, while the skin reaction to ultraviolet light is disturbed, which gives impetus to increased pigment synthesis and keratinization of the skin layer.
Since the keratoma is not an infectious pathology, infection with this type of neoplasm is excluded.
Periungual
Most often, this problem occurs in children 8–16 years old, this neoplasm does not provoke unpleasant sensations, and until it grows to a significant size, it may not interfere with a person in any way.
The transmission of the virus in this case is contact-household, on the hands of such neoplasms appear in people who have the habit of biting their nails, on their feet wearing tight shoes can become a provoking factor.
Methods of transmission of infection
To protect yourself from the appearance of warts, you must know the ways of transmission of infection from a virus carrier to a healthy person.
Papillomavirus infection can occur in one of the following ways:
- direct – contact;
- household – through common household items;
- sexual – the most common route of transmission of the virus;
- vertical – from an infected mother to a child during childbirth.
There is also the concept of “self-infection”. It means that infection occurs when combing an already existing growth – its integrity is damaged, and viral agents spread to healthy tissues, which leads to the appearance of warts of the same type as the existing one.
Transmission through tactile touch of hands and feet
Warts can be transmitted from person to person through direct contact of a healthy person with growths, as they are open sources of infection. Even a light touch is enough for the virus to be on a healthy epithelium.
If the skin of a healthy person is not damaged, infection may not occur, but if there are even minor scratches or the smallest microcracks, the virus will easily enter the body and take a waiting position. As soon as favorable conditions appear for its activation, it will begin to multiply rapidly.
Is HPV transmitted at birth
The papilloma virus can be localized in the basal layer of the epithelium and on the mucous membranes. When a child passes through the birth canal, he is in close contact with the localization of the virus, so there is a fairly high risk of infection.
Is it possible to get infected from another person sexually
The sexual route is the most common route of infection with the papillomavirus. Moreover, the type of sexual contact does not matter – the virus can enter the body of a healthy person during vaginal, oral and anal sex.
I must say that the risk of infection greatly increases if the partner has papillomas and warts on intimate organs. You should be aware that it is impossible to completely exclude infection by using barrier contraception.

Firstly, the condom does not completely cover the genitals, and secondly, the latex product has too large micropores, and through them the virus can enter the body of another person.
In addition, the virus is also transmitted through body fluids, such as saliva. The risk of infection in this case increases in the presence of wounds in the oral cavity of a healthy person.
What factors contribute to the transmission and development of the disease
The following external factors contribute to the development of pathology:
- stress;
- chronic fatigue;
- insufficient rest;
- unbalanced diet – the predominance of refined, carbohydrate, high-calorie foods;
- sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity;
- unprotected sexual contact.
Internal factors:
- hormonal disorders – puberty, pregnancy, premenopausal period;
- failure in the process of digestion as a result of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- exacerbation of chronic infections and acute diseases;
- non-compliance with hygiene standards.
From what moment does a person become a carrier and when does he cease to be dangerous
The incubation period of the papillomavirus in the human body can vary from several weeks to several years. In some cases, in people with strong immunity, the papillomavirus never activates, and they are not even aware of its presence in the body. Provided no skin growths have developed, contact with an infected person may be safe.
Carriers of genital warts remain highly contagious, so they should definitely receive an intensive course of antiviral therapy. If we talk about other, more harmless and not so contagious strains of the papillomavirus, after the removal of the neoplasm, the person ceases to be a source of infection for others.
Do relapses happen?
It is not yet possible to remove the papilloma virus from the body. All treatment is aimed at suppressing its activity and removing emerging growths. Therefore, a guarantee of the impossibility of relapse cannot be given. As soon as provoking factors appear, the virus is activated again, and will cause the appearance of new neoplasms on the skin.
In addition, quite often the cause of recurrence is poor-quality removal of the wart – if even the slightest structure of the neoplasm remains in the skin, the wart will appear again, and may begin to grow profusely.
How to avoid infection
To prevent infection, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Do not walk barefoot in public baths, swimming pools and saunas. Wear only your own beach shoes, do not use other people’s towels and other accessories. It is recommended not to touch the walls, but before you sit down, spread your towel.
- Treat any skin damage immediately with an antiseptic – wounds are an open gate for viruses.
- If a family member has skin growths, common items should be disinfected regularly.
- Before performing manicure or pedicure procedures in salons, make sure that the master uses disposable consumables or that he uses sterilized instruments.
- Shoes should be periodically washed from the inside with soap, and aired and dried every day.
- If it was not possible to avoid contact with the virus carrier, for example, when shaking hands, hands should be washed with soap and water as soon as possible and treated with an antiseptic.
- You need to monitor the state of your immunity and strengthen it with all your might. Do not be exposed to hypothermia, eat right, eliminate bad habits, observe sleep and wakefulness, take immunomodulatory drugs if necessary.
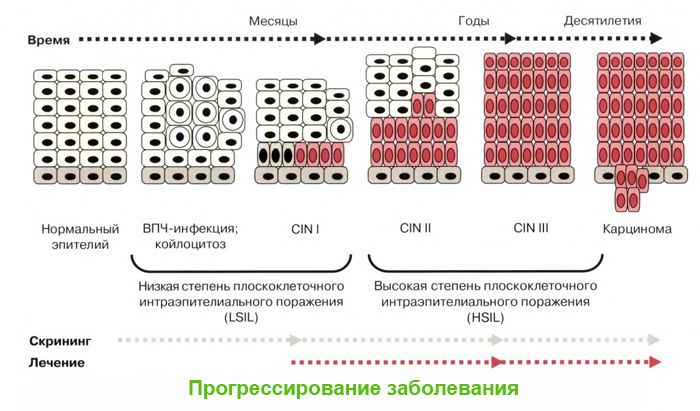
Warts are not only unaesthetic and uncomfortable, if the growth is injured, secondary infection is possible, which will lead to inflammation.
Under certain conditions, benign growths can transform into malignant neoplasms. Therefore, it is so important to take care of your health, and by all means to prevent infection with the papillomavirus.







