Papillomavirus quite easily penetrates into a healthy body and settles in epithelial cells. In some cases, self-healing occurs, and after a few months the virus disappears without a trace.
In other people, HPV is activated and makes itself felt: various kinds of growths appear on the skin and mucous membranes. Although papillomatosis is more common in women, men are also affected by the pathogen.

Содержание:
What are HPV formations on the penis?
Neoplasms on the male genital organ cannot be overlooked. They may not cause discomfort, but they are always clearly visible and palpable, even if they are very small.
The following types of growths are found on the penis :
- Warts . These are dense nodules of a hemispherical shape, which are more often localized at the base of the organ. With timely access to a doctor, they are easily treated and removed without leaving any consequences. Ignoring warts can lead to damage, attachment of infection, spread of the inflammatory process to internal organs and degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
- papillomas . They are similar to warts, but have a pathological nature. White small outgrowths form anywhere on the penis: on the head, frenulum, inside the foreskin and even the urethra, on the trunk and in the pubic area.
- Condylomas . These growths have a different shade, from flesh to dark brown, rapidly increasing in size. Outwardly, they may resemble cauliflower inflorescences, narrowed at the base and expanding towards the top, or spikes, narrowed upwards.
Formations can be single or multiple, sometimes several small papillomas coalesce into one large growth.
The main types of growths on the head in men
Below are the main types of growths that can occur in an intimate place in men. Also find out how warts appear on the penis , diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
pointed
Genital warts have a rough texture, look like warts or resemble cauliflower inflorescences.
Formations appear rarely and mainly in places that are injured during sexual intercourse. In the area of the penis, warty structures ranging in size from 1 mm to several centimeters are found. Gradually they increase in size.
Genital warts often affect the head of the penis, the crown of the head, the frenulum of the foreskin and the inside of the foreskin. As the disease progresses, the rashes occupy a larger area, being localized around the anus or in the inguinal zone.
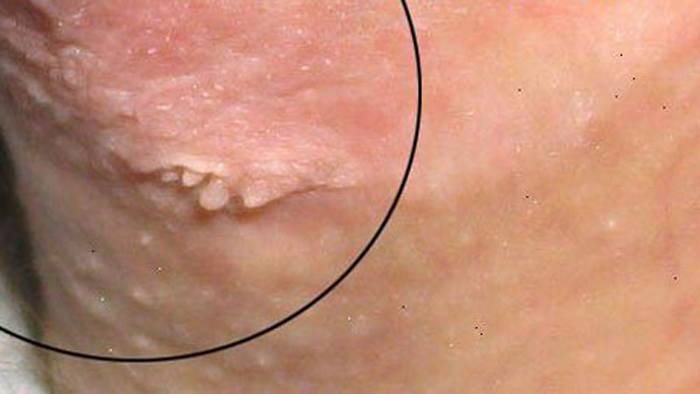
flat
Flat papillomas grow in width, but most of the neoplasm is under the skin. The shade of the growth varies from pinkish to dark brown. Flat papillomas can also be single or multiple.
This type of growths is usually formed in conditions of hyperthermia and high humidity.
The danger of flat neoplasms lies mainly in the fact that they are rarely mistaken for papillomas and are in no hurry to see a doctor.
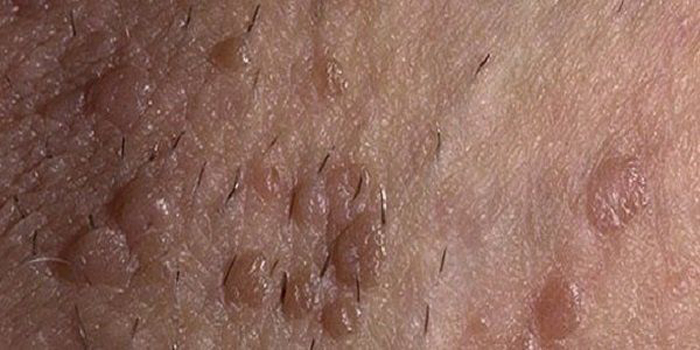
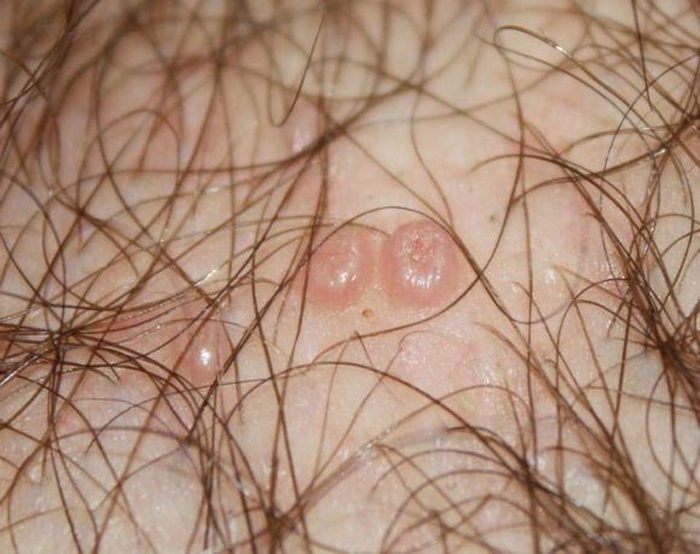
Types and oncogenic danger of growths
Currently, there are three groups of HPV in medicine, depending on their carcinogenicity:
- Viruses with a low degree of oncogenicity.
- Viruses with an average degree of oncogenicity.
- Viruses with a high degree of oncogenicity.
Each group includes a number of HPV strains, which may differ between men and women. The degree of oncogenicity, in fact, is the probability of degeneration into a malignant formation. If the papilloma is not dangerous, it is removed surgically, and the man is no longer worried about the neoplasm.
Viruses with high oncogenicity often lead to cancer.
What is the danger of the disease?
Many men do not attach importance to papillomas and warts in the genital area, believing that if they do not hurt and do not cause discomfort, there is nothing to worry about. In fact, this is a profound misunderstanding.
The occurrence of papilloma on the penis is always associated with the activity of the virus. This is not a pimple that will go away on its own: the pathogen is inside the body and can lead to unpleasant consequences, including:
- Infection of the sexual partner. If a man continues to be sexually active after the discovery of papilloma, in 60% after one contact there is a transfer to a partner. Transmission of the virus to a woman often leads to the development of cervical cancer.
- Damage to neoplasms is accompanied by pain, bleeding. The virus can enter through an open area to the surface of the skin, resulting in the formation of papillomas on adjacent areas of the skin.
- Phimosis is one of the unpleasant and extremely dangerous complications in which the foreskin fuses with the head of the penis.
- The accession of infection, the development of the inflammatory process in the penis.
- The development of malignant tumors.
In addition, papillomas, although they can disappear on their own without medical intervention, still affect the psychological state of a man.
Localization of formations
Depending on the strain of the virus that has entered the male body, papillomas can be localized in any area of the genital organs: on the head or body of the penis, in the frenulum zone, on or under the foreskin, in the groin or in the anus.
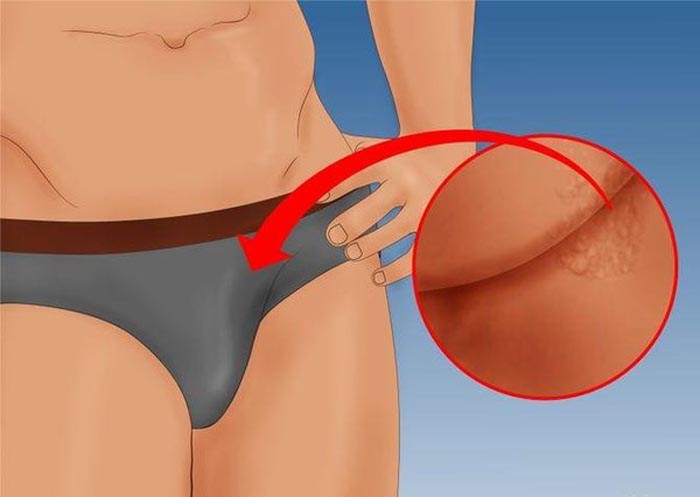
Sometimes growths form in the urethra or in the the anus itself , so it is impossible to detect them at home.
How to treat HPV on the genitals?
The most effective and popular methods of removal, treatment of papilloma in intimate places are listed below.
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy includes the use of medications, but they are not the only treatment. The prescribed drugs only help to suppress the activity of the virus and strengthen the immune system (antiviral, immunostimulating, immunomodulating agents), but the papillomas themselves are removed surgically.
The doctor may prescribe both local remedies and tablets.
Recommendations are also given regarding the diet, adherence to the daily regimen and a healthy lifestyle, sometimes it is recommended to drink a course of vitamins.
Radical Methods
Radical methods include medical manipulations, with the help of which the neoplasm is completely removed. There are both advanced methods and those that are becoming less popular.
Advanced methods are highly sensitive, painless, safe and very effective. They allow you to remove the papilloma completely along with the subcutaneous formation without the likelihood of recurrence, in most cases they do not leave marks on the skin.
However, each of them has its own advantages, disadvantages and contraindications. See also: wart on the penis , effective treatments
Surgical impact
Surgical removal of papilloma is rare, so the method is considered obsolete. It is advisable to use it if the neoplasm has reached a large size or other methods have been ineffective.
During surgical exposure, the doctor uses local or general anesthesia, makes an incision and excised the formation and nearby tissues.
After that, sutures are applied. The rehabilitation period requires compliance with a number of security measures, after which the affected area heals. A small scar or scar may remain at the site of exposure.
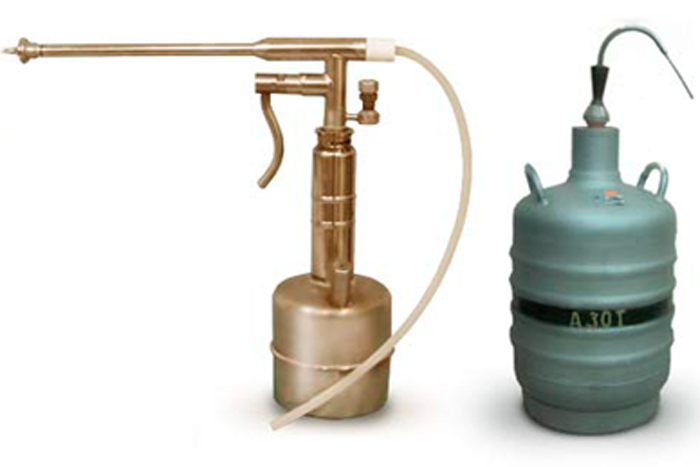
Cryodestruction
This method involves treating papilloma with liquid nitrogen for 30 seconds. As a result, the growth freezes and literally falls off.
For processing, a special apparatus or an ordinary cotton swab can be used, so the procedure is absolutely painless and is done very quickly. As a rule, anesthesia is required for cryodestruction, especially when it comes to intimate places .

Radiosurgery
The radiosurgical method is the removal of papilloma with the help of a special knife based on radio wave exposure. The doctor cuts the tissues of the neoplasm, but the papilloma itself is untouched.
The radio wave has a burning effect on the papilloma, but the procedure itself is absolutely painless, effective, less traumatic and highly sensitive.
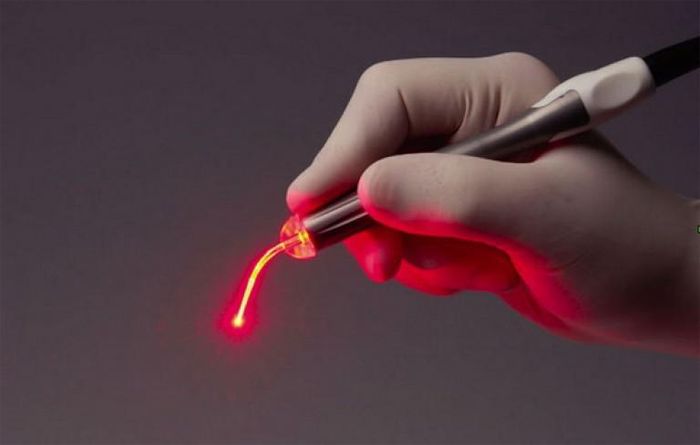
Laser
With laser papilloma removal, the doctor uses a laser beam that melts the growths. The patient experiences only a slight cool tingling, and the procedure itself lasts only a few minutes.
After that, the affected area is covered with a crust, which disappears after two weeks.

Chemical degradation
During destruction, special chemical solutions are used (“Kondolin”, “Solcoderm”), with which the doctor treats neoplasms. Regular processing leads to the fact that the papilloma dries up and disappears.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is used quite often, since under the influence of high temperatures and an electric current of a special frequency, the formation is removed along with the root. The disadvantage of this method is the scarring of tissues.
Average removal cost
The cost of medical manipulations depends on various factors: the pricing policy of the clinic, the region, the degree of disease progression, the chosen method or drug, the affected area, and others.
Removing a simple papilloma can cost, on average, 500-5000 rubles. With an extensive lesion, the cost of treatment increases, and if we are talking about a tiny formation (1-2 mm), the price will not exceed 200-300 rubles.
Folk methods of dealing with the disease
Folk methods are already rarely used, but still some call them the most effective to this day. The use of traditional medicine is allowed only after consulting a doctor.
How can HPV be cured in folk ways?
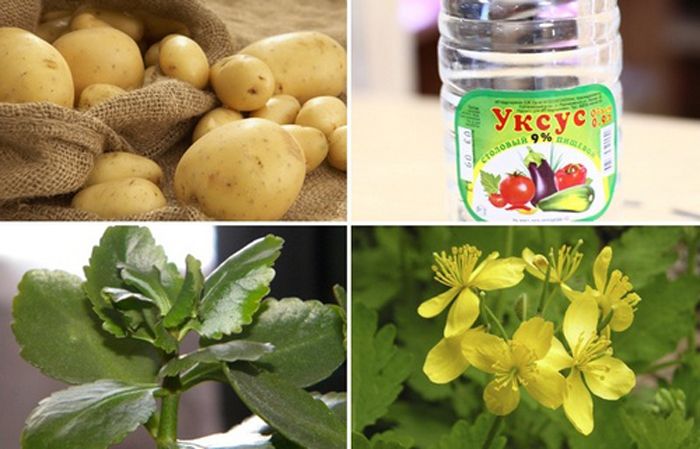
- Treat the growth daily with tea tree oil , mixing it with vegetable oil in a 1:1 ratio.
- Gently cauterize papillomas with iodine without touching healthy tissues.
- Make 5-hour compresses from fresh aloe juice.
- Treat the affected areas with a decoction of celandine (1 part of the plant and 4 parts of water).
- Use baths with a decoction of chamomile and St. John’s wort (1 tablespoon of each plant and 1 liter of boiling water).

Traditional medicine can only be effective in combination with other methods of treatment.
Prevention measures
To date, there is no method that would allow you to protect yourself from HPV once and for all. The virus penetrates mainly during unprotected sexual intercourse, so the main preventive measure is the use of barrier contraceptives and the rejection of promiscuity.
A healthy lifestyle that includes proper nutrition, walking in the fresh air, giving up bad habits and playing sports helps to strengthen the immune system.
If neoplasms are found in the genital area or unpleasant sensations (itching, burning, discomfort) appear during intercourse, you should immediately consult a doctor. When the diagnosis of papillomatosis (HPV) is confirmed, the partner of the man should also be examined.
HPV is affecting young people more and more frequently. However, the appearance of unusual growths in intimate places often makes a man not be afraid of this, but embarrassed. Men are afraid to go to the doctor (dermatovenereologist, urologist), continue to have sex, infecting women, and can start the disease before it transforms into an oncological process.