Содержание:
Introduction
The occurrence of papillomas and other neoplasms on the body is a consequence of infection with HPV (human papillomavirus). The virus is very common in the human population and can affect any part of the body.
Most often, formations are localized in areas with hairline. Papillomas are benign formations, but under certain conditions they can become malignant (turn into a malignant form).
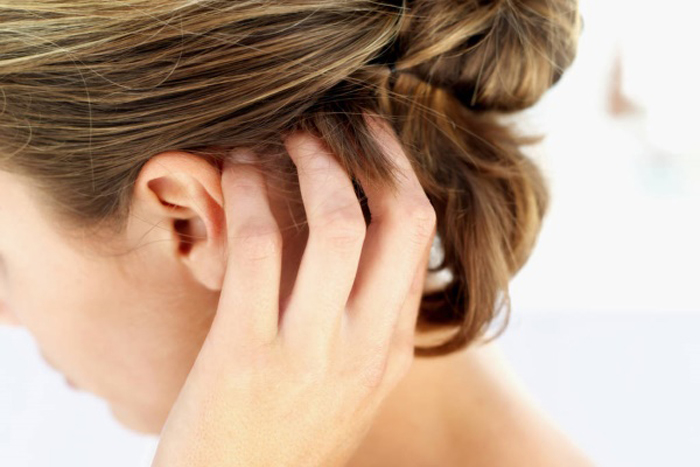

Causes of neoplasms in the scalp in a child and in adults
The main and main reason for the formation of papillomas is HPV (however, there are so-called keratomas – papillomatous formations of a non-infectious nature, they occur with age and are associated with skin aging processes).
This virus is ubiquitous (about 80-90% of the sexually active population), however, it is clinically manifested only under certain conditions, a person can live his whole life without even knowing about its existence if he does not show himself.
Infection with the virus occurs from the carrier (with or without clinical manifestations) through:
- Sexual contact is the most common, most people become infected in this way, mainly as a result of their first sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal, oral).
- Through the blood – during blood transfusion, with poor processing of instruments in hospitals and maternity hospitals. A rarer way, since strict control is established over the observance of the rules of asepsis, antiseptics and blood processing.
- The vertical path – from the mother to the fetus (during pregnancy or childbirth, at the time the child passes through the birth canal).
- Contact-household – through touch, various objects and things, in gyms, saunas, etc. This path only works if there is an entrance gate for the virus (damaged skin).
After entering the body, the virus may not manifest itself for a long time until the factors that contribute to its activation act. These are:
- chronic stress.
- Acute and chronic infectious diseases.
- Abuse of alcohol and smoking.
- Violation of the hormonal balance in the body.
- Pregnancy.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Other conditions leading to a decrease in the immune forces of the body (severe injuries, surgical operations, the use of certain drugs).
One way or another, each of these causes leads to a decrease in immunity, which is the key moment in the occurrence of clinical manifestations of the disease (since the immune system is no longer able to contain the virus).
Varieties
At the moment, more than a hundred varieties of HPV are known to science, which manifest themselves in the same way – in the form of various formations on the surface of the body, only their appearance and localization change. In the international classification of diseases, papillomas belong to section – D23, and papilloma of the scalp – D23.4.
Depending on the type of neoplasm, there are:
- Warts are round, dense, small bumps.
- Plantar papillomas – have a shiny surface, are formed in places of friction (the name was received due to the fact that they are most often formed on the feet).
- Vulgar – rather large and solid formations, are the result of the merger of smaller ones.
- Squamous – flat and smooth, can cause subjective sensations (itching, pain).
- Basal cell – slightly convex, yellow-brown. Over time, darken, as they contain melanin.
- Filiform – elongated yellowish, prone to growth.
- Pointed – formed on the mucous membranes (growing like cauliflower).
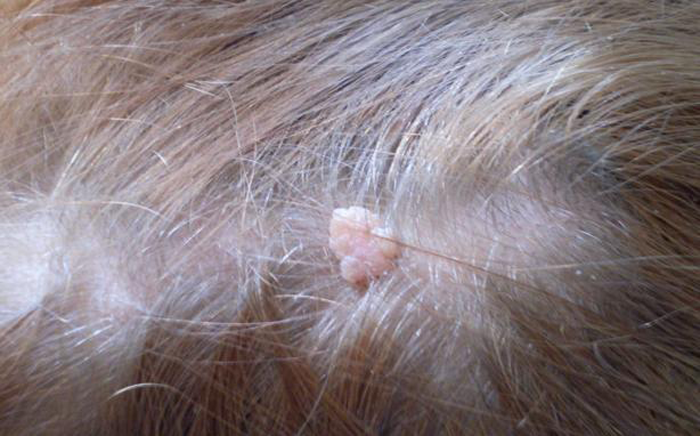
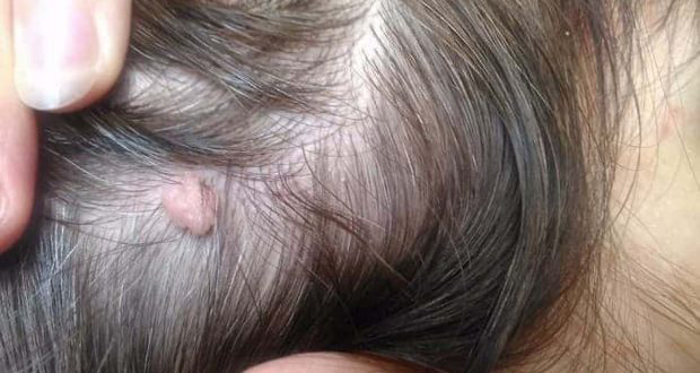
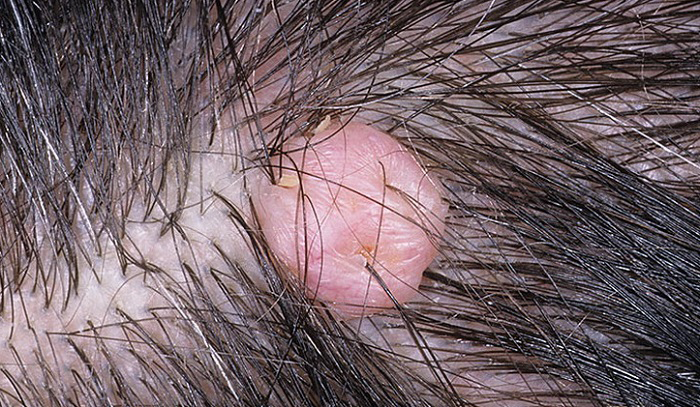
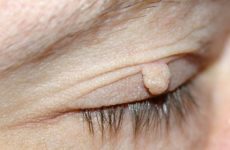
Depending on their number:
- Solitary – often reach large sizes.
- Multiple – often small in size, but can be large. They are located in groups or scattered throughout the body.
Symptoms and signs of HPV in hair
The main manifestation of papilloma on the head is a neoplasm, which can have a variety of shapes and colors (described in the previous paragraph). As a rule, they do not cause any inconvenience to their owners, except for a cosmetic defect.
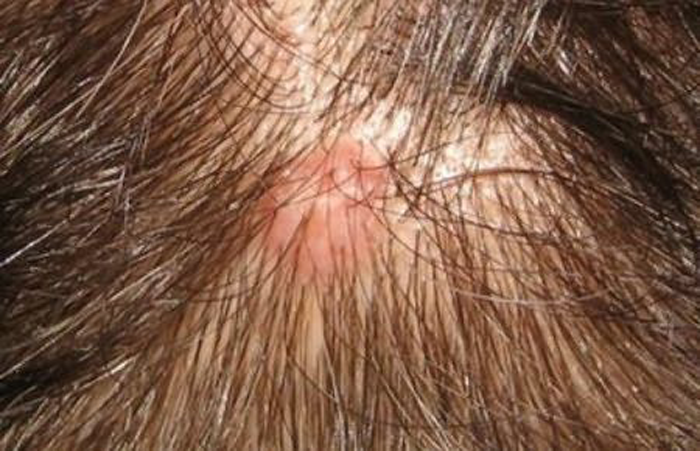
However, on the scalp, they are more exposed than anywhere else when combing, cutting and washing hair, wearing hats. As a result of such influences, papillomas can be damaged and in this case give some clinical symptoms:
- Itching and redness.
- Swelling.
- Bleeding.
- Formation of erosions and ulcers.
The latter is fraught with infection and the occurrence of purulent complications.
Papillomas and other formations of non-viral etiology, as a rule, are less susceptible to damage, since they are denser and protrude less above the skin surface.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method is examination and palpation, as a result of which it is possible to establish the type of formation and suggest a diagnosis. However, to clarify the cause and establish the final diagnosis, additional studies are needed:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – allows you to detect the genetic material of the virus (DNA or RNA) in the blood.
- Serological method – determination of antibodies to HPV in the blood.
- Histological examination – carried out after removal of the papilloma. It consists in examining its cells under a microscope, which makes it possible to judge the malignancy of the process.
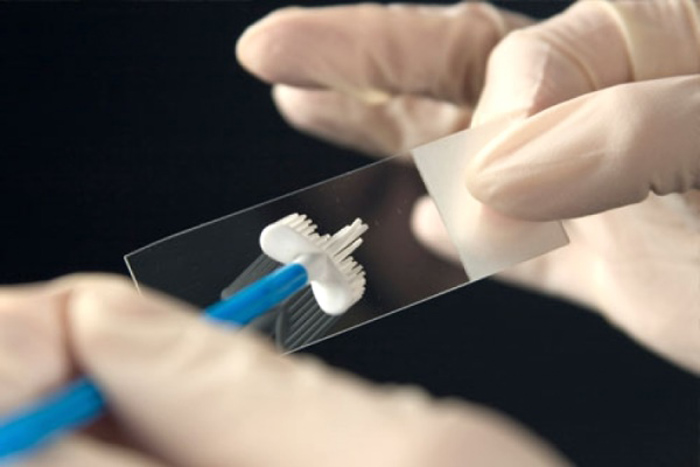
Can HPV turn into cancer?
Malignancy (malignancy) of papillomas is very rare. The reasons that can lead to the transition of the process into malignant are the following:
- Constant irritation and injury.
- Incomplete removal.
- Attachment of other infections.
- Constant and prolonged exposure to the open sun.
- Exposure to various carcinogens.
- immunodeficiency states.
- chronic stress.
- High dose of radiation.
- Age.
Signs that indicate malignant degeneration:
- Color change.
- Increase in size.
- Surface change (becomes bumpy).
- Ulceration.
- Histological signs (violation of cell differentiation, signs of atypia).
- The presence of metastases.
Senile papillomas are generally not prone to malignancy.
Treatment and removal
It is advisable to start treatment as early as possible, this will avoid complications. There are several ways to get rid of papillomas on the head.
Medical
For drug treatment, creams, gels and ointments based on interferon (an antiviral drug) are used, as it helps fight the pathogen. Preparations:
- Salicylic, trichloroacetic and retinoic acids.
- Fluorouracil.
- Panavir .
- Oxolinic ointment and Viferon .
These drugs are used for local therapy. They are applied directly to the formation itself or to the wound after its removal. Such therapy has an antiviral effect and promotes the speedy regeneration of tissues.
Very important in conservative therapy is to increase the body’s immune defenses. For this, immunostimulants are used:
- Methyluracil.
- Prodigiosan.
- Timalin.
- Molgramostin.
- Myelopid.
and various vitamin complexes:
- Aevit.
- Aquadetrim.
- Antioxycaps.
These drugs are prescribed only after consulting with your doctor and conducting appropriate tests.
Folk remedies
Alternative therapy is based on the use of infusions and decoctions to strengthen the body and increase immunity, as well as some local effect on papillomas.
Infusions and decoctions:
- From violets and wormwood.
- Plantain.
- Dill, clover, calamus root, St. John’s wort.
- Daisies and strings.
- Nettle, lemon balm, horsetail and dandelion root.
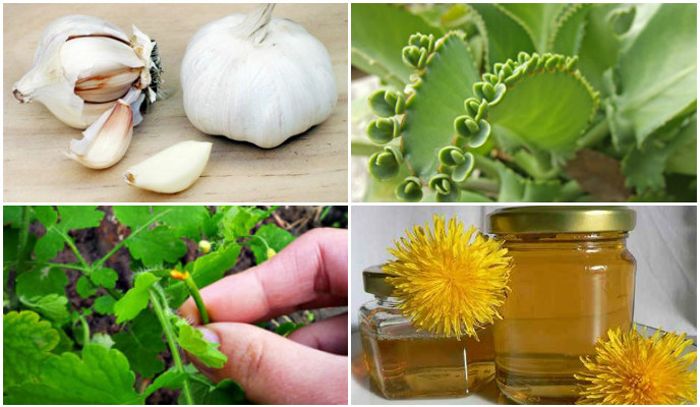

Herbs are poured with hot water and left for a day, after which it is filtered. Take one tablespoon before each meal.
For local exposure:
- Tincture of potato shoots and celandine.
- Tincture of chestnut leaves.
- Lubrication with celandine juice.
- Mask of garlic mixed with cream in a ratio of 1:2.
- Mask of unripe walnuts and kerosene.
- Bandage of Kalanchoe leaves.
- Treatment with acetic acid, lemon juice or hydrogen peroxide.
- Lubrication with essential oils (eucalyptus, tea tree, lemon, etc.) or castor oil.
- Treatment with rowan and wormwood juice.
Hardware technologies
Surgical removal of papilloma is the most effective way to combat this disease, as it allows you to quickly get rid of a cosmetic defect. However, this method does not eliminate the main cause – HPV. Therefore, it is used in combination with drug therapy, which is a very effective combination and reduces the likelihood of relapse many times over.
There are several ways to remove papillomas:
- Cauterization with chemicals – organic and mineral acids are used for these purposes.
- Photodynamic therapy – based on the action of light waves, leading to the death of the virus.
- Freezing (cryolysis) – freezing of education with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the destruction of its cells.
- Electrocoagulation – removal of papilloma with an electric current.
- Laser removal is the most effective, painless and safe way.
- The use of radio wave radiation is not inferior in its effectiveness to the laser technique.
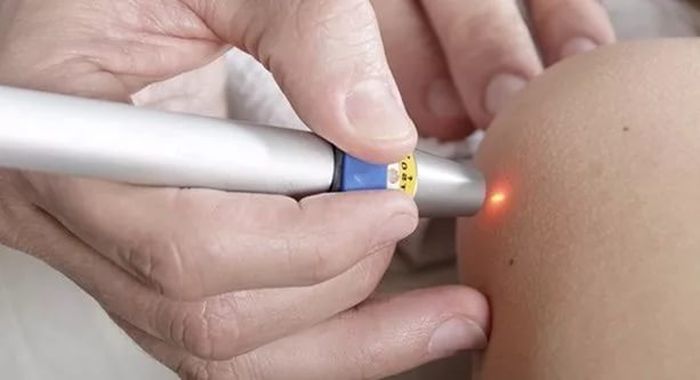
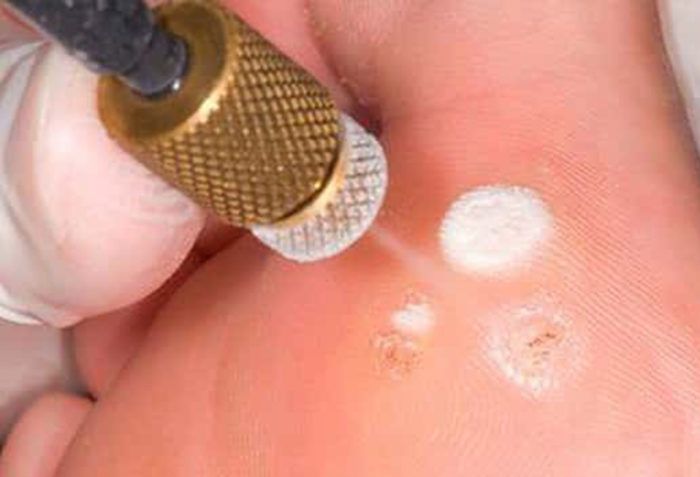
Prevention
Prevention can be divided into two parts: prevention of HPV infection and prevention of papilloma recurrence after treatment.
Vaccines are used to prevent HPV infection, most often it is given to women, however, men can also be given it. Vaccination should be carried out before the onset of sexual activity and only after laboratory confirmation of the absence of HPV in the body.
At the moment, there are two vaccines (Cervarix and Gardasil) that do not contain the genetic material of the virus, so infection from them is impossible. The vaccine contains a shell of the virus that allows the body to produce antibodies. According to doctors, this vaccine will provide immunity for 15 years.
To prevent recurrence of the disease, it is recommended:
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sports.
- Complete and balanced nutrition.
- Avoid stress.
- Self-diagnosis.
- Timely and correct treatment of other diseases.
Conclusion
Papillomas on the head may not manifest themselves in any way, but cause discomfort as a cosmetic defect. However, it is necessary to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Refusal of self-medication will avoid complications. Compliance with all the recommendations of the attending physician will ensure a quick and high-quality recovery.