HPV is a group of viruses from the papillomavirus family. There are 5 genera, 27 species and more than 170 strains of HPV. Each species affects the body in different ways. They are divided into “dangerous” and “non-dangerous”. Papillomavirus in women is a threat because it is endowed with the ability to mutate inside the body.

Содержание:
- 1 What is human papillomavirus
- 2 Ways of transmission of infection
- 3 Who can get infected?
- 4 What types of virus are there?
- 5 What diseases can papilloma cause?
- 6 Why and how dangerous is it?
- 7 What are the symptoms of papilloma in women?
- 8 Diagnosis of papillomavirus
- 9 PCR for human papillomavirus
- 10 How often do you need to take tests?
- 11 What should I do if I have a virus?
- 12 Treatment tactics and prognosis
- 13 Complications and consequences of not treating the disease
- 14 Prevention
What is human papillomavirus
HPV is more dangerous for women than for men. More than 40 types of the virus are capable of selectively affecting the genitals. It is in this case that the infection is extremely dangerous. Human papillomavirus infection in women (for example, type 16 and 18) provokes cervical or breast cancer.
In 99% of cases of such diseases, the cause of oncology in women is the human papillomavirus. The process proceeds slowly (much less often rapidly). An intermediate stage is considered the appearance of genital warts (pointed and flat). The second type is endowed with a high degree of regeneration.
HPV is a chronic infectious disease. Relapses are followed by remissions. HPV significantly affects the immune system, inhibiting it. A woman infected with the virus is at risk. In addition to threatening oncology (at any age), HPV prevents conception and the successful course of pregnancy.
The occurrence and manifestations of pathology directly depend on the type, form of the virus and its concentration in the tissues. A benign form is a form of the virus that is outside the chromosome. Built into the cell’s genome, HPV is defined as malignant.
Ways of transmission of infection
Contact (definitely any) with an infected person or an item of his personal hygiene can lead to infection. The virus is transmitted less frequently in the household way. The most common route of infection is sexual contact.
The means of protection (condom) does not always prevent infection, although it significantly reduces the possibility of infection. There is a high probability of infection (up to 100%) when the partner is a carrier of genital warts. There are several main ways HPV is transmitted:
- Sexual contact.
- Infection by household means: touch, common areas, personal hygiene items, etc.
- From mother to newborn.

Once in the human body, the virus does not immediately manifest itself. A person is a carrier of HPV, but does not suspect it. The first symptoms usually appear three months after infection. Often the incubation period lasts several years. Establishing the exact moment of infection is very difficult. An important factor is the human immune system.
With good immunity of the infection, access is closed. Even if an infection has occurred, it will not manifest itself in any way. Symptoms will only appear if immunity is reduced. HPV ranks second in the number of infected people after genital herpes. Not all variants of transmission of the virus in the household way are established precisely.
Who can get infected?
Everyone is susceptible to HPV infection. Some to a greater extent, others to a lesser extent. There is always a fact of chance, even if all established norms are observed.
- People with low immunity are at risk. When the body fails as a result of prolonged infection, stress, etc. This problem is fertile ground for the virus. Strong immunity is able to resist it.
- Children born to infected parents are also at risk. The problem is not always detected immediately, the virus can “wake up” later, when the child grows up.
- Neglecting the rules of personal hygiene, using uniform items in public places, a person falls into a risk group.
- Young women between the ages of 20 and 24.
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse leads to infection.
- The abuse of alcohol and nicotine opens the way to infection.
- Drug addicts are vulnerable to HPV to a large extent.
What types of virus are there?
Each type has its own name. For example – HPV 1, HPV 2, etc. All viruses are strictly classified into three groups. Classification is carried out on the basis of the ability of the virus to induce neoplastic processes, in other words, to increase the possibility of a tumor.
Three groups of viruses:
- Low risk threshold – HPV 3, 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 61, 72 , 73 .
- The average risk threshold is HPV 30, 35, 45, 52, 53 , 56, 58.
- High risk threshold – HPV 16, 18, 31, 33 , 39 , 50, 59 , 64, 68 , 70.
Approximately 20 types of viruses can cause cancer in women. Dangerous types: HPV 16 (in 50% of cases) and HPV 18 (in 10% of cases).
What diseases can papilloma cause?
Each type of HPV individually affects different systems and causes characteristic diseases. About 70% of women are carriers of papillomavirus. 50% of women have hpv infection. Places of localization: skin, mucous membranes.
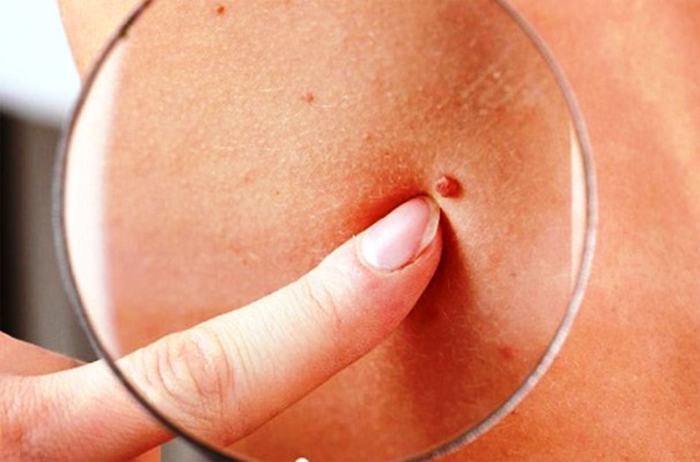
In women, the most dangerous manifestation of infection is warts, which can induce dysplasia. Consequences: cancer of the breast, vagina, cervix, vulva. The papillomavirus is also dangerous for the unborn child: if the mother is a carrier of HPV, the newborn can become infected during childbirth.
Manifestations on the skin are localized in the neck, on the face, in the armpit, on the sole of the foot. The virus appears in the form of papillomas and warts. An extremely rare condition, epidermodysplasia verruciformis, is also caused by HPV. Localization on the mucous membranes leads to epithelial hyperplasia, respiratory papillomatosis, cancer of the lungs, head and neck.
Why and how dangerous is it?
The danger is “unfavorable” viruses. There are about 30 of them. HPV 6 and 11 lead to genital warts, which are not so dangerous and rarely degenerate into a malignant tumor. But HPV 16 and 18 cause cancer in 70% of cases.
Genital warts can cause infertility. They have the ability to change the cervical mucus, which “conducts” the sperm, as a result of which fertilization does not occur.
HPV has a tremendous impact on the immune system, inhibiting it, which leads to frequent infection, etc. The factor is significant for pregnant women: the threat of miscarriage or, due to secondary infection, fetal pathology.
What are the symptoms of papilloma in women?
More often, HPV infection is asymptomatic, and it is detected only during a medical examination, when a Pap smear is done (scraping of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal). They clearly speak about the infection of the neoplasm:
- Warts.
- papillomas.
- Pointed warts.
Severely reduced immunity also suggests infection, as HPV suppresses the immune system.
The presence of neoplasms does not always indicate the presence of a virus that could have been present in the body before, leaving a characteristic mark. If the immune system is strong, it dampens and removes the virus from the body. In this case, it is enough to remove the consequences: papilloma, wart, etc.
Diagnosis of papillomavirus
Primary diagnosis is carried out with a visual examination of the genital organs. To detect hidden pathology, colposcopy is performed (examination with multiple magnification). HPV tests help to identify the virus more accurately. These include PCR analysis, which allows you to accurately (up to 100%) establish the presence of the virus and determine its type.
On examination, a smear is taken for oncocytology from the mucosa. A quantitative HPV test allows you to determine the critical concentration of the virus. The results of the test are taken into account when prescribing treatment. For a thorough histological examination, a biopsy is taken. Pregnant women are an exception; they are not biopsied.

PCR for human papillomavirus
The polymerase chain reaction is the most reliable test. Assign it after histological analysis. The PCR test allows you to detect and examine different forms of viruses. With the help of such diagnostics, the DNA of the virus is detected even when its amount in the blood is extremely small.
With careful observance of the diagnostic technique, the accuracy of the result reaches 100%. Very rarely, amniotic fluid, blood and urine are examined. More often the main material is a smear. The fence is made using a brush-brush, which is carefully inserted into the cervical canal. To obtain an accurate result, preliminary preparation is necessary:
- It is unacceptable to have sexual intercourse two days before the analysis.
- The use of antibacterial soap for intimate hygiene and douching is excluded.
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to take a shower with warm water, without detergents.
Taking antibiotics affects the results of the analysis. When using them, you must warn your doctor. The results are obtained in a day or two or on the day of the analysis. The actual study of the material lasts 4-5 hours.
PCR makes it possible to judge the presence of the virus, its concentration and quantity in tissues. To fix the results, there are specific notations:
- Lg < 3 – the presence of HPV with an extremely low concentration.
- Lg 3–5 is the average amount of virus.
- Lg > 5 – a high degree of virus damage.
With a positive result, a second diagnosis is prescribed to obtain an accurate picture and correct errors. In the absence of a virus, these designations are unacceptable.
How often do you need to take tests?
HPV analysis is recommended to take regularly after 20 years. When planning a pregnancy, such an examination is necessary. An HPV test is performed for suspected infertility, with spontaneous abortion, since papillomavirus is often the cause of such conditions.
The analysis is carried out if infection is suspected to establish the presence and type of virus. Further, they act according to indications: prescribe treatment or say that it is not necessary due to harmlessness. Find out also what HPV is, deciphering the results of the analysis

What should I do if I have a virus?
If neoplasms appear on the skin and other symptoms of HPV, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination that will determine the degree of infection and the percentage of danger. Next – complete the treatment course.
Treatment tactics and prognosis
Tactics of treatment is appointed individually. Is it possible to achieve a complete cure for HPV? There is no single answer. Doctors say that it is impossible to achieve a complete cure and the treatment is not aimed at eliminating the presence of HPV in the body, but at eliminating its manifestation. However, spontaneous healing is often observed (up to 90% of cases).
Treatment, main methods:
- Destructive. Removal of warts. Several methods are used: physical (using laser therapy, electrosurgical excision, cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation), chemical (using ferezol, trichloroacetic acid, solcoderm) and surgical (surgical removal).
- Immunological. An effective method that is used at all stages of treatment. The method involves taking immunomodulators (drugs from a series of interferons, natural immunostimulating agents, Allokin-alpha , which stimulates the production of interferon in the body). In addition to taking medications, they use additional methods that strengthen the immune system: switching to a healthy diet, sports, etc.
- With the help of antiviral drugs. Taking specific antiviral drugs that can have a depressing effect on HPV: injections, dragees, tablets, topical solutions, sprays, etc.
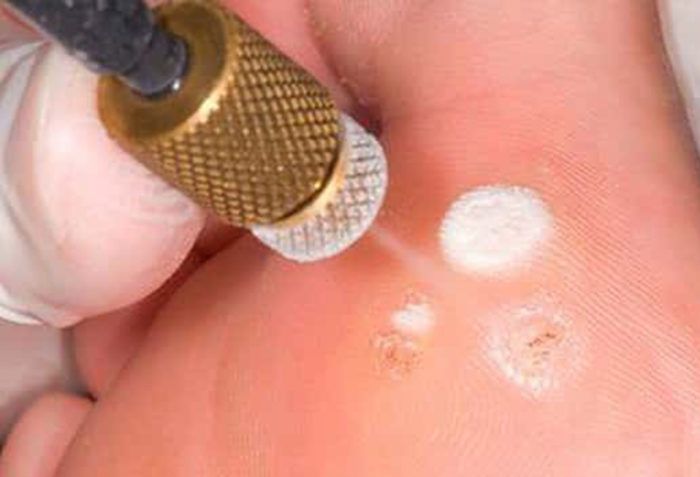
The prognosis depends directly on the type of virus, its localization, concentration, and the state of the immune system. Good immunity is able to reduce the activity of the virus to “no”. When HPV is activated, a combination of all three treatments is appropriate.
Complications and consequences of not treating the disease
Don’t count on “maybe”. HPV can disappear spontaneously, but it can also lead to serious illness. Warts, papillomas, condylomas are external manifestations that can cause serious consequences. No one can guarantee that the virus does not mutate in your body, which can result in infertility, abortion, dysplasia, a malignant tumor, etc.
Damage to the neoplasm on the skin often causes profuse bleeding and infection, which also does not remain without consequences. Timely examination and treatment stop the process. Possibility of full recovery is probable.
Prevention
Preventing HPV infection is a reality. Vaccination is the only way to prevent HPV. In Russia, 2 vaccines against infection are registered: Cervarix and Gardasil.
They are used to prevent cervical cancer. The results of clinical trials prove their safety and effectiveness. In many countries, such vaccination has become mandatory for all girls and girls aged 11 to 17 years.
But the usual means of prevention are obvious and simple:
- Use protective equipment during sexual contact.
- Comprehensively support the precise functioning of the immune system: in addition to playing sports, hardening the body and healthy eating, it is advisable to include dietary supplements that help strengthen immunity in the diet.
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene (in any situation).
- Regular medical examinations, accurate diagnosis and treatment prevent irreversible processes.
Take care of your health and the health of your children!