The most dangerous types of HPV in women often live unnoticed in the body for years, waiting for the moment to come. This problem is very delicate, but cannot but interest each of us: the number of carriers is rapidly moving towards 100% of the world’s population.
Although almost all of us have papillomavirus, it can be insidious and lead to serious diseases. The most dangerous HPV disease is often hidden from the eyes of its owner.

Содержание:
Features of the development of oncogenic viruses
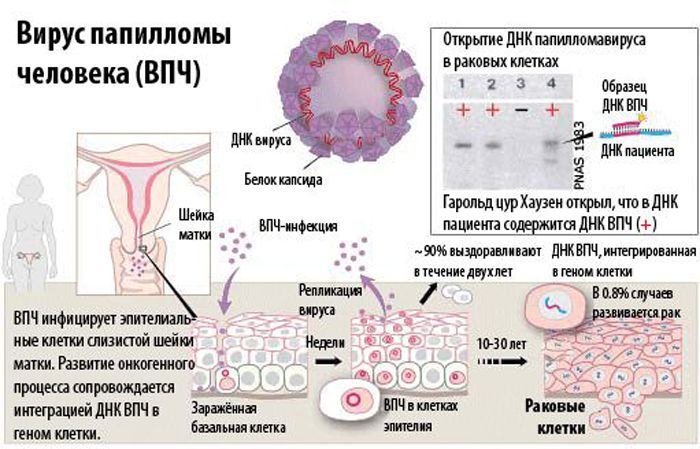
By the time the virus DNA reaches the cell nucleus of a healthy cell, a woman will notice little to no symptoms that point to HPV. You can reverse the process of its implementation, imagining how a healthy cell is “reprogrammed” as if. Simply put, the genetic basis of DNA changes during this process. The cell becomes the enemy, and reproduction continues. What types of oncogenic HPV do women have?
Due to the modification of the cell, an active uncontrolled growth already visible from the outside begins, although usually rather slowly. The disease is manifested by outgrowths on the body or organs, which have many forms, but usually do not differ in color from the surrounding tissues or differ not too much.
Each type of HPV virus has its own strain. Under the influence of some of them, cell formations multiply too rapidly. So much so that they do not have time to mature enough, which is why a group of undifferentiated, that is, atypical for this disease, cells appears. It is they who begin the active secretion of oncogenic protein, which becomes the start for the development of malignant neoplasms.
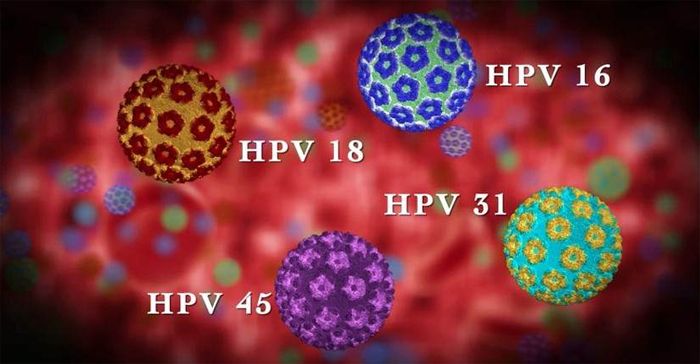
The most dangerous types of HPV for women
Certain HPV type numbers pose the greatest risk to women. Now we are talking about types of virus with high oncogenicity. All of them form the “A-9” group (the following types belong to them: 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 51, 52, 56, 58 , 59 ). The most difficult thing in diagnosis is the incubation period. It can stretch for 20 years, or it can appear in the first year.
Malignant lesions of the cervix are dangerous with the highest risk of mortality. The increase in the number of cases is growing, and the age category of women with cancer is rapidly decreasing. The risk of infection reaches its peak during the onset of a girl’s sexual life. The following are at particular risk:
- disorderly intimate life;
- sexual intercourse without contraception;
- abortions, other medical manipulations;
- wearing intimate piercings, tattoos, non-sterile devices for hair removal, etc.
65% of infections with the most dangerous type of HPV end up with cancer for a woman. Each strain, to some extent, carries the risk of turning into cancer, however, papillomas on the mucous membranes of the female genital organs – this is the reason to actually go running for typing, oncology tests.
The two most dangerous strains
16 type. The course of development does not cause inconvenience. After that, outgrowths of a flat shape appear.
18 type. Similarly, like type 16, it has a high risk of maturation in the form of oncology, but for a long time it goes completely unnoticed.
HPV 31 , 33, 39, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 types are also quite undesirable for the female body, and the course of the virus of all these types is so uniform that it is almost impossible to distinguish them without laboratory tests. Types 31 and 33 are detected more often, both of them are considered precancerous, but unlike HPV types 16-18 , the virus is located and multiplies closer to the surface of the skin and mucous membranes.
What is the danger of papillomavirus?
Most strains of papillomavirus do not pose any danger and darken the mood of a woman only by their appearance during manifestation. That is, their main danger is to spoil the lady’s nerves in the way that for most women, problems with appearance are akin to the apocalypse.
The strains described above are rare, but highly undesirable for anyone. They are highly susceptible to mutations. It is extremely difficult to track changes in the cervix in time due to the fact that only a gynecologist can look into the “root of all troubles”.
Diagnosis of 16 strains of HPV
Diagnosing a virus and its oncological modifications, as a rule, does not cause any difficulty either for a woman or for a doctor. More recently, a couple of decades ago, analyzes were not available either in terms of geographical possibilities or financial ones. Today, the presence of this virus in the body can be detected by several modern analyzes and tests:
- PCR test for the detection of sexual infection, which allows, and to identify HPV, its genotype .
- Histology of the tissue of the cervix (a biopsy is taken in the process of mandatory research – colposcopy).
- The PAP test is used to identify cancerous as well as precancerous cells in the genital tract and cervix.
- Analysis of the scraping of the cells of the vagina, as well as the uterine pharynx, which is carried out according to the results of a smear taken by a kind of “hybrid capture” method, where oncogenic HPV (types 16 and 18) is detected.
These and many other studies, tests allow an oncologist or immunologist (sometimes a dermatologist and gynecologist is involved in the study) to draw up a competent, correct treatment plan.
Treatment of HPV depending on the type of virus, drugs
An essential part of the treatment of the HPV virus and its manifestations is based, first of all, on the direct drug effect on the virus. At the same time, external manifestations are also eliminated. Papillomas, warts, condylomas are subject to mandatory removal.
To date, there is no way to influence the oncogenic manifestations of HPV in advance, so the growth is carefully removed. It is unacceptable to remove the neoplasm with insufficient quality, otherwise a whole “family” of new ones will appear in place of the removed growth.
If an oncogenic strain of HPV is detected, treatment is carried out only in a complex manner and includes:
- external formations are subject to removal and their proliferation;
- increased immunity, both general and drug;
- the use of antiviral drugs to suppress HPV activity;
- prescribe vitamins, possibly sedative herbal tinctures.
Usually, the treatment has a positive effect on the health of the patient, but the negative factors do not go away and this circumstance can revive them again. That is why the matter should not be limited to one removal. And maintenance therapy is very long and requires strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
Is it possible to fully recover from HPV?
It is impossible to get rid of HPV completely. The situation is especially difficult with the most dangerous HPV types, which we have already discussed above. These strains are difficult to treat and a woman has to be rechecked all her life.
The remaining genotypes are not dangerous and disappear in healthy, young women within two to three years (they go back into a passive state) and stop bothering their carrier.
If the virus has a degree of oncogenicity, without treatment, most likely it, under the influence of sex hormones, is transformed into oncology. This outcome can be excluded without neglecting annual preventive examinations, which is required by modern gynecology.
HPV in pregnant women
Few people know that planning a pregnancy is necessary before conception. Women and men undergo a lot of tests, external examinations, specialists. They take care of their health, because the child must be conceived by healthy parents, and its bearing will become a serious stress for the body. Every part of the body and organism of the child is created at the expense of maternal resources.
Pregnancy is impossible without the strongest hormonal changes. Against this background, the human papillomavirus usually activates and growths appear on the body of a pregnant woman. Many of them rush to their gynecologist in horror, wondering how she could get the disease in such an interesting position.
However, we recall that the human papillomavirus can “sleep” for years. And the hormonal failure created only the necessary impetus for his awakening. The presence of dangerous types of HPV is usually detected just at the planning stage or in the early stages.
Finding out the variety will give the gynecologist a reason to prohibit pregnancy and terminate the one that has begun if the papillomas have turned into cancer and threaten the woman’s life. If the type number is not dangerous, standard treatment is carried out and the woman can become pregnant .
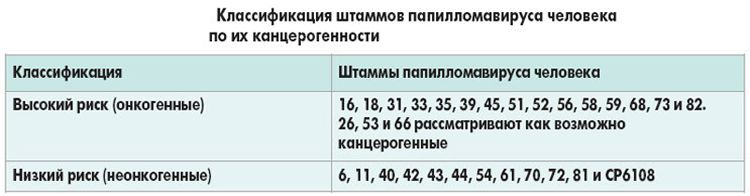
Oncogenic classification
We have already raised the topic of oncogenicity of all types of hpw (as HPV is designated in the analyzes). There are 4 large subtypes, which indicate the extent to which this or that growth is transformed into a malignant neoplasm.
- HPW of the highest oncogenic character (number: 16,18,31,33,39,45,50,56,59,61-62,64, 66,68,70,73 types), where the most dangerous ones are underlined.
- HPW of an average oncogenic nature (number: 26,30,35,52, 53,58,65 ).
- HPW infrequently forming any mutations (number: 6,11,13,32,34,40,41,42,43, 44,51,72 ).
- HPW rarely or never mutates into cancer (others).
It is important to understand that any external changes in papilloma may signal the onset of malignant changes. Blackening of the growth, inflammation of the skin around or the neoplasm itself should be especially alert.
A normal, benign papilloma does not hurt unless it is irritated by clothing or jewelry. Therefore, the appearance of pain at the site of papilloma formation is the worst signal, as well as its blackening.
Prevention of papillomatosis
Prevention can be of two types: infection and exacerbation of the virus. In the first case, it is quite difficult to protect yourself, the virus can be transmitted at the household level. It is important not to wear someone else’s underwear, clothes, not to use towels. During sex, use condoms, and then you need to thoroughly wash yourself and treat the genitals with Miramistin or
Chlorhexidine as directed. Infection occurs through microscopic cracks in the skin, and as a result of unprotected intercourse, infection is 100%.
To avoid rashes on the body, it is important to monitor lifestyle, health, undergo preventive examinations every year, and take tests. Bad habits, nervous strain are excluded. Any disease, even if mild, can reduce the body’s defenses to the level required to activate HPV.




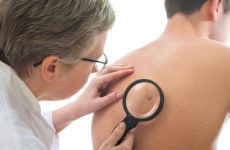

Самое неприятное, что рак шейки матки у женщин долгое время может никак себя не проявлять. Поэтому всем девушкам и женщинам следует регулярно проверяться у гинеколога. В случае эрозии, дисплазии, впч нужно обязательно своевременно обнаружить и начать лечение ВПЧ, чтобы это патологическое состояние ш/м не перешло в рак. Вирус проявляет себя в крайнем случае кондиломами и папилломами.
Пока лечилась изучила много информации о лечении ВПЧ. Прочла, что Аллокин-альфа в стандарты входит “Клинические рекомендации по лечению доброкачественных и предраковых заболеваний шейки матки с позиции профилактики рака” 2017 год. Препарат эффективный. После курса лечения произошла элиминация вируса из организма.