Almost 90% of the world’s population is familiar with papillomas and condylomas – small growths on the surface of human skin.
They can appear in different places, especially in those where there is “moisture” and heat: armpits, under the breasts , on the neck. No exception – the genitals of both men and women.

It is especially necessary to be vigilant for the fairer sex: small and seemingly harmless formations located in the intimate area can be in serious danger, degenerating over time into a malignant tumor.
Содержание:
- 1 What is HPV?
- 2 Reasons for the appearance of neoplasms
- 3 Predisposing factors
- 4 How can you get infected?
- 5 Varieties of papillomaviruses and features of the negative impact on the body
- 6 Localization
- 7 Symptoms and signs
- 8 Which doctor should be contacted?
- 9 How is the disease diagnosed?
- 10 Treatment regimens
- 11 Prevention
What is HPV?
Human papillomavirus is a fairly common disease of a chronic nature, caused by a family of viruses that differ in adherence to “settlement” in the epithelial cells of the body.
At present, about 100 strains of HPV are known to medicine, 40 of which can cause the formation of warts and papillomas on the genitals and in the anus of a woman.
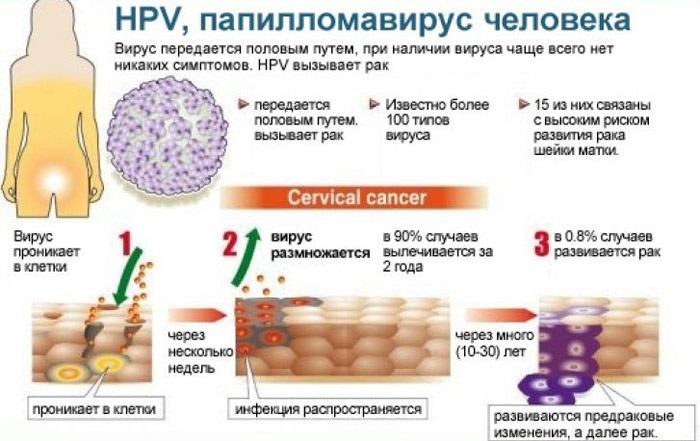
The main danger of this kind of disease is that some types of the virus can cause the growth of neoplasms of a high carcinogenic risk, which is often the cause of the development of oncological diseases of the genital organs.
Reasons for the appearance of neoplasms
The main reason for the unimpeded penetration and development of HPV in a woman’s body is a dysfunction of the immune system.
The fact is that an attempt to invade any virus into a healthy human body in 90% of cases fails. But in the presence of some predisposing factors, the activity of the immune system decreases, as a result of which the virus quietly enters the woman’s body and develops there.
Predisposing factors
The “risk group” includes women who:
- Started having sex early.
- They have several sexual partners, often change them.
- They have a history of other sexually transmitted diseases, both in the acute and chronic periods: chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis.
- Neglect regular hygiene of the genitals.
- For a long time take oral contraceptives or other hormonal drugs.
- Do not use a condom during intercourse.
- Are pregnant.
- They often experience stressful situations.
- They often freeze.
- They smoke, abuse alcohol.
- They suffered severe colds.
- They have a genetic predisposition.

How can you get infected?
HPV can enter the body in a domestic, intimate way and be transmitted from mother to child:
- If the basic rules of personal hygiene are not observed: as a result, the use of things of a person – a carrier of HPV (underwear, towels), when placed on benches in the nude or in a swimsuit in a sauna, bath, pool, in public restrooms.
- During childbirth, when the baby passes through the birth canal of a mother affected by HPV.
- When having sex (including oral, anal) without using barrier contraception.
- When the genitals come into contact without penetration.
- When kissing.

Varieties of papillomaviruses and features of the negative impact on the body
All HPV strains can be conditionally divided into 3 groups: non-oncogenic (do not cause degeneration into a malignant tumor), low-oncogenic (the risk of degeneration is minimal) and high-oncogenic (the risk of developing cancer is very high). Another name for the latter group of strains is HPV-HCR (human papillomavirus of high carcinogenic risk).
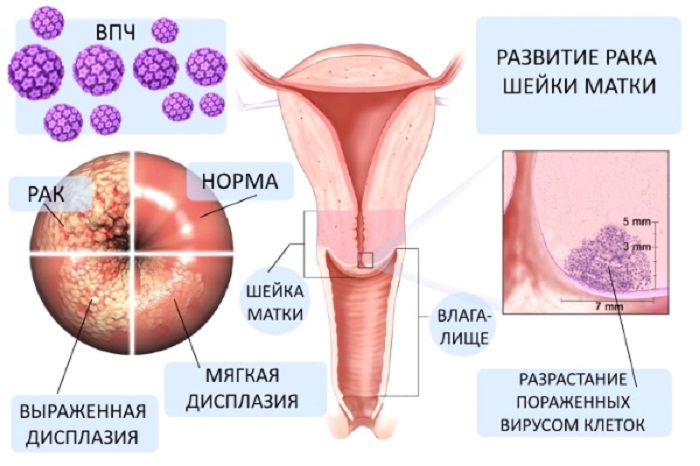
Localization
The most common places in genetics where papilloma can form.
On the cervix
On the cervix, papillomas most often develop, which can lead to dysplasia and degeneration into a malignant formation. As a rule, such phenomena can be caused by HPV types 16 and 18 .
On the labia
The labia is an ideal environment for the development of condylomas – formations that vaguely resemble sacs or papillae in appearance. The characteristic color is flesh, pink or bright red.
As a rule, either one formation or a whole scattering is diagnosed. Such formations cause a constant feeling of discomfort and can also provoke the development of an oncological disease, see also which oncogenic type HPV in women .
Symptoms and signs
The main symptoms of the disease include:
- Itching and burning in the genital area.
- Feeling of discomfort and pain in the pelvic organs.
- Pain during intercourse or immediately after it.
- Bloody discharge after sex.
- Unusual discharge (dark color, bad smell).
- General depression.
The main sign of the development of the disease is the appearance of pathological neoplasms on the skin of the genital organs and in the region of the anus: genital and flat condylomas, papillomas.
Which doctor should be contacted?
Every woman is recommended to visit a gynecologist at least once every six months for a preventive examination. In any case, if you find any growths on the genitals or if you have one or more of the symptoms listed above, a direct road to the gynecological office.
A female doctor diagnoses the disease, prescribes treatment or redirects to a surgeon, and in case of neoplasm degeneration, to an oncologist.

How is the disease diagnosed?
If HPV is suspected, a woman must undergo a comprehensive examination:
- Visual examination by a gynecologist allows you to diagnose the presence of pathogenic neoplasms on the outside of the penis and inside (using a gynecological speculum).
- Colposcopy is a method based on examining sections of the epithelium at a thirtyfold magnification. Sometimes the diagnostic procedure is accompanied by an vinegar test, as a result of which the dysplastic areas turn white.
- cytological analysis . During the examination, a scraping is taken from the cervical canal or cervix, which will allow to detect a possible oncological disease at an early stage.
- PCR – screening analysis , detecting the papillomavirus by the structure of DNA in the collected biomaterial from the genitals.
- Immunological study , the essence of which is to analyze the structure of DNA for the presence of HPV.
Treatment regimens
It is necessary to approach the treatment of HPV in a complex manner. There are several types of therapy:
Local therapy
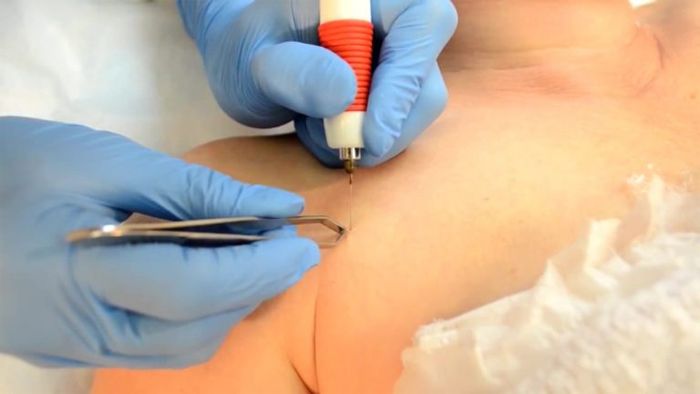
The essence of this method is to remove formations using liquid nitrogen, chemicals, a radio knife or a laser, which is used only after negative test results for the presence of oncogenic cells.
- The radio wave knife affects only the cells of the formation, while not affecting healthy tissues. As a result of its application, wounds practically do not bleed and heal much faster. The use of a radioknife does not cause burns.
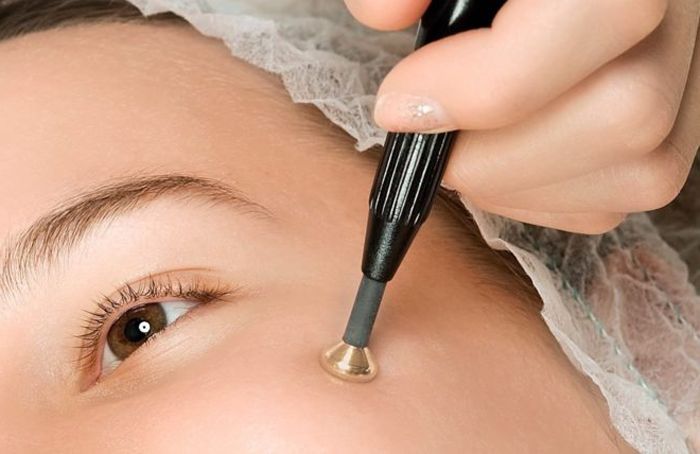

- Electrocoagulation – removal of growths using a device with a loop heated by current. This method blocks the further spread of papilloma formation, but is fraught with possible darkening of the skin at the site of removal or scarring.
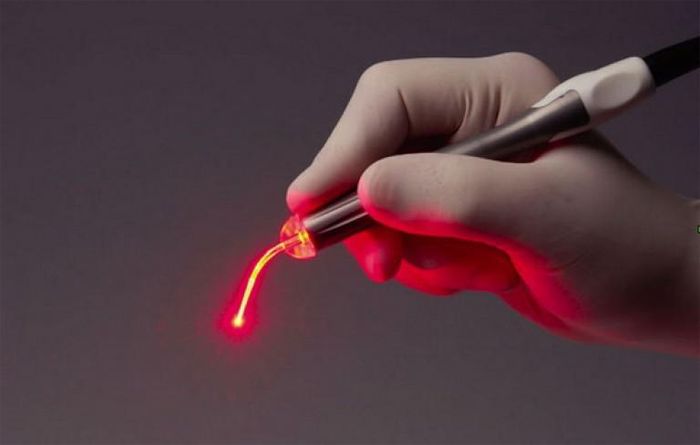
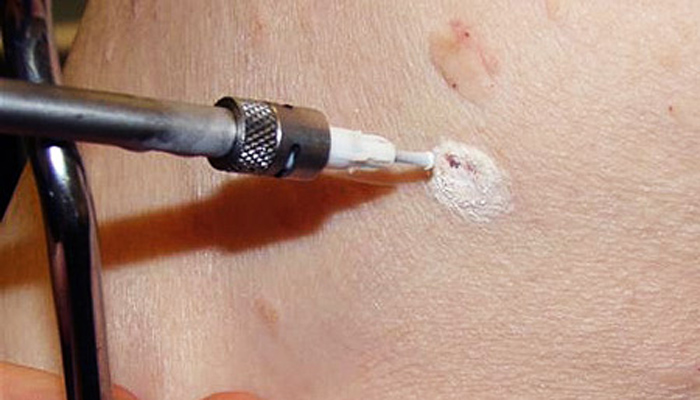
- Laser cauterization allows you to accurately and effectively get rid of growths, minimizing the possible risk of re-formation of papilloma.

- Cryodestruction (treatment with liquid nitrogen) provides nitrogen exposure directly to the area with the formation, due to which the cells of warts and papillomas die off.
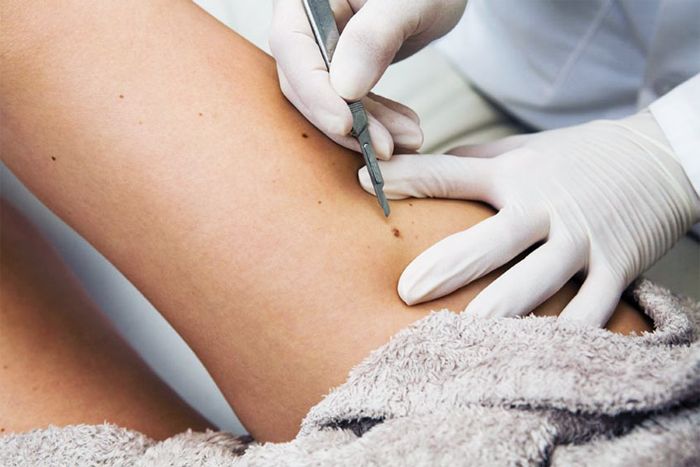
Surgical removal
This method can be considered the most traumatic, since its essence is to excise the affected areas of the skin with a medical scalpel.
It is used only if there is a suspicion of oncological degeneration of formations or severe dysplasia.
Therapy with folk remedies
Only with the permission of the doctor, you can try to remove the formations that have appeared with the help of traditional medicine:
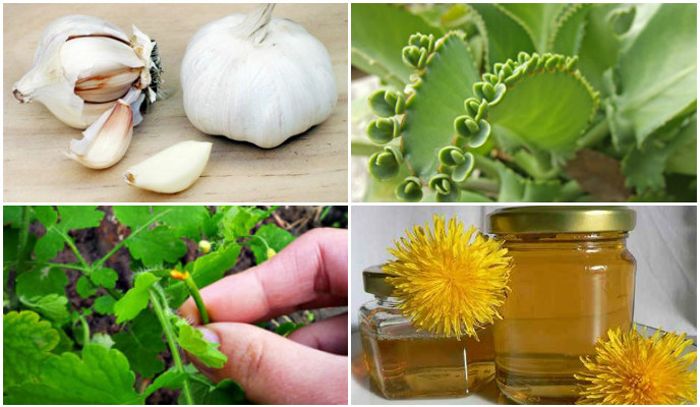
- Celandine can help due to the presence of some toxic substances in its composition. To prepare a remedy, you need to find a fresh stem of the plant, squeeze the juice out of it. They should lubricate the growths and seal them with a plaster soaked also in celandine juice. Course – 3 times a day for 3 days.
- Castor oil contains an acid in its composition that can “eat” growths. To do this, it is necessary to lubricate the affected areas with the substance in the morning and evening for a month.
- A fresh Kalanchoe leaf is cut off and applied to the area with formations, it is imperative to fix it with a bandage. The course is until full recovery.
- 1 tbsp chopped garlic is mixed with 1-2 tablespoons of any cream. The bandage should be treated with a mass, and then attached to the affected area. The product should be used once a day for 3 hours, after which it is necessary to rinse the treated area with water.
- Dandelion : it is necessary to lubricate the growths with its juice several times a day until they disappear completely.

Prevention
Preventing HPV infection is difficult, but possible. To do this, from an early age, the girl should be instilled with the need to comply with certain rules of behavior. Following the same rules will also help women, significantly reducing the risk of infection and the development of HPV in the body.
- A healthy lifestyle, rational nutrition, adherence to the daily routine, avoiding cigarettes and alcohol.
- Prevention of early sexual activity, responsible attitude to the choice of a partner, the use of barrier methods of contraception.
- Instilling elementary hygiene skills: regular hygiene of the genitals, the inadmissibility of using other people’s things, caution in public places.
- Regular examination by a gynecologist (2 times a year).
- Timely treatment of acute and chronic genital infections.
- Strengthening immunity: playing sports, hardening, regular use of vitamin and mineral complexes.
HPV in gynecology is not a sentence: the presence of a “dangerous” strain of the virus in the body does not mean that in the future a woman will become 100% ill with genital cancer.
You can prevent the terrible consequences of this virus by regularly visiting a gynecologist and taking your health responsibly.