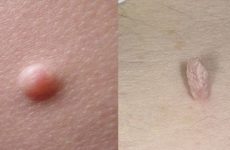
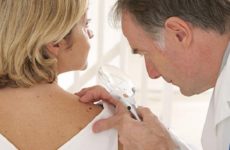
There are several types of tests to detect the HPV virus. Some of them show only the presence or absence of the virus in the body, while others also reveal the amount of each type of HPV. The choice of one or another diagnostic method is determined by a gynecologist.
Содержание:
What is papillomavirus screening?
HPV screening is a complex of medical tests, studies that are aimed at detecting the presence of the HPV virus in the body. Why is it necessary to take these tests? Some types of the virus have a high oncogenic risk, that is, they are associated with the appearance of cancer, most often of the cervix.
Cytological Pap test
The Papanicolaou smear is also called after the name of the Greek scientist. This test allows you to find cancer cells in the epithelium of the vagina and cervix.
Who needs to take this test?
According to medical standards, all women aged 21 years or younger should be tested for the first time if they have an early onset of sexual activity. A smear is done every year for 3 years in a row.
If during this period the test is negative every time, that is, no cancer cells are found, then in the future it is carried out every 3 years until the age of 65 years.
Who needs to take a cytological Pap test?
- Women aged 30 years and older should definitely take this smear at least once.
- Those who have had the HPV virus in a smear at least once.
- Those who have found areas of altered epithelium on the cervix.
HPV WRC advanced analysis
This analysis allows you to determine the presence of DNA of the HCV virus in the epithelium of the cells of the reproductive system. As a rule, the presence of the 15 most oncogenic types of HPV is detected.
DNA PCR analysis
This research method identifies certain types of HPV. Assign this analysis, as a rule, with cytological changes in the Pap smear.
Its advantage lies in the fact that it allows you to detect the virus immediately after infection, when it is in a “sleeping” state, that is, long before the first symptoms of the disease appear.
However, frequent use of this analysis is not justified. The body is able to heal itself from 80 percent of all viral diseases within two years from the moment of infection. Therefore, DNA testing is unnecessary.

PCR analysis is either qualitative or quantitative.
- A qualitative method evaluates the presence or absence of a virus gene. In the form of the study, it is usually written that the virus was detected or not detected. This method is suitable for the primary diagnosis of the HPV virus in the body.
- If the virus is detected, a quantitative assessment is carried out, that is, it is determined which specific types of HPV are found, and in what quantity. Knowing the viral load in a certain amount is important for further treatment tactics.
How can a woman prepare for analysis?
Preparation for testing is simple and does not cause any particular difficulties.
- 48 hours before taking a smear, it is necessary to exclude: sexual intercourse; use of birth control creams, suppositories, or other local contraceptives; use of tampons; vaginal douching, bathing.
- It is better to take smears no earlier than a month after a course of oral antibiotics, and also 2 weeks after using local antibacterial drugs (for example, vaginal suppositories).
- On the day of the test, it is better not to use intimate hygiene products, it will be enough to wash with plain water.
- A smear is also not taken during menstruation or in the presence of inflammation, as well as the first two to three days after the end of menstruation.
- A distorted result can be obtained if you take a smear immediately after a vaginal examination, colposcopy, and ultrasound.
Technology of the procedure
- Material for a smear is taken with a special brush.
- With its help, the doctor gently pinches off pieces of the epithelium from different areas (vagina, cervix).
- Then the gynecologist imprints the material on the surface of the glasses. Thus, a smear is obtained.
- The prepared material is dried in air and sealed, sent to the laboratory for analysis. There, the smear is examined under a microscope for abnormal cells.
Deciphering the results
The interpretation of the cytological Pap test includes 5 classes.
- Class 1 corresponds to a negative result, that is, no pathology was found;
- Grade 2 indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the vagina and cervix;
- Grade 3 speaks of the detection of single abnormal cells as a result of the study;
- an indication of class 4 corresponds to the presence of several malignant cells;
- and, finally, in the presence of class 5, we can talk about a large number of cancer cells in the epithelium.
Interpretation of the results of quantitative PCR analysis:
- HPV DNA was not detected – there is no risk of developing pathology;
- insignificant concentration of the virus (less than 3 lg) – minimal risk of developing oncology;
- a significant concentration of the virus (from 3 to 5 lg) – the presence of a chronic infection with a high risk of oncology;
- a high concentration of the virus (more than 5 lg) – often accompanies already diagnosed cervical cancer.
Extended screening will provide a quantitative result for each type of virus detected. Find out also what HPV is, deciphering the results of the analysis
Where can you do it?
All tests for HPV can be taken in a special laboratory or in a large medical center with its own laboratory. The sampling is carried out during the appointment of a gynecologist.
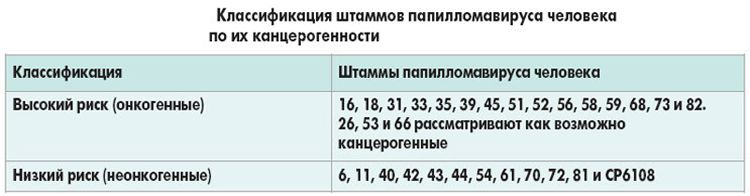
What to do if HPV is found to have a high carcinogenic (oncogenic) risk?
HPV of high oncogenic risk includes 14 types (16, 18, 31 , 33 , 56 , 68 and others). When they are detected, the test results will indicate in what concentration each identified type is located.
These types of virus are dangerous because in some cases they can lead to cancer of the cervix and other organs. However, you should not panic, because this does not always happen.
Usually, when HPV is detected, the doctor directs the patient to a colposcopy (examination of the cervix with a special optical device). During a colposcopy, the doctor takes a biopsy under anesthesia. The taken piece of tissue is sent for cytological examination (study of affected cells).
In the absence of pathological changes on the biopsy, a repeat Pap test is required after a year. No other treatment is given. See also material on the topic: HPV type 16, quantitative analysis, decoding .
Thus, when HPV of high carcinogenic risk is detected, it is necessary, first of all, to pass a PAP test and do a colposcopy. Based on the results of these studies, the doctor will determine further treatment.
So, when should you do an HPV screening? It makes sense to take tests for HPV only after 30 years (under the age of 25 there is no point in taking them, since the virus can leave the body on its own). In addition, it is advisable to diagnose only highly oncogenic types that can lead to cancer. It makes no sense to detect HPV of low carcinogenic risk.