Viral infections manifest themselves in different ways: this is fever, rash, and stool disorders. The most famous diseases that viruses cause are influenza, tonsillitis, hepatitis, encephalitis, and traditionally “childhood” diseases (measles, rubella, mumps).
Oddly enough, warts, or papillomas, also belong to viral infections, namely: to a group of viruses that affect the skin and mucous membranes.

Содержание:
- 1 What is this code: definition and general information
- 2 Can you get a viral plantar wart?
- 3 HPV types according to this code and their features
- 4 Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
- 5 What does a spike look like?
- 6 Places of localization
- 7 Symptoms and signs of infection
- 8 Diagnosis of the disease: what tests are needed?
- 9 Treatment Method
- 10 Preventive therapy
What is this code: definition and general information
ICD-10 is the International Classification of Diseases, without which it is difficult to imagine the activities of medical workers. In fact, this is a list of diseases with a description of survival and mortality statistics, symptoms and treatment. Thanks to this document, the doctor can easily access the necessary data.
Since everything is changing in the world, some diseases disappear, others are discovered, the ICD periodically needs to be corrected. The document is reviewed every ten years under the leadership of the World Health Organization.
The current classification is ICD-10, and the number 10 means that it has been revised for the tenth time. Scientists are also engaged in modifying and simplifying an existing document, and if everything goes according to plan, ICD-11 will enter into force in 2022. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material: papilloma ICD 10 .
The wart itself cannot be transmitted. It is impossible for a sick person to touch a healthy one with a wart, and he also has a neoplasm in this place.
The formation of a growth is associated with the activity of the human papillomavirus (HPV). It is present in the body of almost 80% of the adult population and can be transmitted through sexual and domestic contact, as well as from mother to child.

But even if the virus is transmitted from the carrier to a healthy person, it cannot be argued that the latter will definitely have a wart. In 90% of people, the immune system copes with the pathogen in 6-24 months.
The remaining 10% can live with the virus all their lives without even knowing about its presence. However, it is possible that papilloma will appear as a result of a strong decrease in immunity or an unhealthy lifestyle.
HPV types according to this code and their features
In the ICD-10, the manifestations of the virus are in different sections. For example, viral warts are hidden under code B07, namely: their variety is a simple wart.
Section A63.0 describes anogenital (venereal) warts . Code D41.4 belongs to bladder papilloma, D26.0 to cervical papilloma, D14.1 to laryngeal papilloma.
Further, the classification is based on the location of the growth and includes codes D23.0 to D23.9 (growths of the lips, eyelids, ears and ear canals, face, head and neck, etc.).
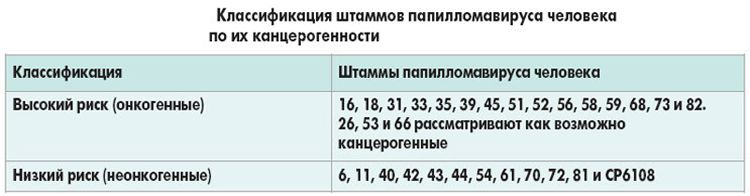
Neoplasms with a high risk of degeneration into cancer are combined into group B97.7.
As for the features, this is, first of all, the degree of oncogenicity. There are strains of viruses that are completely safe, have a low or medium probability of degenerating into cancer, or very dangerous strains.
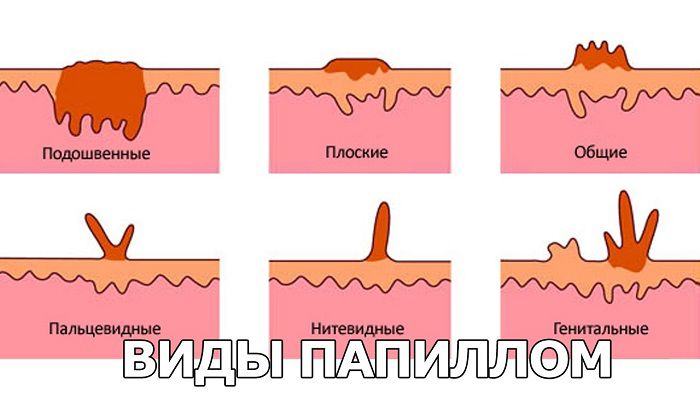
According to their appearance and location, they are distinguished:
- Plantar papillomas , which appear only on the soles and palms. They have an uneven porous surface, do not rise much above the skin, but go deep into the deep layers of the epidermis. Plantar papillomas have a clear border that is pink or pale red in color, a rough surface with a distinct skin pattern.
- Ordinary papillomas (warts) are the most common. They often affect the fingers, palms, soles, or feet and feel and look like a small, flesh-colored papilla.
- Filiform papillomas form in places where the skin is particularly thin. They have an oblong shape and a length of up to 5 mm, but if left untreated, they begin to grow. The upper part of the papilloma may be yellow or pink.
- Flat papillomas are generally very difficult to detect, since they are practically not palpable. This is a small speck, similar to a mosquito bite, but if you look closely, you can see the porous structure. Their shade is often yellow, and the size does not exceed a few millimeters.
- Genital warts are formed only on the mucous membranes, mainly in the genital area and anus. Often they have a color close to the flesh, are prone to rapid growth and multiple distribution.
- Lewandowski-Lutz papillomas most often occur on the feet or palms, have jagged edges, a brown or red tint. Rare, but very dangerous.
- Juvenile papillomas are diagnosed mainly in children born from an infected mother. Their place of localization is the region of the larynx. They are soft, light pink, and can cause breathing, speech, and swallowing problems.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
The virus enters the human body mainly during unprotected sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal), in a public place (bath, sauna, swimming pool, beautician’s office) through microcracks in the skin or through the mother to the child.
The causative agent exists in epithelial cells, and the immune system fights it. If the protective forces of a person are strong, self-healing occurs. In other cases, papillomas appear, which can provoke the following factors:
- weakened immunity against the background of viral and infectious diseases;
- violation or lack of personal hygiene;
- promiscuity;
- malnutrition;
- bad habits (alcohol, drugs, smoking);
- susceptibility to stress;
- hormonal disruptions.
The algorithm for the development of the disease is as follows: first, the virus enters the body of a healthy person, and immunity is mobilized. He fights against it for a long time, after which he either completely “eliminates” the pest, or sharply weakens under the influence of any factors (surgery, severe hypothermia, pregnancy).
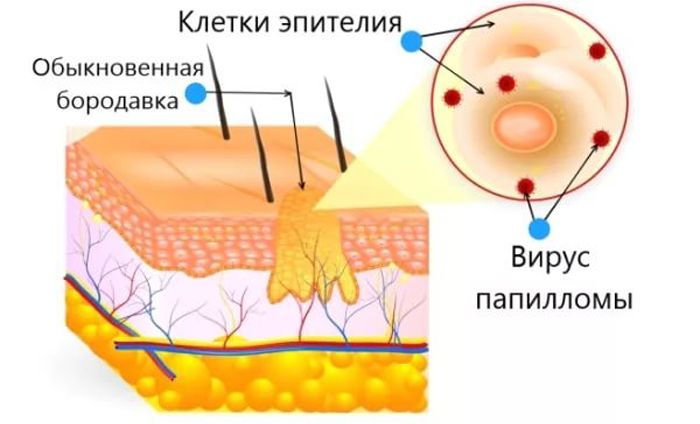
While the immune system does not work, the virus begins to actively infect the DNA of epithelial cells, turning them into atypical ones. The altered cells grow and divide, as a result of which an accumulation of those same cells – papillomas, warts or condylomas – forms above the skin or mucous membrane.
What does a spike look like?
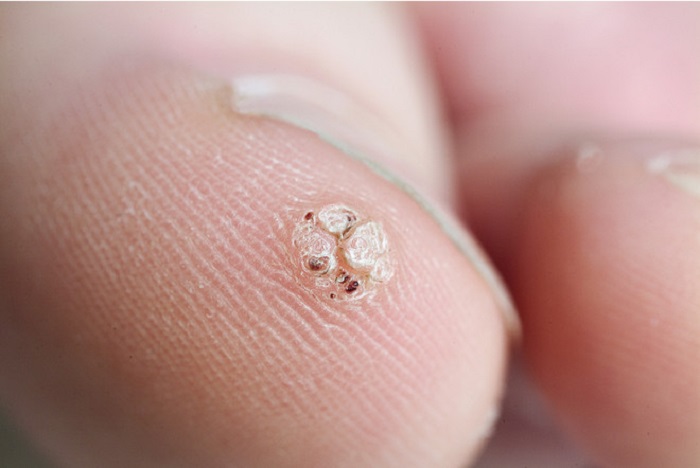
A spike is a warty formation on the sole, between the toes or on them, on the heels , near the nails, less often on the palms and fingers. A growth, unlike a callus, causes severe discomfort and pain when walking, so its presence is often unbearable.
The growths are small in size and yellow in color, protrude above the surface of the skin and grow quite quickly. In structure, the spine is similar to a seal 2–3 cm in diameter with a hole in the center. Often, one neoplasm entails the appearance of others: then they talk about a multiple focus.
Places of localization
All neoplasms associated with papillomavirus can appear anywhere on the body. Even the eyelids, fingers, soles and internal organs are not excluded.
Different strains of viruses and, accordingly, types of papilloma, love different parts of the body: thread-like, for example, prefer places with thin skin (armpits, eyelids), flat and plantar papillomas prefer rough skin (soles, palms).
If we talk about the frequency of occurrence, the leadership belongs to the genital area and anus. Also, papillomas are often found on the face (forehead, chin, eyelids, nasolabial fold), neck, in the armpit area.
Symptoms and signs of infection
Unfortunately, or fortunately, from the moment of infection, the virus does not give itself away. The latent period can last weeks, months, years and even decades: it all depends on the state of immunity.
The appearance of papilloma can proceed in different ways: some people notice a neoplasm when it has already reached an impressive size and can be felt with a finger or even interfere (for example, during sex, shaving, applying cosmetics).
In other people, papilloma growth is accompanied by some signs and symptoms:
- itching;
- burning;
- irritation and peeling of the skin;
- redness of the skin area.
Symptoms of papillomavirus may differ depending on the location. Anal warts may be accompanied by pain during bowel movements, discharge with an unpleasant odor, blood in the stool. With papillomas in the mouth, sometimes there is discomfort when swallowing, chewing food or swallowing.
With the growth of pointed papillomas in the genital area (including under the foreskin and in the vagina), discomfort during sex is disturbing.
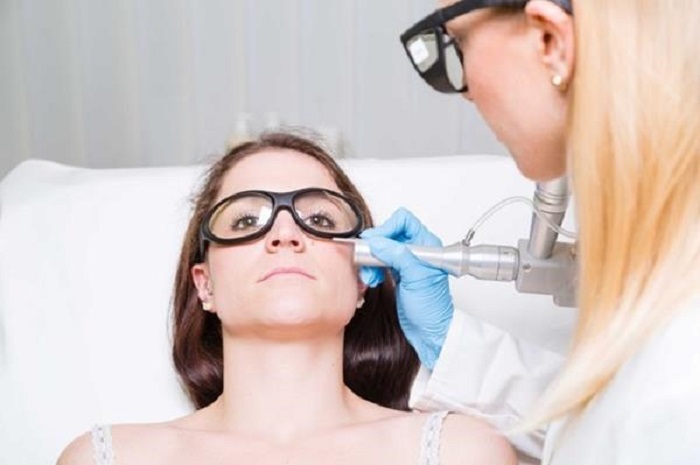
Diagnosis of the disease: what tests are needed?
If a person notices a neoplasm in himself, it must be treated. But before prescribing therapy, the doctor will definitely perform a series of diagnostic procedures to be sure that we are talking about HPV.
These include:
- visual inspection;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- PCR;
- PAP test;
- hybrid capture method;
- ELISA analysis.
A visual examination is used, but on its basis it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis: HPV must be distinguished from lichen, tuberculosis, moles. A blood test is necessary to detect antibodies to the virus, an increased level of leukocytes and other features in it.
The hybrid capture method, or digin test, is only suitable for diagnosing women.
The PAP test is used in gynecology to check for atypia, dysplasia, and the presence of malignant cells. Currently, the method is considered obsolete, so it has been replaced by a more modern one – PCR.
PCR – polymerase chain reaction – is the only method that can determine the presence of a virus in cells before a tumor has appeared. In this case, in the blood or other biomaterial, it is possible to detect sections of the DNA of viruses, their number, type, the likelihood of degeneration into cancer, and establish the timing of infection.
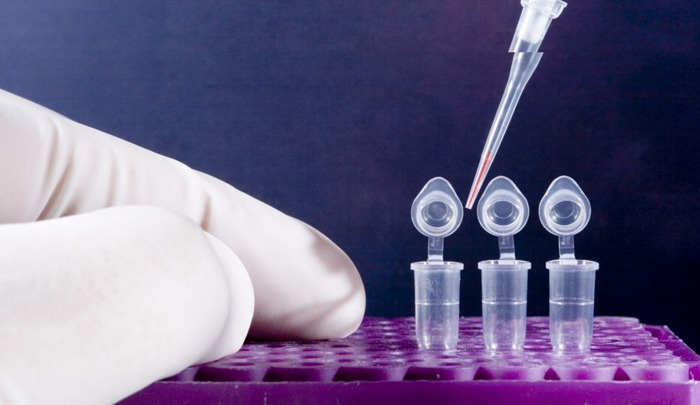
Treatment Method
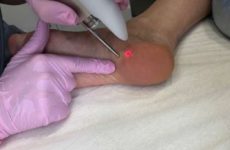
Treatment of neoplasms of a viral nature is always complex and, as a rule, long-term. Almost always, the doctor recommends first removing the growth surgically or by a more modern method (cryolysis, laser removal, electrocoagulation), and then prescribing antiviral drugs and immunomodulators.
Conservative therapy with the help of pharmacy and folk remedies is not always effective.
Non-drug
Non-drug treatment is the fastest and most effective way to get rid of growths with a low likelihood of recurrence. In most cases, drug therapy cannot completely cope with the virus and lead to getting rid of papilloma.
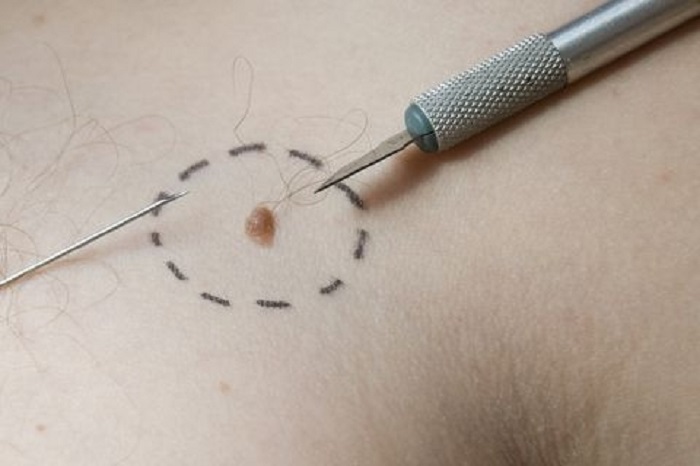
Surgical removal
If the papilloma has a clear border and is large, surgical removal of the growth will be appropriate. This uses local anesthesia. In the operating room, the doctor makes an incision, removes the contents of the resulting skin “hole”, including some healthy cells, and stitches.
The disadvantages of the method include pain, the need to care for a fresh wound (treat with an antiseptic), a long rehabilitation period and the formation of a seam or scar. However, when surgically removed, papilloma tissue can be used for biopsy.
Folk remedies
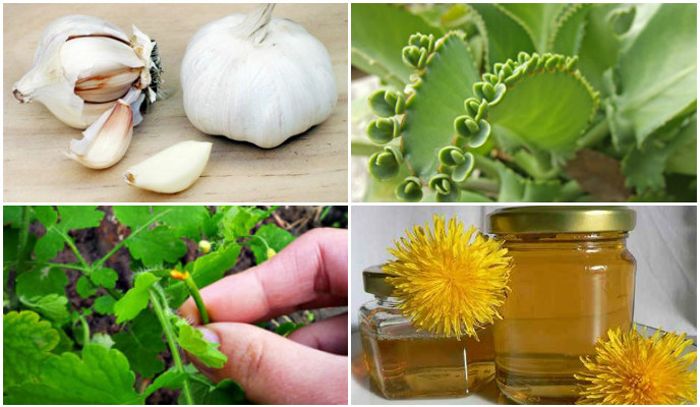
Many people, even in the 21st century, remain supporters of alternative medicine, believing that nothing can cope with diseases better than healing herbs and herbal teas.
The main way to eliminate papilloma folk remedies is cauterization. To do this, use iodine, garlic juice, celandine, aloe, apple cider vinegar, fresh potato juice, essential oils and much more.
A person who is a fan of traditional medicine recipes dips a cotton swab or gauze in the chosen remedy and applies it to the affected area. Thus, over time, the papilloma dries up and falls off, but this is not a fact either.
Treatment with folk remedies takes a long time, affects neighboring healthy areas of the skin and makes it impossible to study a tissue sample to determine the risk of cancer.

Medical
Drug treatment is often ineffective when the papilloma has long been formed. As a rule, therapy with pharmaceutical products is necessary either at an early stage of the disease, or after surgical removal, or in the case when the wart cannot be surgically removed.
Immunomodulatory drugs
Immunomodulators are drugs that help strengthen the immune system. With HPV, tablets, ointments and gels can be prescribed. As a rule, agents for local therapy are effective only in the initial stages of human papillomavirus disease.
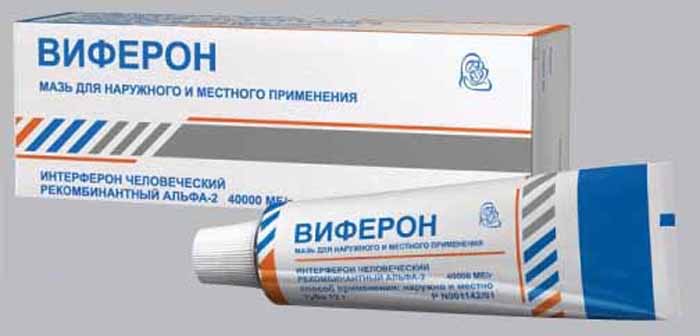
Immunomodulators are herbal and containing interferon. The latter include the popular and effective Viferon, Interferon, Isoprinosine, Genferon. From herbal preparations, drops of Derinat, Dermesil or tablets based on echinacea can be prescribed.
When taking immunomodulatory drugs, it is imperative to supplement therapy with antiviral agents.
Among the tablets, Isoprinosine, Immunozin , Novirin, Allizarin have proven themselves well. Of the ointments, Viferon, Panavir, Superchistotel, Acyclovir are popular .
Antiviral therapy is determined by the doctor, as is the dosage and course of treatment. It is impossible to prescribe medications on your own, especially without diagnosing the disease.
Preventive therapy
In order not to encounter such a nuisance as a wart, you need to follow simple preventive measures.
- Avoid promiscuity and unprotected contact.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap, especially after being in public places.
- Observe personal hygiene.
- Choose the right skin care products, underwear.
- Regularly visit a doctor and undergo a routine examination.
- Eat right, exercise.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Temper and walk more in the fresh air.
For some reason, many believe that papillomas and warts appear only in old age. In fact, HPV activation can occur at any age if a person is infected with it after the first sexual contact or from a sick mother.
In no case should warts and growths be removed on their own or prescribe medications for themselves without medical advice. As a rule, therapy should include the removal of the growth in any way possible, antiviral measures, strengthening the immune system and further monitoring by a doctor.