The human papillomavirus is present in the body of 90% of adults. Infection occurs in different ways: intrauterine, sexual, contact.
It’s almost impossible to protect yourself from it. There are more than 180 varieties of this virus, but only a few of them are really dangerous: they can cause cancer and serious complications during pregnancy.

Содержание:
The impact of HPV on the body of a pregnant woman and the fetus
The correct name for the disease is human papillomavirus. It manifests itself in the form of skin neoplasms. In most cases, these are small skin-colored growths, sometimes brown.
HPV during pregnancy is not the worst diagnosis. The appearance of the virus in the female body does not affect the health and development of the fetus. In addition, doctors have not yet proven that papillomas can affect the course of pregnancy itself. The virus does not lead to intrauterine malformations of the child, does not provoke premature birth or miscarriage, and does not cause other pathologies.
The only case when a virus can be life-threatening for a baby is the presence of anogenital papillomas or genital warts. The cause of such growths is the defeat of the body of a woman with HPV type 11 or type 6. If at the time of conception in the female body the virus was in a latent form, then when carrying a baby, it is likely to appear in the form of papillomas.
If the warts were already present on the body of the pregnant woman before conception, in the process of bearing the fetus, they can grow and change shape. Most often, infection of a child with HPV occurs if papillomas are localized in the genital area and anus. In this case, during childbirth, the infection enters the child’s body. But you should not worry about this, since the immune defense of the newborn is able to cope with the virus.
What is the danger for women and children?
The human papillomavirus does not affect the course of pregnancy and the health of the fetus at all. But pregnancy itself often causes the onset of the development of this disease.
If a woman had genital papillomas before conception, then during the bearing of a child they can grow more actively, and at the same time, vaginal discharge will increase. In this way, the virus provides itself with favorable conditions. However, as a rule, warts do not threaten the child.
HPV cannot affect the fetus, except in cases of spread of papillomas in the mother’s vagina. In this case, there is a risk of infection of the child during his exit through the birth canal. In this case, a serious disease develops – condylomatosis of the larynx. If the papillomas are on other parts of the body, then the fetus cannot become infected with the virus. According to statistics, HPV is transmitted from mother to fetus in 4% of cases.
HPV detected during pregnancy usually does not show up after childbirth. In most cases, spontaneous self-healing occurs.

Causes of papillomavirus infection during pregnancy
HPV transmission occurs in the following ways:
- During intercourse.
- Through contaminated blood.
- Upon contact with affected mucous membranes and skin.
- In rare cases, from mother to child.
Risk factors:
- Low immunity.
- Chaotic sex life.
- Drug addiction.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol abuse.
- The presence of HIV infection.
- The presence of viruses in the body.
- Frequent stress.
Locations of papillomas
Papillomas in pregnant women are often localized in such places:
- Neck.
- Face.
- Armpits.
- Breast.
- Groin.
It is important to note that the condition of a woman’s skin before conceiving a child does not directly affect the appearance of papilloma during pregnancy . It is more correct to say that the very fact of pregnancy is a provoking factor in their appearance. If papillomas were already present on the body, then the risk of their increase during gestation is very high. Most neoplasms occur after the first trimester.
Modern diagnostic methods
Often, the presence of a virus can be judged by the appearance of small formations on the skin and mucous membranes. However, it can be present in the body in a latent form, in which case the infected person does not even know about his disease.
Modern diagnostics is aimed at identifying oncogenic types of papillomavirus:
- Determining the type of virus and specific genotypes .
- Identification of the duration of HPV persistence in the body.
- Determination of viral load and degree of HPV integration into host cells.
When genital papillomas appear in a pregnant woman, they will be determined by a visual examination by a gynecologist. The following methods can be used to confirm the diagnosis:
- biopsy with histological examination;
- cytological examination of smears to detect malignant cells;
- colposcopy;
- PCR to identify HPV types;
- acetic acid test.
Laboratory diagnosis of the presence of HPV is also prescribed in the case when a pregnant woman has cervical erosion or ectopia.
Treatment
Modern medicine offers HPV treatment with surgical and conservative methods. Therapy is carried out with the help of medications:
- cycloferon (Reaferon and Cycloferon);
- antiviral drugs;
- immunomodulatory agents.
However, drug methods do not help to completely overcome the virus, but only reduce its amount in the human body.
The expediency of surgical intervention is determined by the localization of papillomas. If neoplasms have spread in the uterine cervix, their prompt removal is mandatory. Methods can be used for this:
- cryotherapy – freezing;
- cauterization – diathermocoagulation.
Removal of warts on the body is an exclusively cosmetic procedure, since it does not rid the body of the papillomavirus.
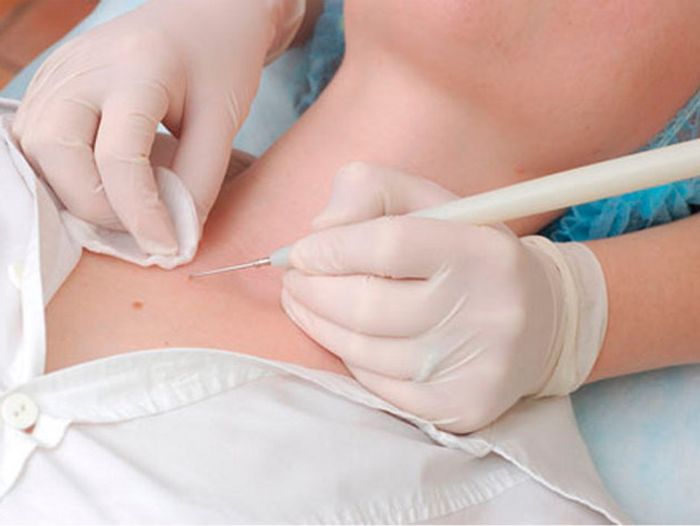
Papillomas and childbirth are not always compatible, since it is quite possible that the child will become infected with the virus from the mother while overcoming the birth canal.
Many antiviral medicines for women carrying a child are strictly prohibited. If HPV was detected before conception, then pregnancy can only be planned after the completion of the therapeutic course. The body must fully recover. Immune protection is the main barrier against infection and pathogenic microorganisms. And it is important to pay due attention to the state of immunity.
If papillomas occur during pregnancy, they do not need to be treated immediately. During the first 28 weeks of gestation, the most important internal organs are laid and formed in the child, and women are forbidden to drink drugs that are contraindicated for pregnant women.
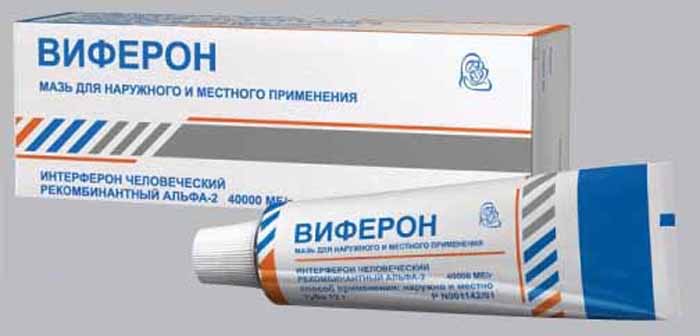
There are medicines approved for use during pregnancy, for example, Viferon. This ointment contains interferon, a substance that strengthens the immune system. Viferon is suitable for removing neoplasms. But it is not recommended to use it on your own without the permission of the doctor.
Possible Complications
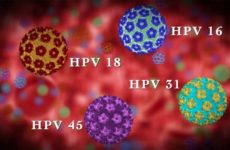
The most dangerous HPV types are 16 and 18, which cause cervical cancer in women. The appearance of HPV during childbearing can pose a threat to the health of not only the woman, but also her baby, if the papillomas are located in the uterus and on the walls of the vagina.
During childbirth, the child may take a breath prematurely, and with it, the infection will enter the child’s body through the respiratory tract. In most cases, the immune defense of newborns copes with the virus. But some babies may develop a rare disease – laryngeal papillomatosis . Thus, complications will be dangerous for the baby.
It is allowed to give birth in the presence of formations in the genital area. But if the papillomas are too large and cannot be cured, doctors will offer another method – a caesarean section. This decision will protect the mother and child from the penetration of HPV into his body.
However, papillomas can also be located in other places on the skin. If they are not in the uterine cervix and vagina, then they do not pose any danger to the fetus, and there will be no complications for the pregnant woman.
If a woman has the opportunity to recover from the virus before pregnancy, this definitely needs to be done. Some strains in advanced form lead to adverse effects. But the baby needs a healthy mother for full development.
The main danger of HPV in a pregnant woman is that in the event of a decrease in immune protection in combination with other viral infections, there is a risk of exacerbation of old or the emergence of new diseases. This can lead to complications of bearing health problems in the fetus. Such patients need to pay attention to enhanced measures to strengthen the immune system and observe a sparing regimen.
In addition, papillomas in women in position can provoke the development of other infectious diseases, for example, thrush – candidiasis, which, in turn, can be transmitted to the fetus.
Prevention
It is possible to prevent the appearance of papillomavirus in a pregnant woman, but not completely. There are a number of ways to reduce risks:
- Do not gain excess body weight.
- Do not wear tight clothing that irritates the skin.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Provide protection against colds and penetration of other viruses and infections into the body.
- Get regular medical check-ups.

However, all these methods do not provide a full guarantee of protection – no one is immune from the appearance of papillomas.
There is no specific treatment for HPV in the world yet. However, a vaccine is now available that prevents damage to the most dangerous types of papillomavirus. It’s called Gardasil .
You can buy a medicine in 60 countries of the world, including Russia. However, vaccination will only help as a preventive measure, not as a cure. The vaccine helps protect against the four most dangerous types of HPV.
It is rational to carry out vaccination before the appearance of conditions of infection, that is, before the onset of sexual activity. Young women are recommended to be vaccinated between the ages of 17 and 26.
Conclusion
Human papillomavirus is not treated during pregnancy, as any antiviral medicines can harm the baby in the womb. This disease is not dangerous, and it is quite possible to give birth to a healthy baby with it. It is recommended to follow preventive measures aimed at protecting the body and strengthening the immune system.