The human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most widespread viruses on the planet. According to the World Health Organization, 70% of the world’s population is infected with one or another type of it. Currently, about 600 types (strains) of HPV are known. Some are not dangerous to humans, while others can lead to cancer.
Содержание:
What is papilloma, localization in men and women
Papilloma is a growth on the skin or mucosa. The only cause of its occurrence is the human papillomavirus (HPV). It penetrates the DNA of a healthy cell and causes it to divide rapidly, forming characteristic growths. The virus is able to penetrate into the deep layers of tissues, but it multiplies on the surface.
Each age is characterized by certain types of papillomas. The pathogen is also characterized by tissue specificity, when each strain of the virus infects certain tissues in certain areas of the body.
Papillomas are found on all kinds of places on the body, below we will consider the most common of them.
On the face
Usually occur in adolescents during puberty and are called flat warts. Such rashes do not exceed 1-2 mm in height and have an oval or round shape. They may go away with time without treatment. If they don’t go away, you should see a dermatologist.
On fingers, toes, palms, feet
They occur mainly in children and are called ordinary (simple or vulgar) warts. They reach a height of 2-3 mm and have a domed shape and a rough surface. They like to be placed near the nail plates, between the fingers.
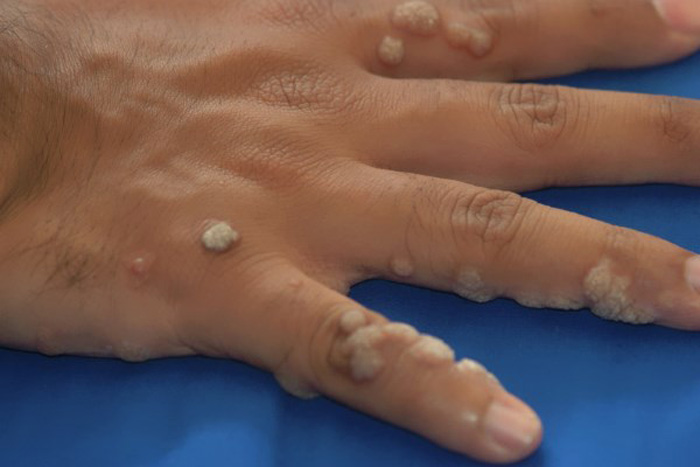
Unlike simple warts, spinules occur mainly on the feet and palms. They are denser and larger in size. Pain when pressed resembles a prick of a sharp thorn and interferes with walking. The spikes are also removed by a dermatologist.
On the neck, eyelids, in the armpits, in the fold under the breasts in women
This species is typical for middle-aged and elderly people, from 35 years and older. They are distinguished by their small size and filamentous shape on a thin stem. Formed in places with thin skin. With age, the number of such warts may increase, they form clusters and darken in color. Such growths can be easily and quickly removed by a dermatologist.
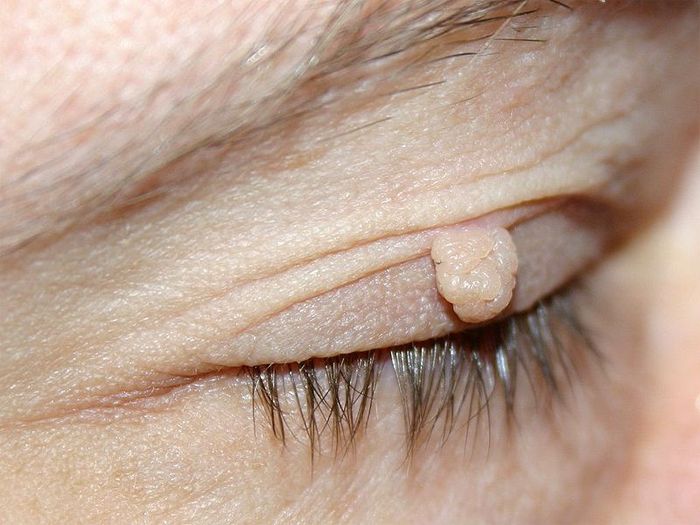
On the genitals of women and men
These growths in appearance resemble cauliflower or cockscomb. They are called genital warts. They are located in the vagina in women, on the penis in men, in the urethra, in the anus, in the mouth.
This virus is transmitted sexually. The probability of infection is highest at the age of 18-35 years, the percentage of infected during this period can reach 50%. Moreover, men are more likely to suffer the disease, and women are more likely to get sick.
In the larynx, trachea
On the mucous membrane of the larynx and trachea, papillomas are formed in the form of multiple papillae. They grow and gradually reduce the lumen of the respiratory tract, interfere with breathing and speaking.
Such formations are especially dangerous in infants due to the threat of suffocation. Infection of a child with a virus occurs during childbirth from a mother with genital warts. Such formations are removed by an ENT doctor.
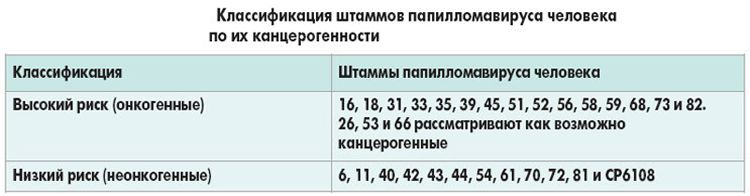
Types of virus by oncogenicity
As mentioned earlier, not all types of HPV are dangerous to humans. According to their ability to cause oncological diseases, they are divided into high-oncogenic, medium-oncogenic and low-oncogenic.
- Non-cancer HPV types: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49.
- Low oncogenic risk types (rarely cause cancer): 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 72 .
- Types of average oncogenic risk (average cancer rate): 26, 30, 35, 52, 53 , 56, 58 , 65.
- Types of high oncogenic risk (high risk of developing cancer): 16, 18, HPV 31 , 33 , 39 , 45, 50, 59 , 61, 62, 64, 68 , 70, 73. Of these, strains 16 and 18 are most common.
Ways of infection
The first and main way of infection is through sexual contact with a virus carrier. This also includes oral and anal contact. It doesn’t matter if he was protected. Infection can also occur when using contraceptives.
The second way is from mother to child.
When a baby gets human papillomavirus infection (PVI) during childbirth. However, an infected mother does not always give birth to an infected child. Thanks to high immunity, the baby can stay healthy.
The third way is contact-household.
In direct contact with the affected areas of the body of a sick person, for example, through a handshake or kisses. It is also possible to get infected through common objects.
For example, when using a swimming pool, a bathhouse, a toilet bowl rim, personal hygiene items. In the case when one of the family members is infected with HPV, the risk of infection of other family members is high.
The fourth way is self-infection.
During shaving or epilation, it is easy to transfer papilloma from one part of the body to another.

Who is at risk
Anyone can become infected at any time in their lives. It is completely impossible to protect yourself from PVI, but you can protect yourself. When the virus enters the body of a healthy person, infection does not occur, since its immune cells destroy the infection. Therefore, the higher the immunity and the stronger the health of a person, the less likely it is to catch PVI.
Let’s single out some risk factors for PVI:
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal disbalance;
- pregnancy, as there is a restructuring of the hormonal background;
- early sexual life and frequent change of partners;
- concomitant STDs (sexually transmitted diseases), such as bacterial vaginosis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.;
- medical procedures and manipulations, such as the insertion and removal of an intrauterine device, instrumental abortion.
How to identify papillomavirus, the main symptoms
The papillomavirus has a long incubation period and the latent nature of the course of the disease. The incubation period refers to the length of time from the moment a pathogen enters the body until the first signs appear.
In HPV, it takes on average from a month to several years. At this time, the patient does not experience discomfort or symptoms. The virus is in a dormant state until the onset of favorable conditions for development.
The appearance of papillomas and warts on the skin and mucous membranes is almost the only clear sign of the disease. It means that the disease is in an active stage and requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Also find out what indirect signs will help you identify HPV.
Stages of PVI development
It is customary to distinguish 3 stages of PVI development:
- Initial stage (hidden) . External manifestations are absent. At this stage, it is impossible to determine the presence of the virus by diagnostic methods. There is no change in tissue structure: the virus has already entered the cell, but the DNA structure remains the same. The pathogen is in a dormant state and its number is minimal.
- Stage of subclinical manifestations . At this stage, small tissue changes that are invisible to the eye are detected. They can be fixed during the diagnosis – colposcopy and histology. At this time, the virus has already invaded the gene of a healthy cell, but has not yet made itself felt.
- Stage of clinical manifestations . Viral cells begin to multiply rapidly, resulting in warts and condylomas.
Diagnostics
Today there are no uniform rules for the diagnosis and treatment of papillomavirus. This is due to the difference in strains and the localization of the pathogen. Despite the fact that doctors of different specializations are engaged in the diagnosis of PVI, it includes the following steps:
- Visual inspection of lesions.
- Collection of biological material.
- Tests for the presence, identification of the type of HPV and the number of viral particles.

Methods for diagnosing HPV of the urogenital type:
- Colposcopy – examination of the cervix with a special microscope. The survey allows you to clarify the presence, size and localization of formations.
- Biopsy – taking tissue samples from the lesion. The procedure allows you to identify a precancerous condition and includes 2 types of studies. Cytology – taking a scraping of the affected area for examination under a microscope. Histology – the collection of a piece of tissue of the affected area for layer-by-layer examination using special formulations and examination under a microscope.
- Research by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) . PCR is a fast and reliable way to diagnose papillomas. Due to the high level of specificity, it makes it possible to isolate a specific causative agent of infection, its type and type, regardless of the stage of pathology. The readiness of the smear analysis is 4-5 hours.
PVI treatment
The main difficulty in the treatment of PVI is that once it enters the human body, it remains there forever. It is impossible to cure completely, it is possible to overcome the active stage of the development of the disease.
Treatment of PVI should be comprehensive and aimed at:
- Suppression of the causative agent of the disease and elimination of living conditions . This means that drugs are needed to fight the virus and restore healthy microflora. In the case when HPV is accompanied or provoked by other sexually transmitted diseases, they must also be treated.
- Elimination of factors that reduce immunity, increase immunity . This includes a wide range of tools: from taking vitamin complexes to hardening. It is important to understand that with strong immunity, the disease will not relapse.
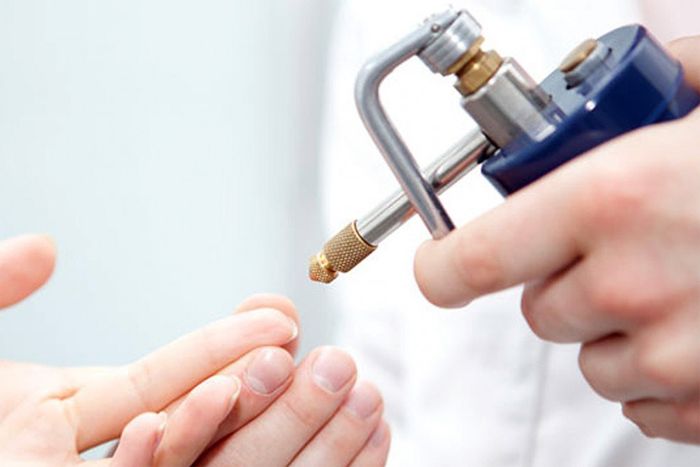
- Removal of neoplasms . Some formations disappear after undergoing medical treatment, but some formations persist and cause inconvenience. They can be removed in the following ways:
- liquid nitrogen;
- directed laser beam;
- thermal damage to papillomas using a high-frequency wave;
- chemical preparations – processing and cauterization;
- radio wave scalpel.
Infection prevention
The most promising method of prevention is vaccination against HPV. It not only protects against infection, but is also used in the treatment of infection. The vaccine is available as a suspension for intramuscular injection. Manufacturers guarantee efficiency up to 95%.
It is equally important to maintain immunity and lead a healthy lifestyle: eat right, give up bad habits, be selective in sexual relations.
Regular visits to the gynecologist and the passage of tests will identify the infection at an early stage. This is especially important for women, since, according to statistics, they get oncogenic type HPV more often than men.
HPV is sometimes called the plague of the 21st century for the extent of its spread and the consequences of the disease. But there is no need to panic and be afraid to go to public places, shake hands or enter into a relationship with a new person. You just need to be attentive to your health, regularly undergo examinations and “know the enemy by sight”.