According to statistics, about 80% of people of reproductive age are carriers of the human papillomavirus (HPV). Due to the fact that the onset of sexual activity has become younger, the average age at which this disease is detected has also changed. For women, this is between the ages of 14 and 24.

Содержание:
- 1 Papillomavirus – where does it come from, causes in gynecology
- 2 Main types and types
- 3 Detailed characteristics of papillomavirus 16, 18 strains
- 4 Papillomavirus during pregnancy, symptoms, effect on conception
- 5 How is papillomavirus infection diagnosed?
- 6 Principles of treatment
- 7 Can it be cured?
- 8 Prevention
Papillomavirus – where does it come from, causes in gynecology
HPV ranks second in the incidence of the female reproductive system after genital herpes.
Among all types of papillomavirus, about 30 of them cause damage to the female genital organs. Of particular danger are flat and genital warts.
Infection with papillomavirus occurs as a result of contact with a person who is a carrier of the virus. Moreover, the patient himself may not suspect that he has this disease. Often the disease can be asymptomatic.
The main ways of infection:
- sexual intercourse , and even if you use a condom, you will not be 100% protected, because the virus particles are negligible and can get on your mucous genitals;
- contact of the damaged skin area with the source of infection . In the pool, in public transport, the toilet at the station there is a risk of contracting HPV. Therefore, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and seal open wounds with a band-aid;
- self-infection . It happens if you already have HPV and manifested itself, for example, in the form of warts in the armpit. You can spread the virus to your genitals if you use the same underarm and bikini razor.

After HPV has entered the body, it can sleep for a long time. Provoke his active actions can:
- weakening of the immune system;
- stressful conditions;
- hormonal failure in the body.
If the immune system is strong, then it can overcome the virus itself. You won’t even notice that you’ve been infected.
Main types and types
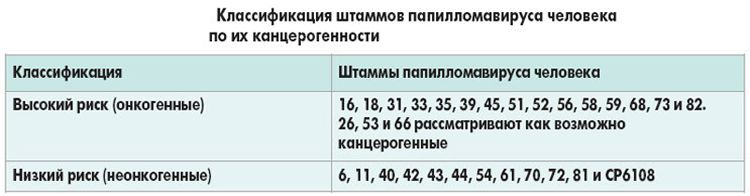
Depending on the risk of developing into a cancerous disease, there are three types of HPV oncogenic type in women :
- Not an oncogenic group . These are 1,2,3,4,5,10,12,14,15,17,19,20,21,22,23,24,26,27,29. They do not develop into a malignant stage.
- Low degree of oncogenicity . These are 6,11,42,43,44, 53,54,55 . In most infected people, the virus remains benign. In addition, vaccines have been developed for these strains.
- The average degree of oncogenicity . These are 31,33,35, 52 , 58 .
- High oncogenic risk . It’s 16,18,36,45, 51 . Basically, condylomas in women develop into oncology . A man often acts only as a carrier of the virus.
Detailed characteristics of papillomavirus 16, 18 strains
These strains are at high risk of developing into cervical cancer. In the body, they exist in two forms: benign, when they do not affect DNA, and malignant, when they already penetrate the chromosomes.
Doctors distinguish four phases of the course of the disease caused by types 16 and 18 of papillomavirus.
- Incubation period . When a virus enters the body, the immune system begins to fight it. With good body resistance, HPV can be overcome within a year.
- External (clinical) manifestations . At this stage, genital warts, round or rough papillomas begin to appear on the mucous membranes.
- Growth , dysplasia of soft tissues. At this stage, condylomas begin to divide, occupy an increasing surface. The virus enters the cells and the DNA of the strain is introduced into the human genome.
- The development of oncology . Body tissues mutate.
Papillomavirus during pregnancy, symptoms, effect on conception
It often happens that women neglect their health. But when pregnancy occurs, the expectant mother must register with the antenatal clinic. And when contacting a gynecologist and after passing a series of tests, the doctor diagnoses the presence of HPV in a woman.
As a rule, warts grow during pregnancy. This is due to the fact that all the forces of the body and useful substances entering it are aimed at the formation of the fetus.
As for the negative impact on the fetus, this is a moot point. Studies have not proven that the presence of HPV in a pregnant woman may be an indication for termination of pregnancy, or for a caesarean section.
HPV does not affect conception. In the case of acute immunodeficiency, problems with conception are possible, but if changes have already occurred in the endometrial tissue of a woman planning a pregnancy. Then the fetus will not be able to gain a foothold and a spontaneous abortion will occur.
If the virus is detected during pregnancy, then treatment begins no earlier than 28 weeks, when the main organs of the baby have already formed.
Features and risks for the fetus
The risk for the fetus may be too large condylomas that are in the birth canal and make it difficult for the child to move along the birth canal.
In exceptional cases, at the most advanced stages, HPV infections were detected in newborns. These are papillomas on the larynx and genitals. This situation can occur during difficult births.
How is papillomavirus infection diagnosed?
The first sign of the presence of the human papillomavirus is the appearance of warts on the body, usually in the armpits, under the mammary glands, on the eyelids. Also find out what indirect signs will help you identify HPV.
HPV carriers develop condylomas, warts on a thin stalk with a wide cap that has a loose structure and grooves. They are localized around the genitals, on the mucous membranes. In the area of the formation of these growths, itching and burning, pain on contact with clothing are observed.
If you find such first signs in yourself, immediately go to the gynecologist. The doctor will conduct a series of studies and tests.
What tests need to be done?
- Colposcopy . This is an examination of the cervix using a colposcope device, which helps to examine in detail the structure of the surface of the female organ and detect neoplasms.
- Cytological smear . Under a microscope, a laboratory assistant can determine if there are cells infected with HPV. Cytology is especially important when a woman cannot be biopsied. This applies to patients who are at risk of developing cancer.
- Histological examination (biopsy) . It is prescribed if there are doubts as a result of a cytological analysis. This study is a collection of a piece of tissue in which they look for cells affected by the virus. This study is carried out in a trusted place with a reliable specialist. If the biopsy is carried out carelessly, it can provoke the development of cancer.
- Blood test . For research, venous blood is taken and the presence of antibodies to HPV in it is detected. This method does not accurately determine the type of virus and its concentration.
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction), done together with a cytological smear. Helps to determine the DNA of the virus. The material is also taken from a smear from the mucous membrane of the cervix.
Principles of treatment
Treatment for HPV varies, depending on the extent of the disease and the strain that is present in the body. After the diagnosis, the doctor will determine what type of virus you have and prescribe an individual treatment.
Medical treatment is divided into three methods.
- Cytotoxic . It acts directly on the cells of the virus. These drugs include Allokin-Alpha . It is administered intravenously and fights viruses that are highly oncogenic.
- The chemical method involves a direct effect on the papilloma. This is Cycloferon, Interferon ointment.
- The immunological method involves increasing the body’s resistance by taking certain medications. These drugs include Genferon, Viferon, Isoprinosine.
Papilloma removal is carried out in several ways:
- Radio wave coagulation . This is the removal of a wart with a radio wave scalpel. The procedure is practically painless. Thanks to the electrode on the scalpel, the intracellular temperature of the papilloma increases, it is removed from the root, the wound is disinfected, and small capillaries are sealed. The operation takes place almost without blood. During the removal process, healthy tissue is not affected.
- Cryodestruction . Removal of formation with liquid nitrogen. During freezing, the cells are no longer supplied with blood and oxygen and die. Because of this, the condyloma turns into a scab and disappears.
- Diathermocoagulation . Removal of papilloma by electric discharge with an electric scalpel. This method is inexpensive compared to laser and radio waves. But it is more painful.
- laser radiation . This is cauterization of papilloma with a laser beam. The method is painless, practically does not leave scars, it is used when removing formations on the eyelids, on the genitals. About a week after the procedure, the wart disappears.
- Surgical removal . The operation is performed under local and general anesthesia. The growth is removed with a surgical scalpel and cauterized with a disinfectant solution. This method is used for malignant tumors and large papillomas.
Folk methods of treatment
When getting rid of papillomas, treatment with folk remedies can also be used . But it is better to use them if you are sure that HPV is not oncogenic in you. Otherwise, you can provoke the development of cancer.
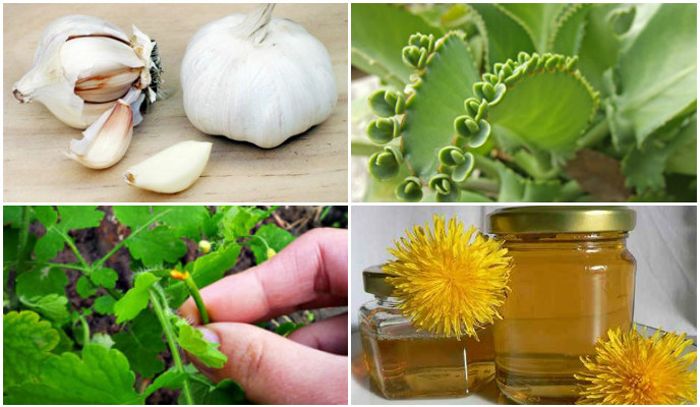

Folk methods include cauterization of warts with celandine , apple cider vinegar. The imposition of dressings from raw potatoes, onions. There are also herbal remedies that stimulate the immune system.
Can it be cured?
Treatment of the human papillomavirus is individual for each woman. The attending physician will take into account all the features of your body, be sure to take into account heredity. All treatment comes down to the localization of the virus, its introduction into the stage of harmless sleep. It is impossible to completely destroy the virus.
Prevention
- Vaccination . Suitable only for those who are not yet infected with HPV. The vaccine is given to women between the ages of 15 and 30. The vaccine contains strains 6,11,16,18.
- Hygiene . Wash your hands after the street. Protect damaged areas of the skin from the external environment. Take a shower after visiting the public pool. On the road, do not hesitate to use a special antibacterial hand gel.

Keep your genitals clean, in hot weather, change your underwear more often so as not to create a humid environment for the development of viruses.
- Permanent sexual partner . Promiscuous sex increases the risk of HPV infection.
- Protected intercourse . Use condoms.
- Avoid constant stress .
- Maintain immunity . In the spring, take vitamins, eat fruits and vegetables. Eat varied and healthy.
- Moderate physical activity also helps to increase endurance and body resistance.
- Refusal of bad habits . Smoking reduces the body’s resistance to viruses.
If you find the first signs of HPV in yourself, immediately consult a doctor, take the necessary tests. Be aware that strains 16 and 18 can develop into cervical cancer. Follow the necessary measures to prevent infection with papillomavirus.