Содержание:
Introduction
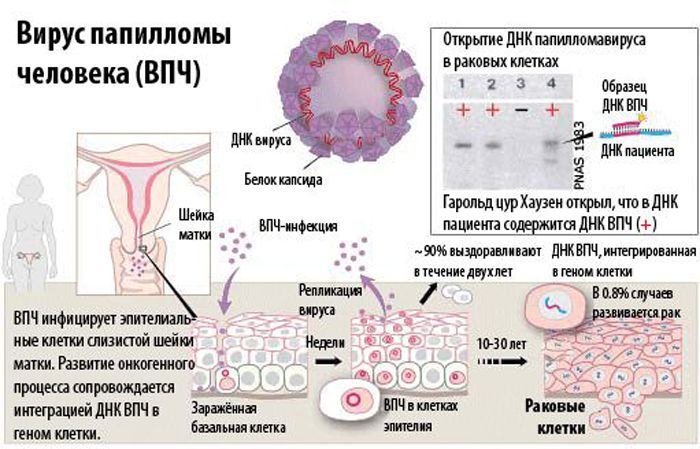
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common viral infection that leads to the formation of warts, papillomas, genital and flat warts, and in some cases, cancer.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), from 60 to 90% of the sexually active population of the planet are carriers of this infection.

Transmission and manifestation of papillomavirus
There are more than 100 species of this viral agent known to science, they can only infect humans. Based on this, the transmission of the virus occurs only from person to person. Moreover, infection can occur both from an actively ill person and from a simple carrier who has had this disease in an active or latent form (in this case, the person does not even suspect that he is the source of the infection).
After a single entry into the body, the virus remains in it forever (usually in a latent form) and a person is able to spread the disease throughout his life. However, under the influence of certain factors, it is able to reactivate or acquire oncogenic properties, and thereby manifest itself again, leading to the development of the disease.
Most often, the virus that has entered the body does not manifest itself in any way (latent course). In this case, a person can live a lifetime without even knowing about the presence of that disease. Or it can occur together with other inflammatory diseases and be masked by their clinical manifestations.

But if HPV still manifests itself, then there are several groups of signs:
- True symptoms (basic).
- indirect symptoms.
- cytological manifestations.
Indirect symptoms of human papillomavirus
These are the signs that cannot unambiguously indicate the presence of this disease, but will help to suspect it if there was contact with a carrier (sick person). In this case, you need to pay special attention and listen to your own body. Indirect signs of the human papillomavirus may include:
- Pain during intercourse.
- Bloody discharge after intercourse (sexual intercourse).
- The genitals exude a sharply unpleasant odor.
- Soreness during bowel movements, traces of fresh blood on the feces (with rectal localization).
- Feeling the presence of a foreign body in the mouth, pharynx, larynx, esophagus. Discomfort during swallowing and breathing (when oral).
It should be remembered that according to all these signs, one can only suspect, and in no way make a diagnosis. If one or more of the above symptoms are found, it is necessary to consult a specialist for competent diagnosis and treatment.
Ways of infection and the main symptoms of the disease
The main most common route of transmission of the pathogen of this infection is sexual (with unprotected intercourse). Moreover, the nature of sexual intercourse does not matter, infection occurs during vaginal, anal and oral copulation. Thus, most people become infected during their first sex.
Another transmission method is vertical. It consists in infection of the fetus, when passing through the birth canal of a sick mother, while the skin of the child comes into contact with the virus-infected epithelial cells of the genital tract. Also, there are suggestions, and the possibility of intrauterine infection of a child in the active phase of the disease.

Infection is also possible through household contact, with the usual handshake, the use of other people’s hygiene products, in public places (baths, swimming pools, gyms, etc.).
As mentioned earlier, the human papillomavirus is characterized by an asymptomatic course, however, under the influence of adverse factors, it can be replaced by the active phase of the disease, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
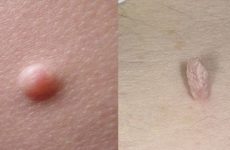
- Warts are benign formations of irregular shape (up to 1 cm). Most often localized on the fingers and knees.
- Papillomas – are soft neoplasms on a leg (thin or thick). The process tends to progress and capture new areas of the skin. They are localized mainly in the area of the labia, on the face, neck, in the armpits.
- Genital warts (genital warts) are soft formations growing on a thin stalk, they are completely similar in color to the skin. They have an uneven surface and are found more often in the groin , on the genitals, on the mucous membranes, around the anus. They grow at an incredible speed, forming whole ridges.
- Bowenoid papulosis (occurs in some cases) – plaque-like formations, pink or yellow, with a smooth surface. More often localized on the surface of the penis, clitoris, labia, near the anus, in the groin, on the thighs and in the oral cavity.
These symptoms are the main ones, however, there are also more specific ones, characteristic of a certain gender, they will be discussed below.
Cytological symptoms of papilloma
All diagnostic methods give very indirect results, on the basis of which it is impossible to unambiguously judge whether there is a disease or not. The “gold standard” in the detection of papillomavirus is a cytological study. Its results make it possible to accurately establish the diagnosis, as well as the strain of the virus that persists in the body and, based on the data obtained, prescribe adequate treatment.
When the virus enters the cells (koilocytosis), it leads to their change, as a result, the appearance of the tissue that they form also changes. During the study, the following pathological changes in cells are detected:
- Cells line up in several rows (multi-row).
- Cells acquire a flattened or other (irregular) shape.
- Violation of the internal structure of cells.
As a rule, such cells are larger than healthy ones and have a perinuclear zone of enlightenment. Their nuclei can be deformed, doubled (multinuclear), acquire a pathological shape and size. All these processes indicate dysplasia (precancerous process).
This means that the cells are in a borderline state: they are already unhealthy, but also non-cancerous. With further progression of the disease, the absence of proper treatment or the action of any provoking factors, the process may become malignant.
Such dangerous complications can be easily avoided if diagnosed in time, carried out good treatment and prevention.
Women’s symptoms
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the genital organs, women are more susceptible to various sexually transmitted infections. The human papillomavirus is no exception; it easily enters a woman’s body at the first sexual contact. However, in most cases, a healthy immune system suppresses its development, which leads to a latent course of the disease.
In some cases, the disease may manifest itself with minor symptoms, but still proceeds unnoticed, as it is hidden by menstruation or other diseases of the reproductive system occurring during this period (erosion and pseudo-erosion of the cervix, endocervicitis, vulvovaginitis, etc.). In such situations, it is very difficult to identify the disease.
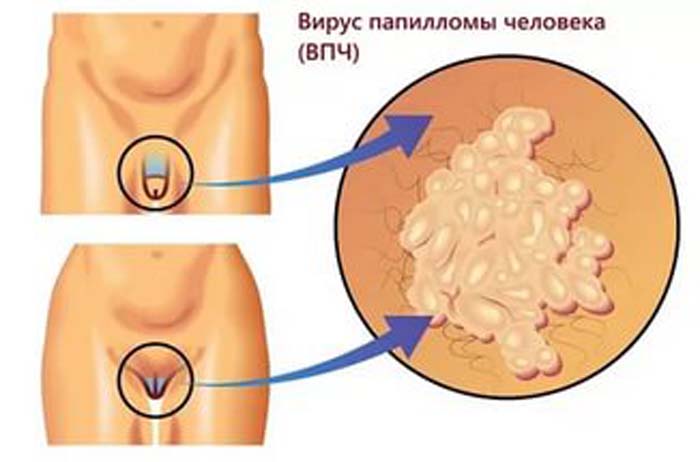
If papillomatosis occurs separately (without other diseases), then it may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- The formation of warts, warts and papillomas in the genital area, anus, perineum and other parts of the body.
- Feeling of itching and burning in the genital area. This is due to the rapid growth of warts.
- Difficulty urinating. When the outflow of urine is obstructed by warts, condylomas, papillomas.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Discharge from the genital tract outside the menstrual cycle, as a rule, has an unpleasant odor.
But it should be remembered that one hundred of these symptoms can be observed in other diseases. They are the basis for further diagnostic search and cytological examination.
Male symptoms
In the male half of the world’s population, the risk of the transition of the process to oncological is much lower, but still there is a place to be. Symptoms of the disease in men are not much different from women, they include:
- Feeling of discomfort and foreign body inside the penis or on its surface.
- Pain during intercourse, there may be spotting.
- Urination disorders, due to the closure of the urethra by neoplasms.
The most common localization of the process in men:
- Scrotum.
- The head of the penis.
- Bridle.
- around the anus.
A significant difference in men is that condylomas quickly spread and are localized in groups. During an erection, they stretch along with the skin and cause very severe pain, they can crack and bleed.
One of the varieties of the human papillomavirus, characteristic only for men, is Bowen’s disease. It is characterized by the rapid spread of small round growths over the surface of the entire body. Depending on the location, the formations are able to have a different color.
This process belongs to oncological (intraepidermal cancer), but its course is relatively favorable, since it does not penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin. Since it is located in the epidermis itself (does not go beyond the basement membrane), there is the possibility of safe removal.
Vaccination and diagnostics
To date, the diagnosis of HPV is not particularly difficult. With the help of modern methods, it is possible to detect a virus, even if it is not clinically manifested in any way. A referral for research is issued by a gynecologist, urologist or dermatologist.
High-tech techniques allow not only to detect the virus, but also to determine its type, which provides information about its pathogenicity (ability to cause disease).
In modern practice, the following HPV detection methods are used:
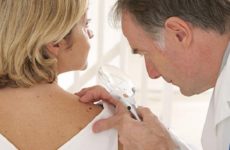
- Colposcopy is an endoscopic examination of the cervix using a colposcope. This method allows you to examine in detail the mucous membranes in real time, detect pathological formations and study them at different degrees of magnification, if necessary, take material for histological examination.
- Cytological method – for this method it is necessary to take a smear from the mucous membranes (cervix, urethra , etc.). After that, a preparation is made and examined under a microscope. If specific cells (koilocytes, dyskeratocytes) are found in the smear, the result is considered positive. The results are interpreted as follows: grades 1 and 2 are considered negative (healthy), grade 3 is intermediate and requires additional diagnostic tests, grades 4 and 5 indicate the presence of an oncological process.
- Histological examination – from a piece of tissue taken during colposcopy, a microscopic preparation is made and studied under a microscope.
- The search for antibodies to HPV in the blood is used for early diagnosis of the disease, as it allows you to identify the virus even before the development of clinical manifestations. The only drawback of the method is the inability to determine the type of virus and its concentration.
- Amplification or Digene-test is a modern and very accurate technique, in which there are no drawbacks inherent in the method for detecting antibodies. With it, you can not only detect the virus, but also determine its type and concentration.
- Non-amplification or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – based on the detection of virus DNA in the human body, any biological fluid can be used for diagnosis.
The human papillomavirus vaccine is most often given to young women, but men can also be vaccinated. It is carried out before the onset of sexual activity and after laboratory confirmation of the absence of the virus in the body.
Two vaccines are currently in use: Cervarix and Gardasil. They consist of the shell of the virus and do not contain its DNA, so infection with the virus from vaccination is impossible. According to the results of scientific research, the effect of the vaccine lasts for 15 years, from the date of vaccination.
In addition to preventive vaccines that protect the body from disease, therapeutic ones have also been developed that are used to treat the virus, especially its oncogenic strains. This type of vaccine is at the stage of clinical trials and has not yet been widely introduced into medical practice. See also material on the topic: HPV type 16, quantitative analysis, decoding .
Conclusion
The human papillomavirus is very common and can cause serious illness. For this reason, in no case should you ignore the symptoms and, if you suspect a disease, consult a doctor. For all young people who have not begun to have sex, vaccination is recommended to avoid infection.