Dermatologists, infectious disease specialists and virologists often face the diagnosis of papillomavirus infection. Recently, the number of diseases that this viral agent provokes has increased many times over, and in most cases the virus is registered in women. The main types of HPV diagnostics will be discussed below.
Содержание:
- 1 What is this disease
- 2 When do I need to sign up for an examination?
- 3 How often should I be tested for papillomavirus?
- 4 How to find out the type of human papillomavirus?
- 5 Features of male and female pathology
- 6 Modern diagnostic methods
- 7 Preparation for testing
- 8 Biomaterial sampling rules
- 9 Deciphering the results
- 10 Research cost
What is this disease
HPV (human papillomavirus) is a viral family that provokes the appearance of papillomas, warts, dysplasia, and can also give impetus to the development of oncological diseases of the genital organs (cervix).
In the modern world, HPV is the most common viral infection of the genital organs. Doctors know more than 100 strains of HPV, among which 30 are viruses of a highly oncogenic type, find out which HPVs of an oncogenic type in women , the rest are viruses of medium and low oncogenicity.
You can become infected with the papillomavirus not only through sexual contact, but also through everyday contact with a carrier or through common household items. In addition, the risk of transmission of the virus from an infected mother to the fetus is not excluded.
According to statistics, 80% of the world’s population is infected with the papilloma virus. Therefore, the chance of infection is very high. Therefore, doctors recommend regularly undergoing examinations for the presence of a virus in the body and, if necessary, conducting appropriate treatment that will keep the infection in a latent state.
When do I need to sign up for an examination?
Indications for analysis for HPV are:
- the presence of an actively multiplying growth on the mucous membranes and skin;
- discharge from the genital organs of an uncharacteristic type or erosive manifestations in the affected area;
- the presence of itching, pain, burning and other symptoms in the area of growth development;
- infertility, premature birth or frequent miscarriages;
- diagnosis of the pathogen in the sexual partner;
- the presence of casual and promiscuous sexual contacts;
- suspicion of the presence of a pathogen during a routine preventive examination.
In addition, testing for HPV is recommended if you have:
- warts;
- warts;
- tissue dysplasia.
How often should I be tested for papillomavirus?
Women under 30 are recommended to be tested for HPV 2 times a year. It is advisable for women and men over 35 years of age to undergo these studies once a year. See also material on the topic: HPV type 16, quantitative analysis, decoding .
How to find out the type of human papillomavirus?
As already mentioned, the classification of HPV is based on the degree of its oncogenicity. Virus genotyping is necessary to determine the severity of the pathology and select the optimal treatment regimen. Most often, PCR diagnostics and the Digene test are used for this purpose.
Features of male and female pathology
In women, the development of HPV can go unnoticed for a long time – against the background of inflammation of the genital organs – endocervicitis, pseudo-erosion, vulvovaginitis, in addition, the virus is almost always combined with other infections – trichomoniasis, herpes, chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea.
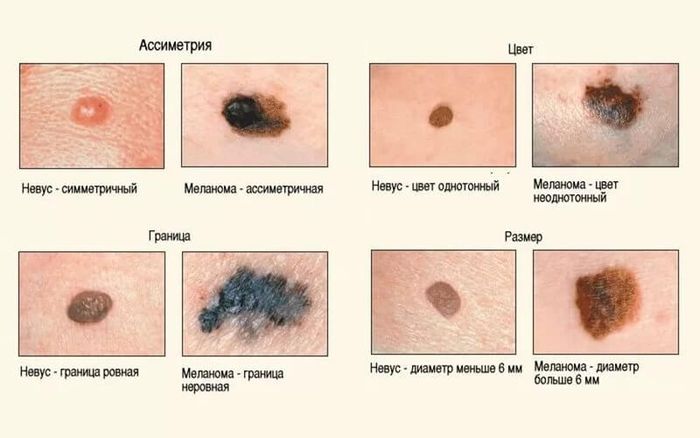
The clinical picture of the presence of a viral infection in the female body:
- burning and itching in the genital area;
- atypical discharge;
- difficulty and pain when urinating;
- discomfort and pain during intimacy;
- condylomatosis .

Warts can affect the vagina, vulva, urethra, cervix, rectum, anus, perineum.
In men, HPV is also a long time, it may not manifest itself in any way, and the man turns out to be only a carrier of the infection. Just like in women, HPV in men is combined with chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes and other sexually transmitted infections.
Signs in men:
- discomfort in the genital area;
- the presence of secretions;
- pain during urination and intimacy;
- condylomatosis.
Condylomas in men appear on the foreskin, on the frenulum, in the anus.
Modern diagnostic methods
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor refers the patient to a series of specialized tests. Women, before taking tests, should undergo a gynecological examination. Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary tests; it is not advisable to rely on the experience of friends and acquaintances in this matter.
The following analyzes are described in detail, with the help of which you can not only determine the presence of a virus in the body, but also find out its type and prevalence.
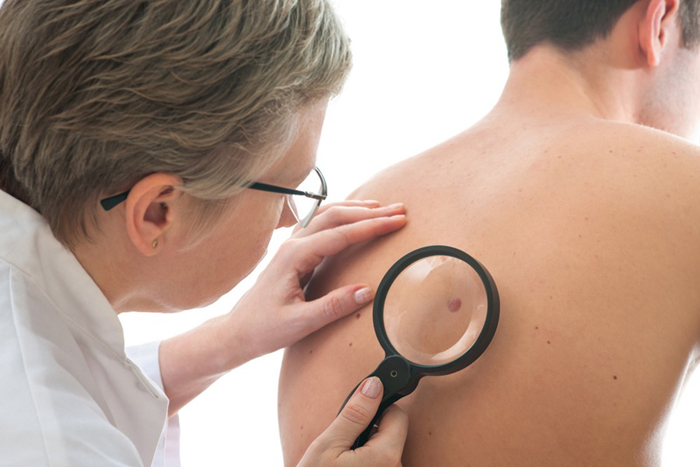
Screening for papillomavirus infection
During the clinical trial, the doctor examines the body and genitals of the patient (women are examined in the gynecological chair).
All manipulations should be carried out in good light. The primary task of a specialist is to distinguish viral elements from other diseases of the dermis and mucous membranes.
Quantitative Analysis
The quantitative determination of the virus is aimed at detecting the presence of pathology, as well as the degree of activity of the virus. These indicators are also needed to determine the level of oncogenicity of the virus.
The study is carried out by the polymer reaction method, and is mandatory in the absence of any symptoms due to the small number of viral agents in the human body.
Unlike qualitative PCR analysis, quantitative analysis not only gives a “negative” or “positive” answer, but also determines the concentration of viral agents. Without quantitative analysis, further diagnosis is considered useless.
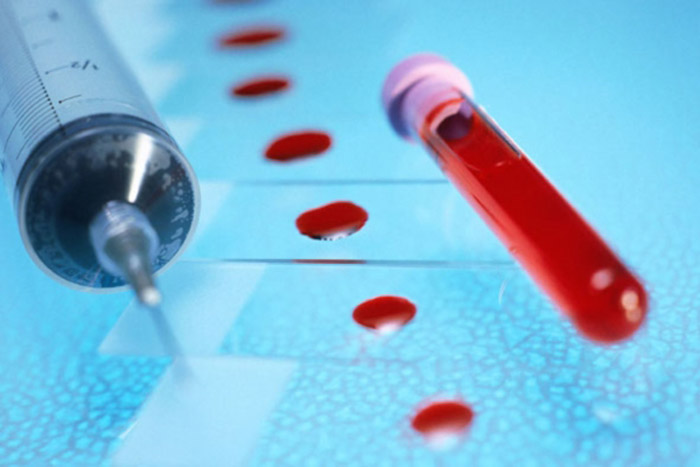
General analysis of blood and urine
It must be said that a general analysis of blood and urine cannot outstrip the presence of a pathogenic virus in the body. However, these tests are prescribed to identify concomitant sexually transmitted pathologies, since there are almost always several pathogens. A general blood test can determine the presence of the following pathologies:
- mycoplasmosis;
- chlamydia;
- HIV and others.
Find out also what HPV is, deciphering the results of the analysis
How is it carried out and what does PCR show
PCR for HPV is a very accurate diagnostic method, since in this case not traces of the presence of the virus are detected, but directly the DNA of the pathogen.
This analysis can be carried out on urine, blood, saliva and other biological fluids, but the most preferred material is a smear – in men from the urethra, in women from the cervix.
The smear is taken with a special brush and sent to the laboratory for examination, the result will be ready in three days.
If the analysis is carried out by blood, it must be remembered that blood for PCR is taken on an empty stomach. Urine for analysis must be collected in the morning, and it should be in the laboratory no later than 4 hours later.
For all types of analysis, it is necessary to give up sexual intercourse, alcohol and smoking in a couple of days. In addition, it is necessary to discuss with the doctor the use of medications and antiviral drugs, which can distort the picture of the disease.
Digene test
It is also an extremely sensitive research method, which can both detect the presence of a virus in the body, and establish its type, and determine the concentration of the virus.
The method has the following advantages:
- allows to detect 18 strains of the virus, of which 13 have a high oncogenicity;
- painlessness – a standard smear;
- relatively quickly you can get the results of the study;
- samples can be used for cytological examination;
- high precision and simplicity.

Antibodies
Papillomavirus in the blood is determined using enzyme immunoassay. This is a rather sensitive analysis and its results are very accurate.
The principle of the technique is the detection of antibodies to the human papillomavirus in the patient’s blood. At the same time, it is impossible to determine the strain of the virus. In fact, this technique only proves a person’s contact with a virus, which the immune system could well suppress.
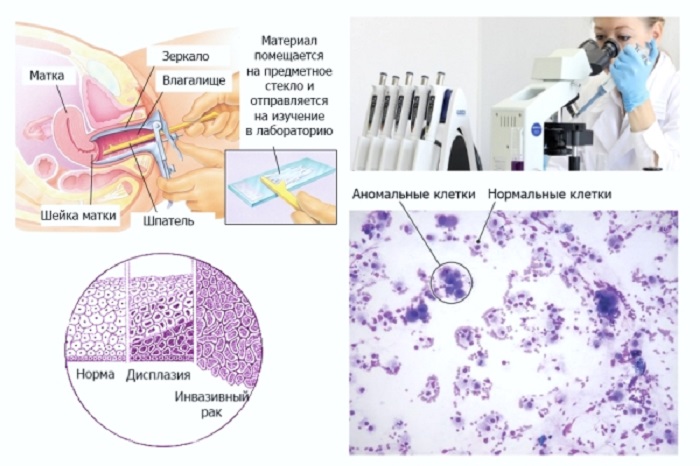
Cytological examination
For cytological examination, a smear from the cervix in women or from the urethra in men will be required. This method allows you to determine the presence of the virus, its type, number and changes in mucosal cells.
Colposcopy
With the help of colposcopy, it is impossible to determine the presence of a virus in the body, since this is not a laboratory analysis, but an instrumental examination of the vulva and cervix.
However, this method is often used in the diagnosis of HPV, since it can be used to obtain material for laboratory research, and in addition, to identify the presence of genital warts, precancerous changes and oncological processes.
Histological examination
To conduct a histological analysis, it is necessary to conduct a biopsy, it is necessary to obtain material for research.
Next, the specialist processes the sample with a special solution, resulting in a histological block. It is cut into thin slices.
Stained with dyes and examined under a microscope. This is a very important stage of the study, as it allows you to establish the presence of malignant cells with 100% certainty. The analysis will be ready in 10 days.
polymerase chain reaction
PCR can be carried out by 4 methods:
- A qualitative method is confirmation or refutation of the presence of a virus in the body.
- Genotyping is the determination of the type of virus. Also, this method is used to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
- The combined method is a highly specialized method that combines the two previous ones. It is most often prescribed for suspected presence of a highly oncogenic strain of papillomavirus.
- Quantitative – determines the concentration and development of the virus.
Preparation for testing
Of course, the preparation for the delivery of tests depends on which research method was prescribed by the doctor. The specialist should inform the patient in detail about the nuances of the preparatory stage.
If we summarize all the rules for preparing for HPV testing, they look like this:
- Stop taking all medications, especially antiviral drugs.
- A couple of weeks before the tests, review your diet, exclude fatty, smoked and spicy foods from it.
- Stop drinking alcohol for a few days.
- Do not smoke on the day of the test.
- On the eve of the test, try to reduce mental and physical stress.
- Before giving a smear, women are not recommended to urinate for 2 hours.
- For 3 days, women should exclude the use of intimate hygiene products that can have a bactericidal effect.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for 2 days.
Biomaterial sampling rules
Blood is taken on an empty stomach, the tube must be closed with a lid and turned upside down so that the blood mixes well with the anticoagulant. Blood can be stored for no more than 6 hours at a temperature of 20-25 degrees. If blood is taken for quantitative analysis, the storage temperature should not exceed 2-8 degrees Celsius.
For urine analysis, the first morning portion is needed in the amount of 15-20 ml. urine collection should be carried out only after a quality toilet of the external genital organs.
During menstruation, urine should not be collected. Storage conditions of the obtained material – no more than 3 days, in a sterile container at a temperature of 2-8 degrees Celsius.
Scraping discharge from the vagina, cervical canal or urethra is taken with a probe. The collected material is transferred to a sterile tube, which is tightly closed and labeled.
In some cases, biopsy material is required. In this case, it is collected from the source of infection. Pieces of tissue are placed in sterile test tubes, which are tightly closed and stored at room temperature for no more than 6 hours.
Deciphering the results
Only a doctor can interpret the results of HPV tests. Of course, normally the result should be negative. The results of PCR and Digene-test are calculated in the Lg coefficient, it indicates the relative amount of viral agents.
As for the antibody test, it is measured in IU / ml, and indicates how long ago the infection occurred and how strong the immune system’s response to the pathogen is.
Positive
If the result shows less than 3 Lg, this indicates an insignificant concentration of viruses, if 3-5 Lg is a clinically significant concentration, more than 5 Lg – a high content of viral infection.
If, when analyzing for the presence of antibodies, the result is IgM – this means that the body has been recently infected, IgG means that the virus has been in the body for a long time.
Negative
A negative analysis indicates that no detectable HPV strains were detected in the course of the above studies. This means that the person is not a carrier of the virus.
Research cost
Price depending on the research method:
- Digene test – about 5000 rubles.
- PAP – Digene-test – about 7,000 rubles.
- PCR – 1000 rubles.
The danger of the human papillomavirus should not be underestimated, despite the fact that not all strains of this infection have a high oncogenic index, many of them can lead to serious and fatal diseases.
It is possible to determine the oncogenicity of the virus only in the laboratory, so each person should regularly take the necessary tests and consult with a specialist. This is the only way to prevent the development of oncology and reduce the dermatological manifestations of the virus.