Содержание:
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What types of infection affect the female body
- 3 Causes and predisposing factors
- 4 Mechanism of infection
- 5 Clinical picture of the infection
- 6 What does the human papillomavirus look like?
- 7 Symptoms and main manifestations of papillomavirus in the female body
- 8 Why are neoplasms dangerous?
- 9 Diagnostics
- 10 Is it worth it to treat and how to cure papillomas?
- 11 What is papillomavirus therapy?
- 12 Disease prevention
- 13 Vaccination against papillomavirus
- 14 Conclusion
Introduction
The human papillomavirus causes pathological formations, papillomas, on the body. At first glance, the growths are completely harmless.
However, in some cases, they can become malignant and lead to a cancerous tumor. How to protect yourself from infection and whether it is possible to cure the disease, later in the article.

What types of infection affect the female body
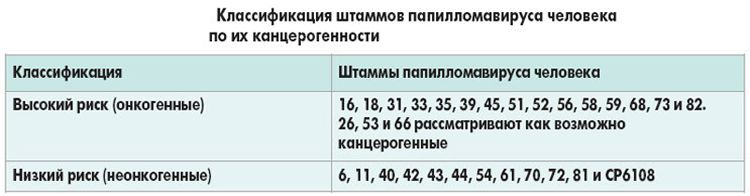
Specialists distinguish human papillomavirus by the degree of oncogenicity, which of them:
- Oncogenic . The group includes HPV types 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. They never cause cervical cancer. HPV oncogenic type in women .
- Low degree of oncogenicity . This includes 6, 11, 42, 43, 44 types of the virus. On their own, they are not capable of causing a malignant neoplasm in the cervix, vulva, or anus . However, they can become fertile ground for cancerous tumors.
- High degree of oncogenicity . This is the most dangerous group. It includes HPV types 16, 18, 31 , 35, 39, 45, 51 , 56 , 59 and 68 . Infection in four out of five cases causes a malignant neoplasm of the cervix, vulva and anus, and also provokes the risk of developing breast cancer.
Causes and predisposing factors
The causative agent of papillomatosis is the human papillomavirus. This is a DNA-containing virus that penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin. There are predisposing factors that contribute to the development of infection:
- congenital and acquired immunodeficiency;
- the first year after pregnancy (mother’s immunity is noticeably reduced due to changes in hormonal levels);
- early onset of sexual activity;
- promiscuous intimate relationships, accompanied by frequent changes of partners;
- casual sexual intimacy;
- HIV infection;
- acute viral diseases;
- chronic pathology of the reproductive system;
- diabetes;
- bad habits;
- immunosuppressive therapy;
- frequent abortions;
- STDs;
- long-term use of COCs.
Any of these factors are risk factors for infection. Read also: HPV pills , an overview of effective drugs.
Mechanism of infection
The disease can be transmitted in several ways. These include:
- Sexual : during unprotected traditional, anal and oral sex, as well as petting.
- Transplacental : when the child passes through the birth canal of the mother.
- Contact household : through a handshake, personal hygiene items, household items.

Clinical picture of the infection
Papillomatosis often occurs hidden and is detected during a routine examination. A sick woman should not ignore the following symptoms:
- burning in the genitals;
- spotting outside the menstrual cycle;
- the appearance on the skin and mucous membranes of painless neoplasms in the form of warts, genital warts.
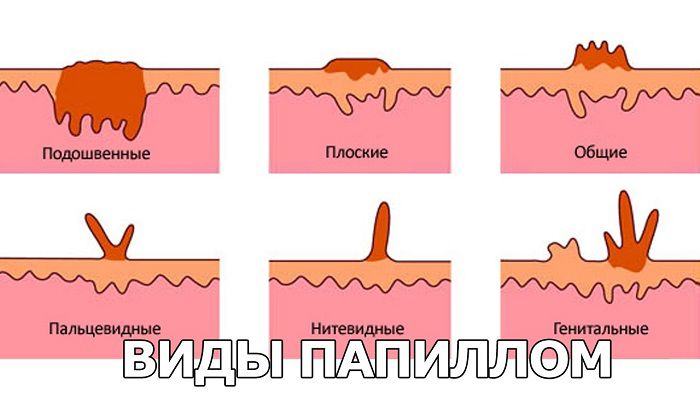
What does the human papillomavirus look like?
HPV takes the form of the following neoplasms:
- Warts . These are rounded pale pink growths with a harsh structure and a rough surface, having a diameter of 2–10 mm. Their boundaries are clearly marked. The formations are painless and do not cause discomfort. Usual localization – places with increased skin trauma (hands, knees, elbows).
- Plantar warts . Formed when HPV is infected in areas where shoes rub or squeeze the feet. The skin at the site of the growth becomes thick. The wart does not have clear contours.
- Pointed warts . Appear on the mucous membranes and skin of the reproductive organs – the labia, cervix, vagina. Sometimes the virus enters the bladder, urethra, anus and mouth, forming growths there. The appearance of such neoplasms can be compared with cauliflower. They are convex, have uneven edges.
- Bowenoid papulosis . They are small flat outgrowths. Most often they are localized in the genital area.
Symptoms and main manifestations of papillomavirus in the female body
Depending on the type of neoplasm, the infection takes on certain characteristic signs. More about them below.
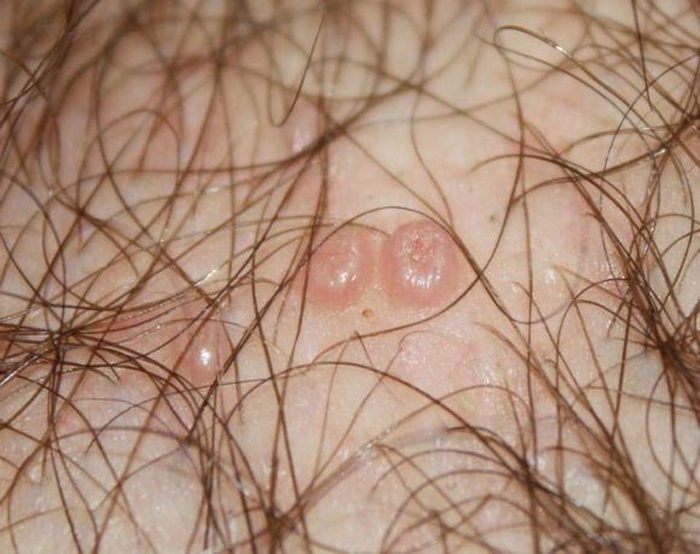
Papillomas
On examination, the doctor determines pinkish growths rising above the surface of the skin. They do not bother the patient at all, because they do not cause pain or discomfort. A woman may be disturbed by aesthetic discomfort, since the formations protrude ugly on the skin.
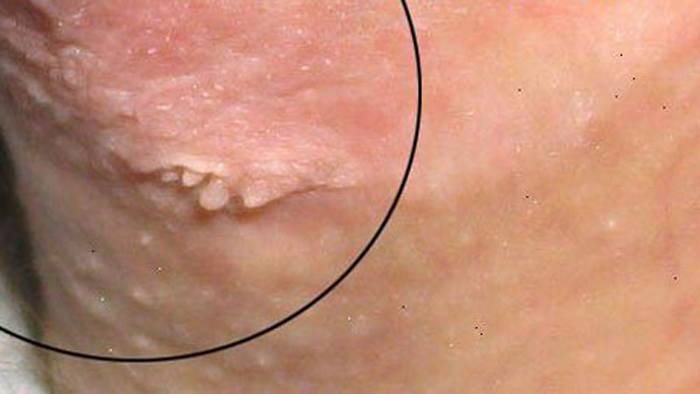
genital warts
They are pinkish-brown formations from the papillary layer of the dermis, having a thin leg. They are located in the anogenital region. Can be placed in groups or singly. Warts have a bumpy surface and uneven edges, which is why it is compared to cauliflower.
With the growth of the neoplasm, the woman feels unpleasant symptoms:
- When localized in the area of the labia, the clitoris, the patient feels itching in an intimate place. She feels discomfort while moving. In the intermenstrual period, blood comes out of the genital tract or after intimacy. Over time, a greenish-yellow or milky discharge with an unpleasant odor appears.
- When genital warts appear in the lower gastrointestinal tract, there is pain during defecation and blood.
- If they are located in the urethra or bladder, a woman is worried about frequent urination.
- The lymph nodes in the body may be enlarged.
Why are neoplasms dangerous?
Papillomatosis is not a harmless disease. In some cases, they threaten serious consequences:
- Oncogenic types lead to dysplastic processes, and this is a precancerous pathology. According to statistics, 10% of cases of papillomatous neoplasms lead to the development of genital cancer. In addition, the disease can provoke a malignant tumor of the breast.
- The human papillomavirus is a favorable environment for the attachment of sexually transmitted diseases.
- With frequent trauma, a secondary bacterial microflora may join, which will lead to an inflammatory process.
- During childbirth, it is highly likely that a sick mother infects the baby as it moves through the birth canal.
Diagnostics
To identify the disease, you need to carry out the following methods:
- A routine gynecological examination reveals growths on the skin of the labia, clitoris, and vagina.
- To examine the cervix, the doctor performs a colposcopy. This examination of the cervical region using special equipment. An extended colposcopy is usually done because it can detect cervical cancer. During the study, the doctor may take the material for a biopsy.
- PCR: is the “gold standard” of diagnostics. This is the most accurate method that confirms the presence of HPV and determines the number of viral bodies in a woman’s body. If the doctor knows the number of the virus, he can estimate the likelihood of a malignant neoplasm in the cervix.
- Cytological examination reveals the type of HPV and its oncogenicity.
- A smear from the vagina and cervix on the flora: used to identify concomitant pathologies (syphilis, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis).
Is it worth it to treat and how to cure papillomas?
If oncogenic papillomas or genital warts are detected, their formation should not be ignored. It is important to undergo timely and complete therapy. This will avoid dangerous consequences. Find out how papillomavirus infection is treated in women, drugs , a review of funds.
What is papillomavirus therapy?
The doctor selects a scheme depending on the type of pathology and concomitant diseases. The principles of human papillomavirus treatment are the removal of genital warts and growths, antiviral therapy, and an increase in immune forces.
For precancerous processes, it is necessary:
- medical correction;
- physical and chemical removal (laser, liquid nitrogen, cauterization).
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with very interesting material on the topic: papillomavirus, treatment, drugs .
Surgical removal
Removal of neoplasms with a scalpel is carried out less frequently compared to modern methods of treatment (radio wave excision, laser coagulation, diathermocoagulation).
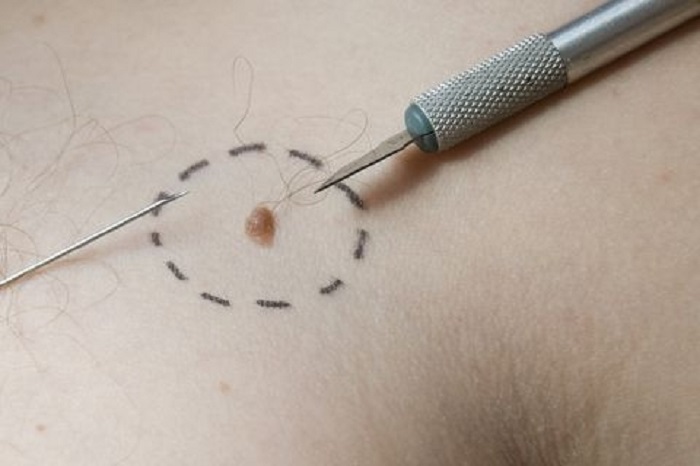
This is due to the fact that surgical removal is accompanied by scarring, pain and a long postoperative period. Most often it is prescribed for the treatment of malignant neoplasms caused by HPV.
Immunomodulators for papillomavirus
Medicines in this group restore and support the immune system. They prevent the development of the viral process. Read also human papillomavirus infection, treatment drugs , a review of effective drugs.
For these purposes, the attending physician prescribes:
- Grippferon.
- Ribomunil.
- Derinat.
- Ingavirin.
- Cycloferon.
Antibiotics
Since the drugs of this group are powerless against a viral infection, their use is not required. However, when the bacterial microflora joins with the development of the inflammatory process, the doctor can prescribe them. Usually assigned:
- synthetic penicillins (Panklav, Amoxiclav);
- cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, cefazolin);
- fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin).
Local preparations
Allows you to directly influence the neoplasm. For treatment appoint:
- candles;
- solutions;
- ointments.
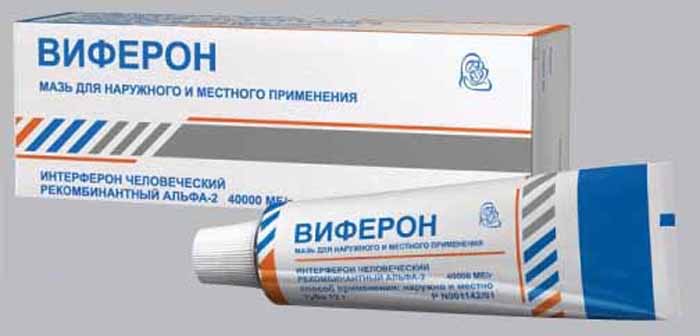
Candles
The doctor may prescribe this form of drug release:
- Viferon.
- Ganferon.
These are antiviral suppositories necessary for non-specific protection of the body against HPV.
Ointments for papillomavirus infection
Used for topical application. Can be used for antiviral protection, providing antimicrobial action.
- Solcoderm : the composition contains a complex of acids (oxalic, acetic, nitric and lactic). Usually use the ointment after surgery. For 1 procedure, an area is processed, the size of which does not exceed 5 cm.
- Bonafton : used twice a day for two weeks, an ointment is applied to the affected area and kept for about 10 minutes. Local treatment should be combined with taking pills.
The following drugs may also be prescribed:
- Viferon.
- Oxolinic ointment.
- Salicylic ointment.
- Clareol .
- Vishnevsky ointment.
- Levomekol.
Cytostatics
These are drugs that inhibit pathological cell division. They are applied topically to skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus. What is usually given:
- podoxifylline : comes in the form of a cream. Apply to the affected area 2 times a day for three days;
- 5-fluorouracil : used as a cream to treat genital warts.
Since the causative agent of growths is a virus, drugs in this group affect the body’s defenses against this infection.
Most often, Aldara and Keravort ointment is prescribed. Apply a thin layer to the affected area before going to bed. A day later, the procedure is repeated. The course of therapy is 7 days.
The doctor may prescribe systemic antiviral drugs ( Panavir ). The drug inhibits HPV protein synthesis and promotes the production of endogenous interferon.
The product is produced in the form of ampoules. It is administered intravenously according to the scheme: in the first week – every 3 days, in the second – every 4 days.
Folk methods
Alternative therapy can be effective in removing growths. The main thing is to carry it out strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Celandine juice
Cut off the stem of the plant closer to the root. It must be squeezed, and the resulting drop should be sent to the neoplasm. After 2-3 days, it should fall off on its own. If this does not happen, the procedure is repeated.

potato juice
Take 1 young tuber. Wash it thoroughly and chop finely. The mass is then strained to obtain potato juice. Use the product until the build-up falls off.

Ammonia
Take a band-aid and cut a window in it. It must fully correspond to the size of the neoplasm. The patch is glued in such a way that the growth is in the hole, and all surrounding tissue is protected.
A cotton swab is dipped in ammonia. After 5 sec. press it to the papilloma. The procedure is repeated once a day until the build-up darkens and decreases in size.
Fir oil and celandine
The ingredients are mixed with each other in a ratio of 1:1. Then the resulting product is applied to the papilloma. The procedure is repeated 2 times a day until the build-up decreases in size.
Disease prevention
Preventive treatment is indicated for women with a burdened heredity for malignant tumors and a high concentration of antibodies to HPV. If the normal epithelial structure is disturbed, therapeutic measures are prescribed.
Doctors distinguish between active and passive prevention of the disease. The first is vaccination, and the second is non-specific measures.
Recommendations to reduce the chance of infection:
- Have sexual intercourse with a barrier contraceptive, do not lead a promiscuous intimate life.
- Eliminate their life of bad habits.
- Conduct regular intimate hygiene.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Get a gynecological exam at least once a year.
- If the mother has genital warts, perform a caesarean section so as not to infect the child.
- Treat common diseases and sexually transmitted infections in a timely manner.
- Take a break from taking COCs (strictly under the supervision of your doctor!).
Vaccination against papillomavirus
The procedure is desirable for girls 12-14 years old. If done even later, the effectiveness of the vaccination is significantly reduced. Two vaccines have been developed against HPV: Gardasil and Cervarix .
Gerdasil reduces the likelihood of infection with HPV types 16, 18, 6 and 11. Cervarix protects against types 16 and 18 of the human papillomavirus.
Conclusion
Depending on the type of HPV, it can be oncogenic or non-oncogenic. When a woman notices papillomas or warts on her body, she should immediately consult a doctor. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infection. Also read how HPV drugs are treated .







Лечите ВПЧ не ждите онкопроцессов. Мне своевременно помог Аллокин-альфа.