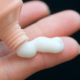
Treatment of a virus that forms rashes and tumors in intimate places is an important measure for the safety of the health of one’s own and those around them. No one is immune from an infection that can be transmitted by household means and not show its symptoms for a long time.
Compliance with the rules of hygiene and other precautions will avoid the formation of genital warts, which are a signal of infection with the human papillomavirus .
Содержание:
- 1 What does a genital papilloma look like?
- 2 How common are they?
- 3 Why do they appear?
- 4 Where do growths most often appear?
- 5 The danger of papillomas on the genitals
- 6 Symptoms
- 7 Diagnostics
- 8 Treatment of genital papillomas
- 9 How to get rid, remove the build-up at home?
- 10 Removal in the clinic
- 11 Medicines for the treatment of HPV
- 12 Measures to prevent condylomatosis
What does a genital papilloma look like?
It is a formation in the form of a mushroom, which is based on a leg and a wider area adjacent to it. The main causative agent of this infectious disease is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is transmitted to a healthy body through any contact with the mucous membrane of an infected person.
The infection has a long incubation period. Under unfavorable conditions for the reproduction of the virus, latent existence can last up to several decades. When the granule is activated, rapid cell replication occurs, resulting in the formation of a nipple-like growth. Its color may differ from the color of the surrounding skin or mucosa. The size of the vulvar condyloma varies greatly and can reach 15 cm in length. The forms of genital rashes also differ significantly.
They are divided into types:
- Pointed.
- In the form of spots.
- in the form of papules.
- Bowenoid papulosis and Bowen’s disease.
- Giant condyloma of Buschke-Levenstein.
- in the form of neoplasia.
Genital warts look like flesh-pink vesicles that are attached to the skin with a thin stalk. As a result, cone-shaped processes are formed. Usually each of them grows up to 1-3 mm in length.
Wide condylomas have an extensive leg and are a sign of secondary syphilis. The lesion in the form of a spot is gray-white, pink and brown, and is not recognized by touch. Papules are warts bundled into nodules. They are more rounded and smooth.
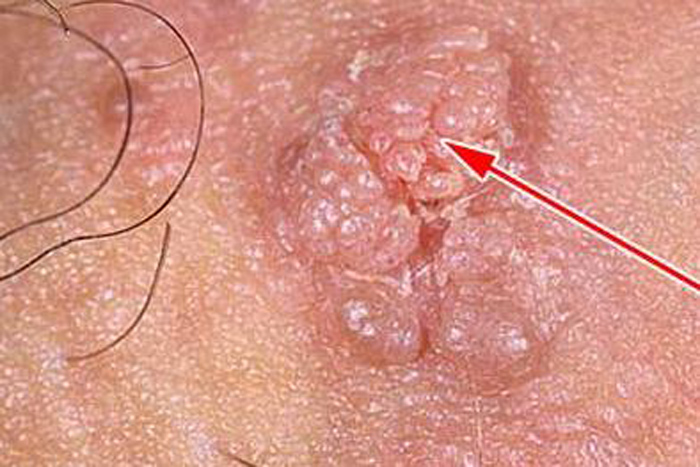
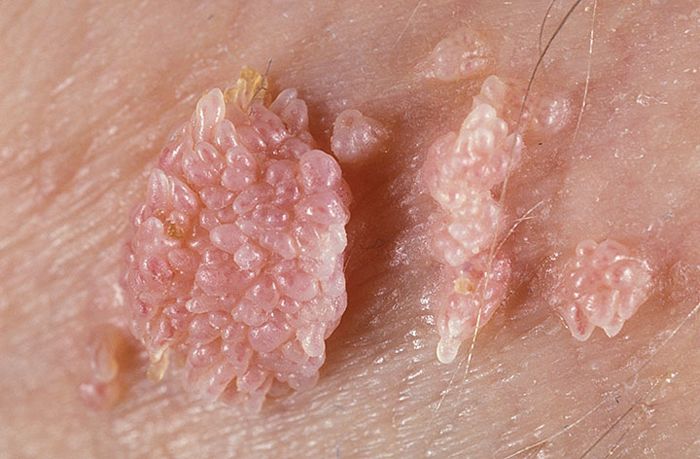
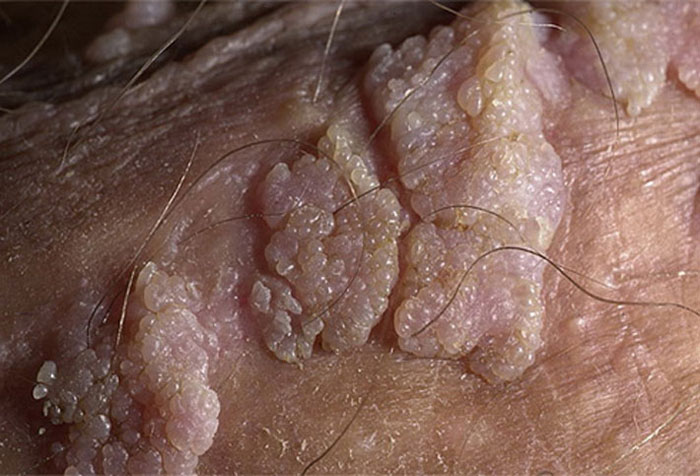
Bowenoid papulosis is a consequence of the growth of wart nodules and spots. It is characterized by a velvety moist surface layer. On the mucous membranes, the formations acquire red and brown shades, and on the skin – gray, brown or even black.
Giant condyloma Buschke-Levenstein is formed as a result of the merger of many viral growths. Their cells can affect the entire surface of the genitals and nearby tissues. In this case, the disease passes into the stage of squamous cell carcinoma.
Neoplasia is otherwise called a tumor. A neoplasm appears as a result of a mutation in the genes of the virus. The accumulation of warts form a large surface of the affected area under the influence of accelerated tissue growth.
How common are they?
Estimating the prevalence of HPV is difficult. In most cases, the symptoms of infection are hidden, and patients seek help if genital warts appear in the active phase of virus reproduction. As a result of a study conducted by American scientists, data were published on the presence of HPV in 74% of the US population.
Among volunteers aged 15 to 49, only one in four Americans was not infected. In Russia, every third person is a carrier of the virus. This confirms the fact that people are illiterate and do not know about such a disease, continuing to spread it covertly.
Based on this, there is an assumption that anyone who has ever had sexual intercourse can be infected. In the US, papillomavirus is the second most expensive diagnosis and treatment after AIDS. Natural immunity copes with the infection within 2 years in 90% of cases. According to statistics, the appearance of genital warts occurs in only 1% of the sexually active population.
Why do they appear?
The main factor in the manifestation of the virus is the poor functioning of the immune system. An additional factor is considered vaginal, anal or oral intercourse with an HPV carrier.
Also, condylomas are formed as a result of a kiss, household contact, or when the virus enters the mucous membrane and skin through microtrauma. Now HPV includes 27 different types and more than 600 strains, 40 of which cause damage to anogenital sites.
Where do growths most often appear?
The practice of treating warts gives the following statistics on the formation of warts:
Among women:
- Cervix.
- Anus area.
- The mucous membrane of the vagina.
- At the edge of the urethra.
- Upper and lower labia.
- Pubic and lower abdomen.
- Mouth and lips.
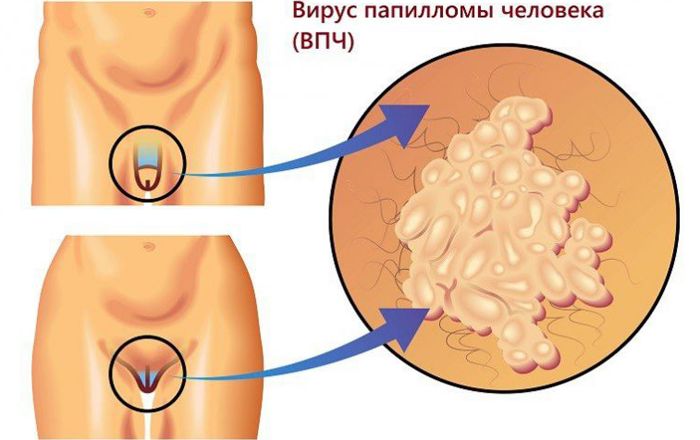
For men:
- The head of the penis.
- Scrotum.
- Anus area.
- The area of the urethra.
- Pubic and belly.
- Mouth and larynx.
Separate warts on the pubis , scrotum, labia do not cause pain, but only make them look unaesthetic. Others, on the contrary, can not only cause a lot of inconvenience, but also cause severe itching. Growths in the anus, urethra can provoke infection through ulcers and cracks. The area of the vagina and penis often bleeds during intercourse and emits a rotting odor.
The danger of papillomas on the genitals
Papillomavirus is not dangerous to the body and can be cured by the immune system. However, the growths (papillomas, condylomas) of some strains modify their DNA, as a result of which the tumor is transformed into a malignant one. The risk of complications is high.
With poor nutrition, poor lifestyle, chronic diseases and stress, neoplasms can develop into cancer. Currently, the most common type is cervical cancer in women and penile cancer in men. The presence of oncopapillomovirus is detected in the laboratory. Outwardly, the development of cancer is indicated by the growth of genital warts on the skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms
- The formation of wart vesicles and spots.
- Discomfort in the intimate area.
- Itching and burning.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Bad smell in sepsis.
- Swelling and redness in case of warts injury.
- No symptoms in the inactive phase.

Diagnostics
To detect HPV, a blood test for antibodies is performed in the latent course of the disease. Reception begins with a clinical examination of the patient. In case of detection of genital warts, a gynecological examination and a cervical smear or ureteroscopy are prescribed.
Sometimes the help of a cytologist is needed to conduct a PAP smear test of the cervical mucosa. It is able to detect changes in the structures of low-risk oncoviruses. Colposcopy and biopsy can determine the stage of infection and the risk of developing cancer. Histological examination based on biomaterials determines the pathology with an accuracy of up to 98%. The final stage is HPV typing in its presence. The latest development was the digene test.
It completely characterizes the virus, starting with typing, ending with determining the degree of risk of oncological disease and concentration in tissues. In the presence of warts, the patient undergoes an abbreviated list of examination methods, the main purpose of which is to recognize the strain and classify the risk.

Treatment of genital papillomas
It is based on the observance of 3 stages recommended by the doctor:
- Removal of growth.
- Taking antiviral drugs.
- Strengthening the immune system.
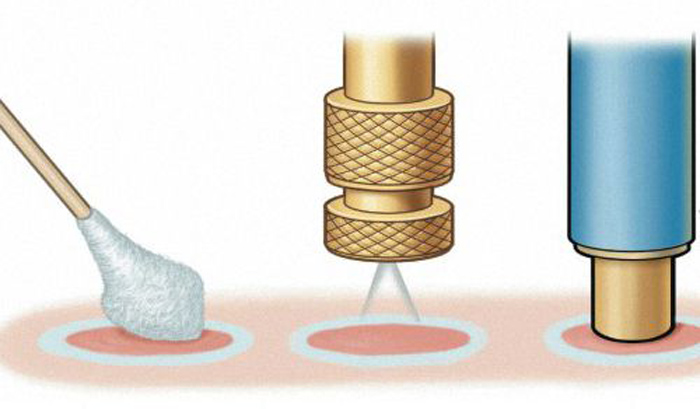
The process of removing genital warts is carried out in different ways using local anesthetics:
- Surgical scalpel.
- Laser coagulation.
- Radio wave method and ultrasound.
- Cryodestruction.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Diathermocoagulation.
Surgical removal is allowed with a large size of condyloma. The skin area is then tightened with medical threads. The dissection of growths with a laser leaves almost no wounds and occurs without pain.
The radio wave method involves burning out condyloma with the Surgitron apparatus. Delamination occurs under the action of high-frequency waves. The cost of the procedure guarantees the absence of complications. Ultrasound is also the safest method.
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen as the active ingredient. Frozen condyloma falls off, leaving a small wound. Electro- and diathermocoagulation burn out formations, but leave scars on the skin. These methods are not recommended for nulliparous girls.
How to get rid, remove the build-up at home?
At home, you can use methods that contribute to the death of genital warts. Safe are:
- Iodine.
- Celandine.
- Garlic.
- Onion.
- Honey and propolis.
- Apple vinegar.
- Egg white.
Iodine effectively cauterizes warts with repeated use. Over time, they dry out and fall off. In this case, only the affected surface is wetted. The course is repeated 2 times a day. Together with iodine, antiseptics are used to heal the resulting wound.
Celandine in the form of tincture or freshly squeezed helps to neutralize the vital functions of the build-up. The condyloma dies and falls off along with the leg. The composition is applied 3 times a day.
The juice of garlic and onion is detrimental to pathogenic microorganisms, it contains a lot of tannins and antiseptics. Papillomas disappear quickly and painlessly. When mixed with vinegar, compresses are of the highest quality.
A compress of aloe vera juice, honey and plantain leaves is considered the most effective remedy. It is kept for 15 minutes 2 times a day. Propolis can simply be placed under the plaster to dry the skin. After 14 days, the desired result will appear.
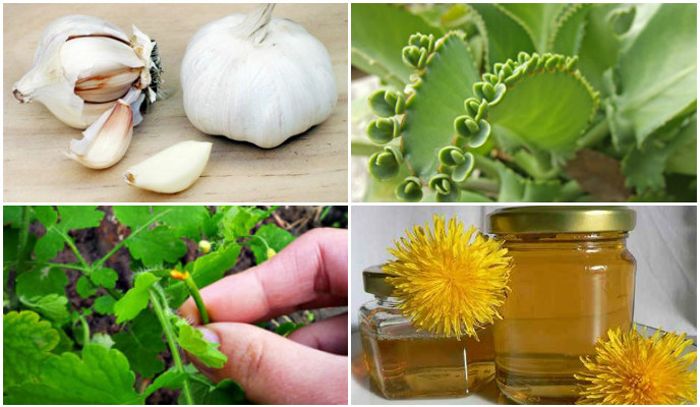

Apple cider vinegar is applied at night, with proper use, condyloma disappears in a week. Boiled egg white helps to reduce the size of genital warts. In the fight against the removal of external manifestations of HPV is not suitable.
Removal in the clinic
Patients are pre-diagnosed to identify the type of virus and its origin. For this, various methods of laboratory analysis of biomaterial are used. Women are additionally prescribed colposcopy and cytological examination.
After receiving the test results, therapy is prescribed depending on the complexity of the disease. Today, medicine is replete with a variety of physical and surgical methods for removing genital warts. Most often, they resort to the use of a laser, ultrasound, and more conservative methods.
Everything happens on an outpatient basis with the use of painkillers. Along with this, a course of antiviral and immune drugs is prescribed. In case of recurrence, re-extraction is carried out. Often combined methods of therapy to achieve the desired result.
Medicines for the treatment of HPV
Treatment of HPV is carried out in a complex with the use of:
- antiviral drugs topically and in the form of injections;
- medicines with chemical compositions;
- immunomodulators and vitamins;
- antibiotics;
- cytostatics.
Often, patients need the help of several doctors, usually a gynecologist, venereologist, dermatologist. Antiviral vaccination is considered a more effective method than tablets, suppositories and ointments. However, among the antiviral drugs, isoprinosine ( analogues of isoprinosine ) and groprinosine are isolated in the form of tablets. They fight the virus and stimulate the immune system, as a result of which the external manifestations of HPV disappear.
Panavir (candles, injections) and ointments based on acyclovir are widely used . They act on the skin without complications. Chemical compounds are designed to burn papilloma and do not eliminate the problem of the presence of the virus. Apply locally. Condilin and ferezol in the form of solutions dry the affected area well, the disadvantage is removed only externally.
Immunomodulatory drugs help suppress the growth of formations and prevent relapse. Neovir, viferon and licopid are used most often. Their action also prevents the development of oncoviruses. Antibiotics are prescribed in case of inflammation and in the presence of sexually transmitted diseases. A wide range of their action adversely affects the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition to them, formulations with bifidobacteria are taken.
Cytostatics are prescribed when precancerous warts are detected. The most aggressive drugs are 5-fluorouracil, podophyllin, bleomycin, and podophyllotoxin. All of them are aimed at destroying the development of cancer cells.
Measures to prevent condylomatosis
Anogenital condylomatosis is a disease characterized by the accumulation of genital warts in the anus and genitals. In appearance, the formation resembles a cauliflower. It is caused by HPV of certain strains. Therefore, there are no specific preventive measures against infection.
Protection during sexual intercourse does not protect a person by 100%. Also, the pathogen is transmitted through any household contact when it enters the body. The only method that prevents the development of condylomatosis is the vaccination of children before puberty. Additional precautions include maintaining immunity, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and maintaining personal hygiene.
Condylomas are benign formations. Consultation and their treatment are obligatory. Any external factor can provoke the virus to modify, resulting in the formation of cancerous metastases. Modern medicine copes with the manifestation of the virus both externally and at the molecular level.