A wart that appears on the pubis can bring much more trouble than the spoiled appearance of the intimate area. If you do not want small papillomas to cause big problems, give them a little more attention.

Содержание:
Pubic warts in men and women: where does the attack come from?
The cause of warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which can only be obtained through contact with the skin and mucous membranes of an infected person.
But this does not mean that growths appear instantly. You may not notice signs of infection until the time is right for infection.
Appearance of neoplasms
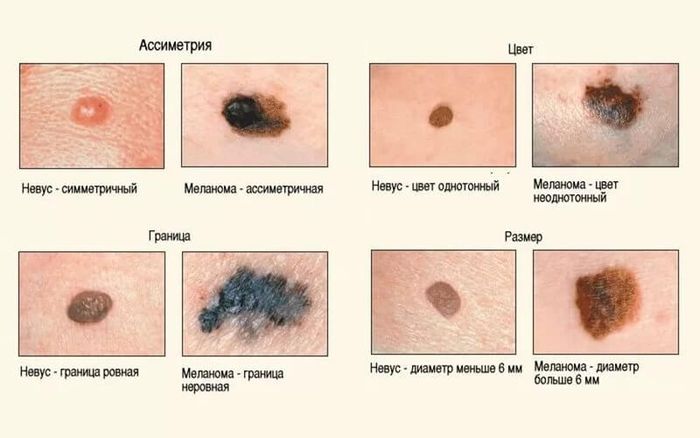
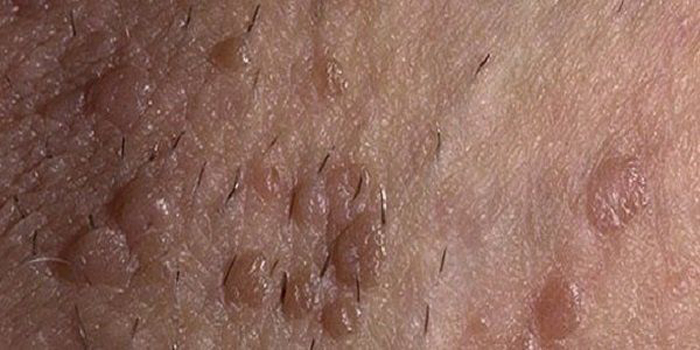
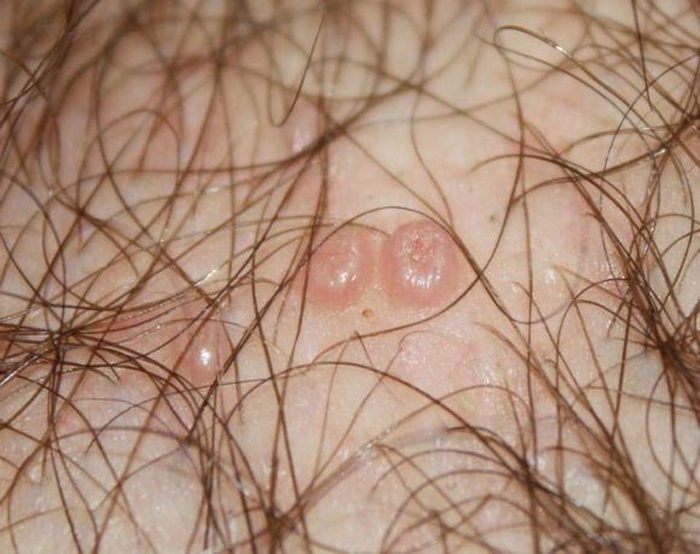
Warts that appear on the pubis and genitals are not like small growths from 2 to 5 mm in height and approximately the same diameter. Color varies from flesh to dark brown. The growths can be single or form a large conglomerate.
Reasons for the appearance
Genital warts have a long incubation period, so they may appear to have appeared for no reason. But the appearance of warts on the pubis and genitals always indicates HPV infection, which occurs only from an infected person.
Most often, this problem occurs in those who are promiscuous or forget about protection during intercourse with an unfamiliar partner.
If you’re just starting a relationship, it’s a good idea to get tested for HPV before you stop using condoms.
Here are the main causes of papillomas on the pubis and in the genital area:
- Touching infected skin or mucous membranes.
- Sexual contact with an infected person. You can become infected through both vaginal and oral contact.
- If the mother is infected with the virus, it will be transmitted to the child at the time of birth.
- Use of personal hygiene products for the patient (towels, razors).
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Even if a person has become a carrier of HPV, this does not mean that the disease must manifest itself in the future. But if the virus is activated, it is expressed in the following symptoms:
- Burning and pain (typical for men).
- Itching (typical for women).
- Painful cracks in the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
- The appearance of papilloma.
- When the vagina is affected, unpleasant sensations appear during intercourse.
- If papillomas appear in the urethra, this can cause difficulty in the process of urination.
To diagnose the disease, you need to consult a doctor (a woman to a gynecologist, a man to a urologist). The doctor will conduct an initial examination and prescribe additional tests to establish an accurate diagnosis, and to make sure that the detected formations are of good quality.
Types of additional examination:
- Histological examination. It is necessary to obtain general information about the origin of papilloma. With this analysis, you can determine whether the formation is benign or cancerous.
- PCR diagnostics. The most modern and effective method to accurately determine the type of virus.
Types of genital formations
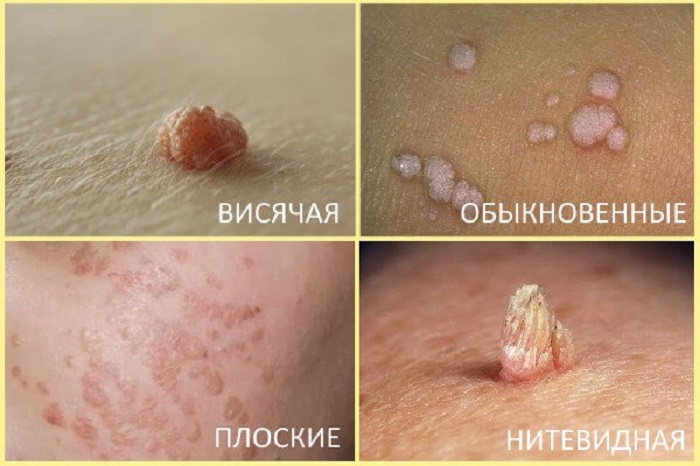
Two types of warts may appear on the pubis: filiform papillomas (acrochords) and pointed warts (or condylomas).
- Filiform . Their size does not exceed 5 mm and look like small papules. Sometimes they grow on a thin stalk. May be flesh or brownish.
- Pointed . Usually their size does not exceed 2 mm. They have a lobed structure and outwardly resemble small papillae or a cockscomb growing on a thin stalk. They are pink or flesh in color.
What diseases can growths indicate?
Genital papillomas appear only under favorable conditions for the activation of the HPV virus. And this happens with a decrease in immunity and hormonal failure in the body, against which these diseases develop:
- Metabolic disease.
- Diabetes.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Benign or malignant tumors.
- Osteoporosis.
- Various gynecological diseases.
- Infertility.
- Immunodeficiency.
- STIs affecting the genital mucosa.
It happens that HPV is activated when helminths appear. This leads to the following problems:
- Giardiasis.
- Enterobiasis.
- Ascariasis.
Are pubic growths dangerous?
Below we will separately consider each possible case when warts may appear and the danger they can carry.

For men
Genital papillomas can lead to viral prostatitis and the appearance of malignant tumors. If warts grow in the urethra, it may lead to surgery to remove them. See also: wart on the penis , effective treatments
For women
The danger of HPV for women in the first place is that the virus can develop directly in the vaginal mucosa, which will allow it to remain invisible for a long time. This can lead to cancer of the uterus or ovaries, and as a result, long-term treatment and surgery.
During pregnancy
Genital papillomas on the body of pregnant women do not differ in anything special. Such warts are most often small in size and flesh-colored. For the future baby, such formations are not harmful.
If the papillomas are located directly in the vagina, there is a chance that the child may become infected with HPV at the time of birth. But most often, the immune system of the newborn is quite strong, and easily copes with the virus.
In rare cases, a baby who received the HPV virus from the mother may develop neoplasms directly on the respiratory tract.

In what cases should you seek medical help?
If you find warts on the pubis or genitals, in any case, you should consult a doctor who will conduct all the necessary tests. This will eliminate the possibility of dangerous consequences of the neoplasm.
Should they be removed?
Treatment of intimate warts is a whole range of activities, part of which is their removal. But the most important thing in this process is a decrease in HPV activity. The process of getting rid of genital papillomas is divided into 3 stages:
- Prevention of virus replication by taking antiviral drugs.
- Strengthening immunity with the help of immunomodulatory drugs.
- Removal of papilloma.
No one is immune from the appearance of intimate warts. But since they can be a symptom of unpleasant diseases, you should not delay a visit to the doctor when they appear. The sooner you start treatment, the more chances to avoid unpleasant consequences.