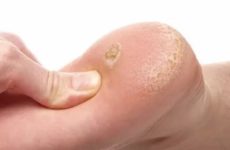
Genital warts are small growths located on the skin or mucous membrane of the genital organs. Doctors call them warts.
They appear and actively grow when the human papillomavirus is activated – the vast majority of people on the planet are infected with it.
These neoplasms cause not only physical, but also psychological discomfort, so their owners are interested in solving the problem as soon as possible.
Содержание:
- 1 What it is?
- 2 Varieties
- 3 Are tumors oncogenic?
- 4 Risk factors and causes
- 5 Methods of transmission of the virus
- 6 Places of localization of neoplasms
- 7 Characteristic symptoms and manifestations
- 8 What are dangerous for human health
- 9 Do I need to see a doctor
- 10 Diagnostic methods
- 11 Features of treatment
- 12 Prevention of the onset of the disease
What it is?
Intimate warts do not occur just like that, the main reason is the infection of a person with the papillomavirus, which occurs during unprotected sexual contact with a virus carrier.
The virus may not be activated immediately, for this it needs certain conditions, as a rule, this is a decrease in human immunity, hormonal disorders, pregnancy, and so on.
Varieties
Genital warts are classified as follows:
- Anogenital or genital warts . These are flesh or red structures, which can be either single or multiple. They are easily injured and grow very quickly, uniting in groups and forming growths resembling cauliflower.
- Papillary – smooth and round warts that slightly rise above the surface of the skin. Most often observed on the labia of women.
- Bushke-Levenshtein condylomas or giant warts are uncommon. They are characterized by rapid growth and destruction of surrounding tissues. In some cases, this pathology can transform into a malignant neoplasm.
- Flat warts are mostly asymptomatic, and very rarely accompanied by itching or discharge. The most common localization of such neoplasms is the vaginal mucosa or cervix in women.
Are tumors oncogenic?
As you know, the papilloma virus can be of various types, which are classified into:
- non-oncogenic strains;
- strains with a low oncogenic index;
- highly oncogenic strains.
Depending on the strain, outgrowths with different oncogenic claims appear on the skin and mucous membrane of a person.
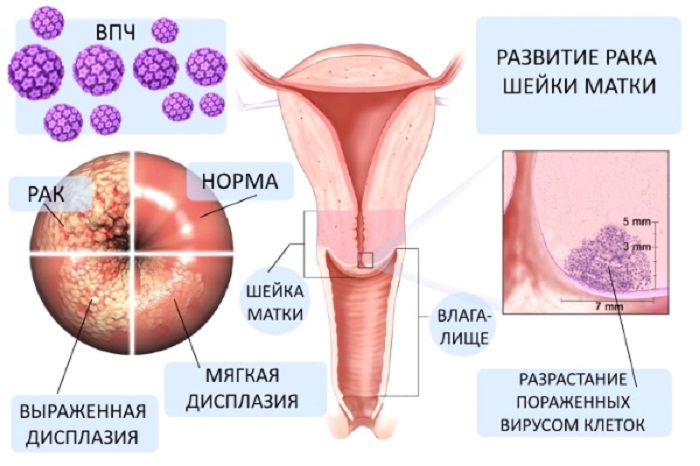
In most cases, genital warts have a low oncogenic index, that is, in fact, they are benign, but under certain conditions they can transform into a malignant neoplasm.
Risk factors and causes
Genital warts appear with a frequent change of sexual partners, as well as after sexual infections. In women, their appearance can be triggered by pregnancy and childbirth, vaginal dysbacteriosis, and weakening of the immune system.
In men, the appearance of genital warts most often occurs when the body is not able to resist the infectious process, that is, with strong immunity, the manifestation of the disease will be suppressed.
Women at risk for developing intimate warts include:
- having a weak immune defense;
- experiencing frequent stress and emotional overload;
- taking antibiotics for a long time;
- having a fungal, chlamydial or gonorrheal infection;
- entering into frequent and promiscuous relationships;
- malnourished;
- having abortions;
- pregnant and lactating mothers.
Men at risk:
- having bad habits;
- taking hormonal drugs;
- suffering from beriberi;
- having pathologies of the immune system;
- not fully resting;
- prolonged and regularly overtired;
- with hyperthermia or hypothermia.
Methods of transmission of the virus
Despite the fact that the papillomavirus is most often transmitted sexually, other ways of its transmission are not excluded, namely:
- Contact-household way . The papilloma virus does not live long in open space, but if people use the same towel, washcloth, underwear or bed linen, infection is quite possible.
- perinatal route . Infection with the virus of a child can occur from an infected mother during childbirth.
- In public places – swimming pools, saunas, baths, beaches and so on. Infection in kindergarten, schools and workplaces is not excluded, but this is possible only with low human immunity and through close contact with virus carriers or their contaminated household items.
Places of localization of neoplasms
Venereal warts can occur not only in intimate places , but also in the mouth, on the lips and tongue. It depends on the form of sexual relations between partners.
In men
In men, genital warts are localized:
- on the penis ;
- on the scrotum;
- in the perineum;
- in the urethra;
- around the anus.
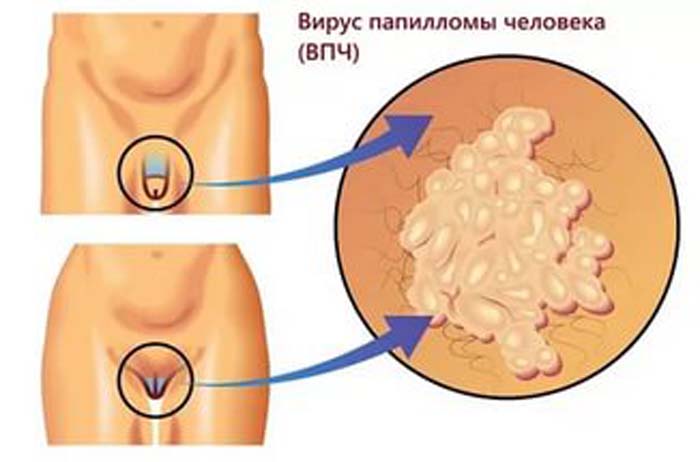
Among women
Growths in women are observed:
- in front of the vagina;
- on the clitoris;
- on the labia;
- on the cervix;
- at the mouth of the urethra ;
- around the anus.
Characteristic symptoms and manifestations
Symptomatic manifestations of genital warts are observed quite rarely. Itching, burning, discharge and other uncomfortable phenomena do not bother the patient in all cases.
If growths appear at the mouth of the urethra, it is possible to block the lumen of the urethra, which leads to problems with urination – delay, soreness.
In some cases, genital warts cause discomfort and pain during intercourse, and discomfort can also occur when rubbing underwear.
If the neoplasm degenerates from benign to malignant, unreasonable weight loss, lethargy, loss of appetite are possible.
What are dangerous for human health
Even if the neoplasms do not cause any negative symptoms, not going to the doctor is the wrong option.
The biggest danger of genital warts is their transformation into a malignant pathology, in addition, immunity weakens, as the virus inhibits healthy cellular structures and harms the entire body as a whole.
There are also the following hazards:
- growths can interfere with the normal discharge of urine and feces;
- violate intimate life – sexual contact causes pain;
- causing constant discomfort, can provoke the appearance of depression.
Do I need to see a doctor
In order to avoid negative consequences, it is imperative to consult a doctor. The problems of genital warts are dealt with by a urologist, gynecologist or dermatologist.
Diagnostic methods
In order to establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo the following diagnostics:
- visual inspection;
- PCR;
- cytological examination;
- molecular biological research;
- histological examination.
Features of treatment
At the moment, there is no drug that could save a person from the papillomavirus and its manifestations. All therapeutic methods are aimed only at eliminating the symptoms.
In some cases, genital warts may disappear on their own, however, while the person remains a virus carrier forever, and if favorable conditions arise, the clinical picture will reappear. See also: wart on the penis , effective treatments
Medical therapy
As a medical treatment, the doctor usually prescribes antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.
Cytostatics:
- Podophyllotoxin.
- Podophyllin.
- 5-fluorouracil.
Immunomodulators:
- Cycloferon .
- Laferon and other derivatives of interferon.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are allowed to be used only after consulting a doctor and an accurate diagnosis. The most common are:
- treatment of growths with iodine ;
- treatment of genital warts with celandine juice, you can also use the oil of this plant.
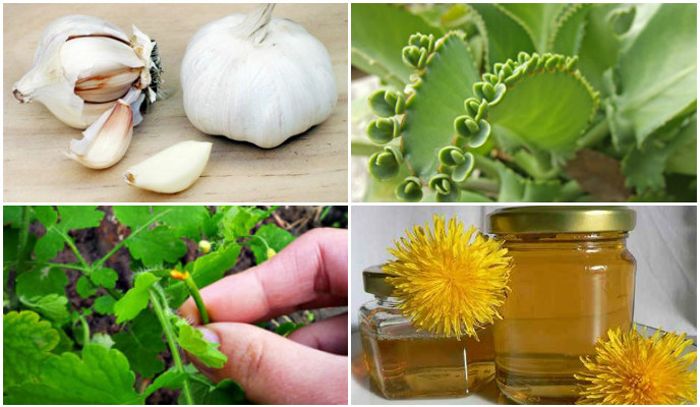

In addition, are used:
- onions, garlic;
- Rowan;
- lemon;
- a mixture of red wine, lemon, garlic and apple juice;
- infusion of chamomile and St. John’s wort.
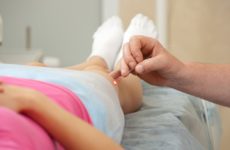
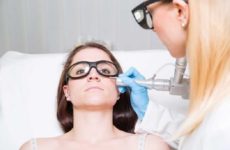
Removal of growths
You can remove pathological growths in the following ways:
- The impact of drugs – cauterization. Removal is carried out only by a qualified specialist, since rather aggressive preparations are used for this purpose, for example, triacetic acid or Fluorouracil preparations.
- Surgical removal – with liquid nitrogen or laser.
- Removal using the apparatus “Surgitron” .
But the removal of genital warts cannot be considered 100% either, it happens that after removal, the growth reappears in the same or another place.
Thus, we can conclude that there is no universal remedy to get rid of neoplasms in intimate places , but this does not mean at all that it is not necessary to treat and remove them.
Prevention of the onset of the disease
Prevention of the occurrence of genital warts is as follows:
- refusal of casual sexual contacts;
- use of barrier contraception with an untested or non-permanent partner;
- compliance with the general rules of personal and intimate hygiene;
- timely treatment of warts in the early stages;
- vaccination against the papillomavirus, which is done before the onset of sexual activity.
It is very important to consult a doctor immediately after the detection of genital warts, undergo a diagnosis and begin adequate treatment.