The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of DNA viruses that, invading healthy cells, provoke their uncontrolled division.
This phenomenon leads to the fact that the tissues begin to grow pathologically, as a result of which defects appear on the skin – warts, papillomas, condylomas.
The papilloma virus can remain in the human body in a latent state for years, that is, it does not show activity. But with a decrease in immunity, it becomes more active and begins its pathological activity.
Содержание:
Human papillomavirus classification
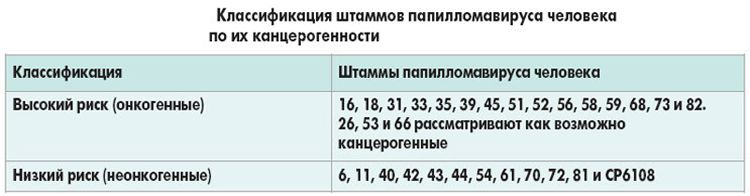
Under oncogenic classification understand the separation of types of the virus, taking into account the likelihood of developing an oncological disease. There are currently three groups:
- The first group includes strains 1,2,3,4,5 . If one of these viruses is found in a woman’s body, it can be assumed that the patient is not threatened with the development of oncology due to HPV. That is, these strains do not have an oncogenic index. Do not forget that in the future a woman can become infected with other strains of papillomatosis.
- The second group includes strain 6,11,42,43,44 . These viruses have a low oncogenic index. This means that in the presence of certain provoking factors, these strains can give impetus to mutation processes in cells, and this, in turn, can cause the development of cancer.
- The third group of viruses has a high oncogenic activity. It includes 16,18,31, 33,35 , 39,45,51 , 52,56 , 59 , 68 strains . In the course of clinical observations, it has been proven that the presence of these viruses in the body increases the risk of developing cancer of the cervix and mammary glands by several times.
Of course, not in all cases, the presence of a virus in the body (even a high oncogenic index) must necessarily provoke oncology.
It is only a question of risk, however, knowing that there is a papilloma virus of a low or high oncogenic index in her blood, a woman should be more attentive to her health and be regularly observed by a specialist.
What is the danger of strain types 16 and 18
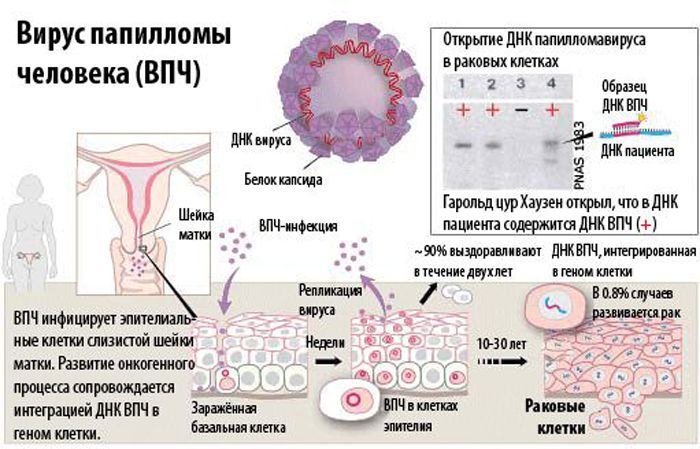
When papillomavirus serotype 16 or 18 is found in a woman’s body, the doctor must warn the patient that she has an increased risk of developing dysplastic processes in the uterus, vagina and other organs of the pelvic region.
That is, there is a risk of developing cancer. 16 and 18, the strain settles and multiplies in the cervical canal and penetrates into the deep layers of the mucous genital organs of a woman.
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of the development of the virus:
- First stage . stage of incubation. HPV is in the body of a woman, but is not activated. Depending on the strength of the immune system, the virus is in such a dormant state, it can be from two weeks to 10 years or more. The aging of the body, the presence of various diseases and other provoking factors reduce the resistance of the body, and the virus enters the second stage.
- Second stage . Stage of clinical manifestation. The virus begins to multiply actively, which leads to visible skin changes. Round, pointed, flat, pedunculated, rough, smooth, and so on neoplasms appear. They can be localized on the eyelids, lips, mucous membranes.
- Third stage . Stage of tissue dysplasia. The DNA of the virus is integrated into the cellular genome and destroys a healthy cell. This process is irreversible, which means that the tissue structure changes irrevocably.
- Fourth stage . Stage of appearance of cancer cells. Under the influence of HPV, DNA mutates, and an invasive form of oncology develops.
When does cancer develop?
Clinically, the presence of HPV may not manifest itself for a long time, and a woman may not even suspect that there is a time bomb inside her.
The activation of the virus begins in the presence of the following provoking factors:
- decreased immune defense;
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- abortions;
- lack of personal hygiene rules;
- hypothermia;
- infection with sexually transmitted infections.
Symptoms and ways of transmission of the onco risk virus
The symptomatology of the disease is as follows:
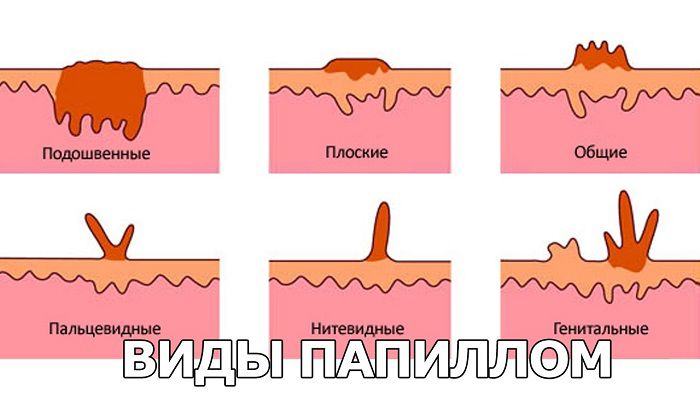
- Genital warts are harmless neoplasms of pale pink or flesh color. They can cause discomfort in the form of burning and itching. As a rule, the place of their localization is the cervix.
- Flat warts . The place of localization is the genitals, upon contact with underwear, they can be damaged and cause bleeding. Such condylomas can degenerate into oncology.
- Warts . Dark growths that appear as a result of infection with strains of low oncogenicity. For health, they do not pose a threat, and most often appear on the palms and soles of the feet.
- Bowenoid papulosis . This is a rash in the area of the labia, which is read as a precancerous condition.
The main route of transmission of HPV is considered to be sexual contact with a virus carrier. Statistics show that primary infection occurs in the first year of sexual activity.
At this time, 50% of all cases of infection are noted. Moreover, the virus is transmitted not only during vaginal intercourse, but also during oral and anal.
There is also a vertical route of infection. In this case, the fetus becomes infected when passing through the birth canal of an infected mother.
If a pregnant woman denounces the active phase of the development of the virus, she is recommended to have a caesarean section. The infection is not transmitted through the placental barrier.
The household method of infection is no less common. Close contact with a sick person or sharing personal hygiene items allows the virus to spread to a healthy body.
It penetrates through microdamages of the skin, but, according to doctors, only low-oncogenic or non-oncogenic strains can be infected in this way, they do not provoke oncology, but cause unpleasant neoplasms and rashes on the skin.
The specifics of the course in women
The first genital warts are diagnosed in women aged 15 to 30 who live an active sex life. After the age of 25, all women are recommended to take an HPV test.
Virus types 16 and 18 in women can lead to a malignant process in the cervix. This is why doctors urge women to have their annual pelvic exam so strongly. Only timely diagnosis of the virus and proper treatment can prevent the development of a deadly disease.
As for pregnancy, the papilloma virus does not interfere with either conception or childbearing. The exception is cases when neoplasms grow in the cervix and prevent the penetration of spermatozoa.
Also, negative consequences are possible with serious changes in the pelvic organs, which were provoked by a viral infection.
Which doctor should I contact?
The papilloma virus is treated by doctors of a narrow focus, in accordance with the location of the pathological neoplasm:
- a dermatologist or venereologist treats growths that have arisen on the body;
- the gynecologist prescribes therapy for genital warts;
- the dentist treats papillomas of the oral cavity;
- an ophthalmologist diagnoses and treats growths in the eyelids;
- the surgeon is engaged in the removal of benign neoplasms;
- an oncologist observes neoplasms that can transform into malignant ones.

Diagnostic methods
The doctor prescribes:
- colposcopy – examination of the cervix with special equipment, during which tissue changes can be detected;
- a smear for cytology, which allows you to determine the structure of modified tissues;
- histology – to establish the strain of the virus;
- treatment of the cervix with a special solution to identify areas affected by the virus;
- a blood test to determine the virus carrier;
- PCR to establish the structure of DNA, determine the type of virus and the degree of its development;
- Digen test to determine the oncogenicity of the virus.
Treatment
Having become infected with the papilloma virus once, a woman will have to live with it all her life. The fact is that it is impossible to eliminate the papilloma virus, the treatment of pathology is aimed only at inhibiting its activity.
Conservative therapy:
- Panavir is an antiviral agent that helps to deactivate HPV.
- Viferon is a means of understanding immunity.
- Isoprinosine – eliminates the symptoms of HPV and helps to weaken the activity of the virus.
- Genferon – prevents the spread of the virus throughout the body.
In addition, appointed:
- Epigen intima – a spray for stopping inflammation, itching and burning in the genital area.
- Verrukacid – a means for cauterization of papillomas, is used only by a doctor.
- Solcoderm is an acid that removes growths.
- Cryopharma – freezes the build-up, as a result of which it disappears on its own and leaves no traces behind.
- Supercleaner is a harmless to the body remedy that cauterizes papillomas, but it must be used very carefully so as not to damage healthy tissues.

Surgical removal of papillomas can be carried out in the following ways:
- Cryotherapy is a painless and reliable removal of papillomas with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser therapy – does not leave scars, the laser action limit is well controlled, the procedure is painless.
- Electrocoagulation – does not affect healthy tissue areas, therefore it can be used in relation to small neoplasms.
- The radio wave method is a quick procedure that completely eliminates the possibility of infection.
- Surgical intervention – removal with a scalpel. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Forecast
With the timely detection of papillomavirus, lifelong monitoring of it and increased immunity, the dangerous consequences of oncogenic strains can be prevented.
Prevention
To prevent infection with papillomavirus infection, you must adhere to the following rules:
- observe hygiene measures in public places;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Healthy food;
- get enough sleep;
- take vitamin complexes;
- have only one verified sexual partner.
As for the HPV vaccine, there are currently two vaccines, but it is advisable to put them only if there is no virus in the body. Therefore, they mainly vaccinate young girls who do not yet have an intimate life.







