How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma ? Under the influence of various factors, benign neoplasms may appear on the skin: moles, papillomas, warts.
Most of them are harmless, do not cause inconvenience and may eventually disappear by themselves. Others need to be treated, and not only to eliminate a cosmetic defect, but also to prevent serious consequences for health and life. But many do not know what to do when a new mole or papilloma appears, and how to distinguish them from each other.
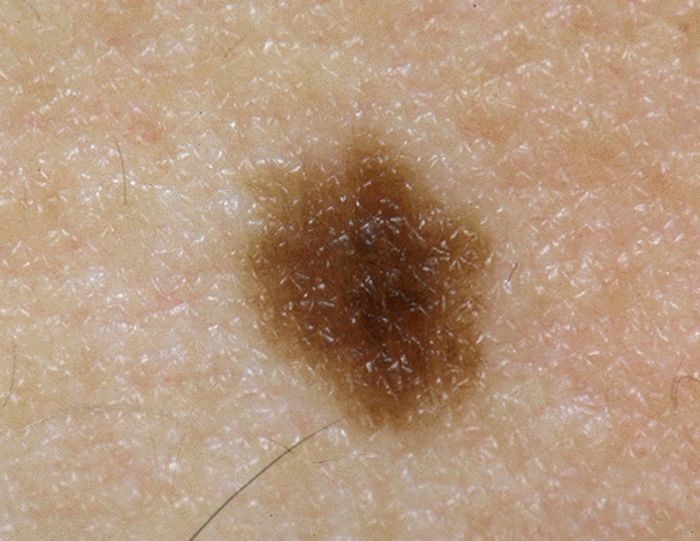
What are nevi
In medical terminology, moles are called “nevi”. Most often, they are congenital and are the result of improper development of skin pigment cells – melanocytes. Thus, birthmarks and moles are laid even during fetal development, and appear in a child at the age of 1-2 years.
They can grow in proportion to body size and reach their final size by puberty. With age, involution (reverse development) of nevi occurs.
In older people, there is a decrease in the number of moles on the body. It is possible for new nevi to form due to sun exposure or hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy.
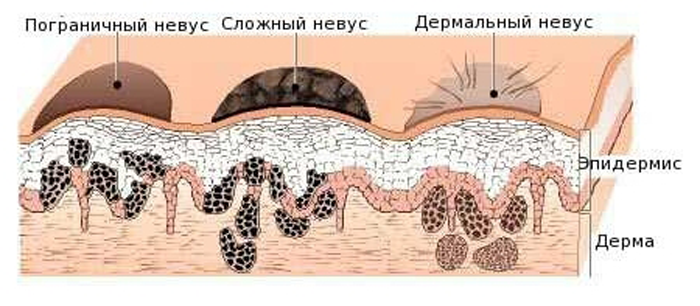
Depending on the location in the layers of the skin, moles are divided into the following types:
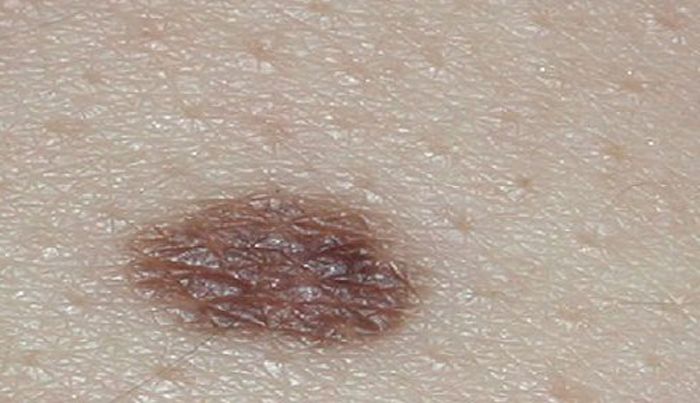
- Borderline nevus. It is located in the upper layers of the skin at the border of the epidermis and dermis. This species includes flat round nevi of pronounced color.
- Complex nevus. It is an intermediate stage of the border and intradermal nevus. Neoplasm cells are located both in the epidermis and inside the dermis. It still has a bright color, but is raised above the surface of the skin in the form of a papule or nodule.
- Intradermal nevus. Completely immersed in the dermis. Here, nevus cells lose their ability to accumulate melanin pigment and gradually lighten. Such nevi are easily mistaken for papillomatous formations, as they are often wart-shaped or pedunculated .
Where do papillomas come from
The nature of papilloma formation is completely different. Unlike moles, they are an external sign of a disease caused by the human papillomatosis virus. This virus is quite widespread in the human population and has many varieties, more than 20 of which are dangerous in terms of the potential development of cancer.

It is possible to accurately determine which strain of HPV caused the disease in a particular person only with the help of laboratory tests. Therefore, it makes sense to visit a doctor when papillomas appear, even if they do not cause inconvenience.
How to distinguish
In order to better understand how to distinguish a papilloma from a mole, it is necessary to find out how these neoplasms generally differ, and what they have in common.
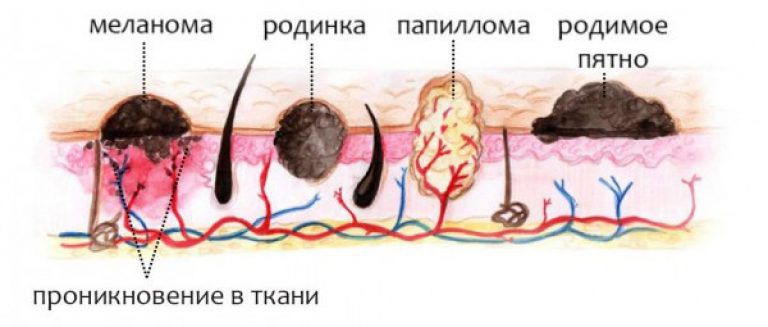
What is the difference between a papilloma and a mole:
- different nature of origin. Nevi are formed as a result of the degeneration of pigment cells at the development stage, and papillomas occur under the influence of a virus on skin cells.
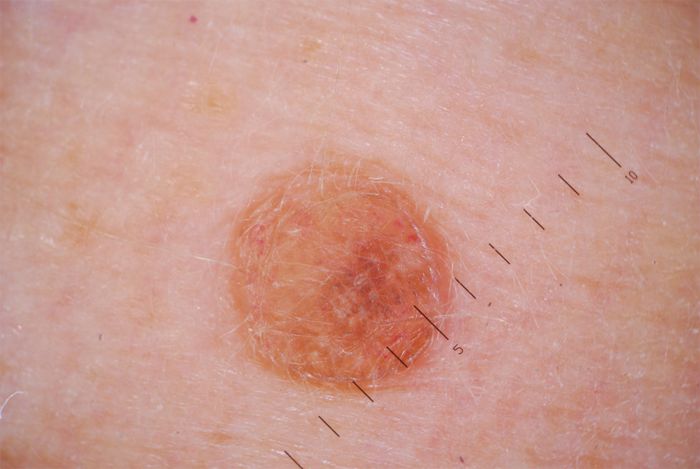
- Height. Papillomas are characterized by a sharp appearance, rapid growth and spread. Moles grow only in childhood and in proportion to the growth of the whole body. An increase in a mole in size in adulthood is a reason for an immediate visit to the doctor.
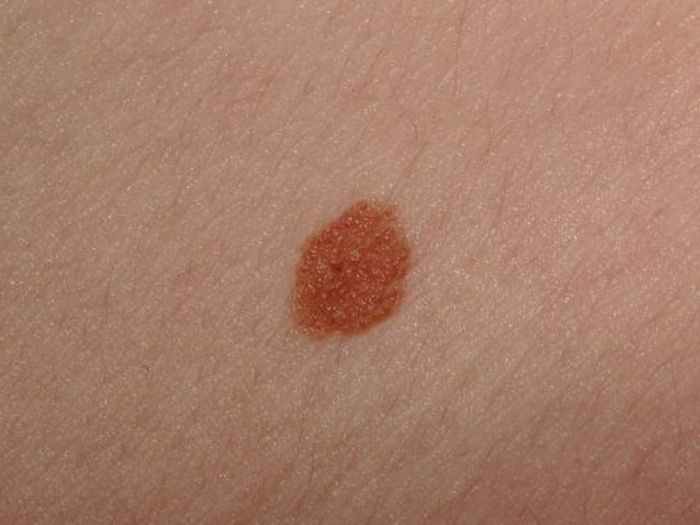
- location on the body. Papillomas on the body are always located in groups, most often in folds, places of friction, sometimes on the genitals . For nevi, a solitary location is characteristic.
- Color. Moles most often have an intense uniform color, and most papillomas are pale in color.
- Vessels. Papillomas are easily identified by the presence of blood vessels inside the neoplasm. Moles are homogeneous accumulations of cells.
- Density. Moles and papillomas are different to the touch. The former usually have a dense structure, the latter are more loose.
- Form. Moles, with the exception of congenital birthmarks, almost always have a regular round shape. Papillomas are elongated, conical, mastoid in shape, in the form of a thread, often located on a stem, but rarely rounded.
General signs:
- The presence of visible changes on the skin. Often, the appearance of benign neoplasms in open areas of the body becomes the cause of psychological experiences. In addition, in places of increased injury risk and friction, they can cause physical discomfort.
- Oncogenicity. It has been proven that part of the nevi under the influence of external factors turns into melanoma – skin cancer. Most often, ultraviolet radiation or trauma to the nevus acts as such a factor. Oncogenic strains of HPV can cause uncontrolled cell growth and division even in the absence of external influences. Scientists attribute 80% of cases of cervical cancer, as well as cancer of the vulva and rectum, to the presence of this virus in the body.
Thus, in order to protect yourself from the consequences that can provoke benign neoplasms on the skin, it is necessary to carefully monitor their condition. When new papillomas appear and when the condition of the nevi changes, it is necessary to see a doctor. All manipulations to remove them should also be performed by a specialist, if necessary, sending the material for analysis.